* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Genetic Engine
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
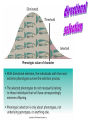
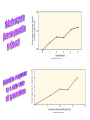
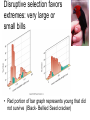
The Genetic Engine; Darwin and Natural Selection Hardy Weinberg (link to Video introduction) Modern Biology & Genetics • Gregor Mendel’s genetic theory of inheritance • The connection between traits and heredity explored The connection between Mendel and Hardy Weinberg • Use phenotype to identify frequency of recessive trait • Take the square root to identify frequency of the recessive allele • Use this to get frequency of the dominant allele Sample: 4 recessive individuals out of 100 • Frequency of the recessive phenotype will be equal to q2 – • Note, q = frequency of the recessive allele – • if 4 out of 100 are recessive, q2 = .04 So, q = the square root of .04 = .2 Heterozygous dominant frequency can now be calculated • P=1-q • P =. 1-.2 = .8 • Heterozygous dominant frequency can now be calculated • 2pq = 2(.2)(.8) = .32 • Check your work! • p2 + 2pq= q2 = 1 • .64 + .32 +. 04 = 1.0 Coloration in the Scarlet tiger moth • Coloration in this species had been previously shown to behave as a single-locus, two-allele system with incomplete dominance. Data for 1612 individuals are given below: – – – – White-spotted (AA) =1469 Intermediate (Aa) = 138 Little spotting (aa) =5 Calculate the following frequencies: A= a= AA = Aa = aa = – Link for answer More Practice • One in 1700 US Caucasian newborns have cystic fibrous. (use C for normal which is dominant over c for cystic fibrous) – What percent of the above population have cystic fibrous (note, this is cc = q2) – What is the frequency of the recessive allele? (q) – What is the frequency of the dominant allele? (p) – Calculate or state, the frequency of the 3 phenotypes – Link to answers Yet more practice If 9% of an African population is born with a severe form of sickle-cell anemia (ss), what percentage of the population will be more resistant to malaria because they are heterozygous (Ss) for the sickle-cell gene? – – – – – Calculate q2 (Phenotype frequency) Calculate q (Recessive Allele frequency) Calculate p (dominant allele frequency) Calculate 2pq and q2 & CHECK YOUR WORK Link to answer Conditions for Hardy Weinberg Five conditions needed to insure gene pool stability (null condition for “no evolution”) 1. A large breeding population 2. Random mating 3. No change in allelic frequency due to mutation 4. No immigration or emigration 5. No natural selection What about natural selection? • video • Multiple generations of selection – natural or artificial will change a character substantially • Cumulative selective response (in one generation) • Cumulative selection differential (sum of the effect over all generations) How might stabilizing selection work? • Why shouldn’t evolution favor really, really, really, really really tall people? • Mortality rates for very small and very large infants • Stabilizing selection favors intermediate characteristics Disruptive selection favors extremes: very large or small bills • Red portion of bar graph represents young that did not survive (Black- Bellied Seed cracker) Disruptive selection can lead to speciation “Truisms” about natural selection • Natural selection can “happen” if the trait undergoing selective pressure is genetically determined • Natural selection can only work toward traits' that increase fitness for survival and reproduction • Natural selection acts by changing the frequency of alleles in the gene pool over time – thus phenotypes do not “disappear” all at once. • Evolutionary rates are linked to generation time • For vertebrates like man with long generation times, , evolutionary change is slow, massive mutations tend to be eliminated quickly Evolution? • Natural selection favors organisms that have traits that are “good enough”; and usually acts on just a few characteristics – Extremes are rarely selected for Many important life forms have short generation times • HIV: the ultimate evolver • Resistance in bacteria