Neuman Chapter - Department of Chemistry
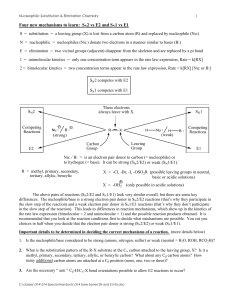
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but ...
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but ...
aq - Haverford Alchemy
... What is aqueous? What is an aqueous reaction? What are some types of aqueous reactions? Why might these be important? Give examples. • Aqueous reactions cannot take place without water. What do you already know about water that will help us understand aqueous reactions? Aqueous Reactions ...
... What is aqueous? What is an aqueous reaction? What are some types of aqueous reactions? Why might these be important? Give examples. • Aqueous reactions cannot take place without water. What do you already know about water that will help us understand aqueous reactions? Aqueous Reactions ...
The behaviour of esters in the presence of
... salts which yield methyl esters and trimethylamine between about 250 and 350°C. This procedure was sometimes referred to as “pyrolytic methylation” and was applied more recently to improve the gas chromatographi~ resolution of mixtures of fatty acids. In a number of more recent papers [7-lo] natural ...
... salts which yield methyl esters and trimethylamine between about 250 and 350°C. This procedure was sometimes referred to as “pyrolytic methylation” and was applied more recently to improve the gas chromatographi~ resolution of mixtures of fatty acids. In a number of more recent papers [7-lo] natural ...
Green synthesis of 2-amino-7-hydroxy-4-aryl-4H
... groups. Obviously, functionalization of chromene derivatives has played an ever increasing role in the synthetic approaches to promising compounds in the field of medicinal chemistry. On the other hand, functionalized chromenes appeared as an important structural component in both biologically activ ...
... groups. Obviously, functionalization of chromene derivatives has played an ever increasing role in the synthetic approaches to promising compounds in the field of medicinal chemistry. On the other hand, functionalized chromenes appeared as an important structural component in both biologically activ ...
Relevance of the Physicochemical Properties of Calcined Quail
... The basicity of the catalyst was studied by temperatureprogrammed desorption of CO2 . Approximately 100 mg of sample was pretreated with a stream of helium at 800∘ C for 30 min (10∘ C min−1 and 60 mL min−1 ). The reaction temperature was then decreased to 100∘ C, and a flow of pure CO2 (60 mL min−1 ...
... The basicity of the catalyst was studied by temperatureprogrammed desorption of CO2 . Approximately 100 mg of sample was pretreated with a stream of helium at 800∘ C for 30 min (10∘ C min−1 and 60 mL min−1 ). The reaction temperature was then decreased to 100∘ C, and a flow of pure CO2 (60 mL min−1 ...
CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 1
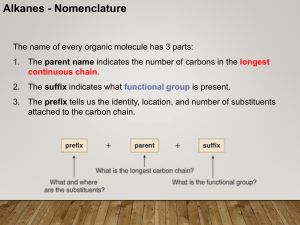
... • If two or more identical substituents are bonded to the longest chain, use prefixes to indicate how many: di- for two groups, trifor three groups, tetra- for four groups, and so forth. ...
... • If two or more identical substituents are bonded to the longest chain, use prefixes to indicate how many: di- for two groups, trifor three groups, tetra- for four groups, and so forth. ...
Alkyl halide
... Alkyl halides can also be prepared from alkenes by reaction with Nbromosuccinimide (NBS) in the presence of light • Bromine is substituted for hydrogen at the position next to the double bond – the allylic position ...
... Alkyl halides can also be prepared from alkenes by reaction with Nbromosuccinimide (NBS) in the presence of light • Bromine is substituted for hydrogen at the position next to the double bond – the allylic position ...
CHEMICAL REACTIVITY AND MECHANISMS, AND SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS 1.
... steric effect; larger groups interfere with the approaching nucleophile). SN1 reactions are faster for 3° substrates (because the more stable the carbocation, the faster the reaction; this means 3° > 2° >> 1° > CH3). Vinylic (R2C=CR-) and aromatic substrates are unreactive in either reaction type. A ...
... steric effect; larger groups interfere with the approaching nucleophile). SN1 reactions are faster for 3° substrates (because the more stable the carbocation, the faster the reaction; this means 3° > 2° >> 1° > CH3). Vinylic (R2C=CR-) and aromatic substrates are unreactive in either reaction type. A ...
Cracking (chemistry)

In petroleum geology and chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the precursors. The rate of cracking and the end products are strongly dependent on the temperature and presence of catalysts. Cracking is the breakdown of a large alkane into smaller, more useful alkanes and alkenes. Simply put, hydrocarbon cracking is the process of breaking a long-chain of hydrocarbons into short ones. More loosely, outside the field of petroleum chemistry, the term ""cracking"" is used to describe any type of splitting of molecules under the influence of heat, catalysts and solvents, such as in processes of destructive distillation or pyrolysis. Fluid catalytic cracking produces a high yield of petrol and LPG, while hydrocracking is a major source of jet fuel, Diesel fuel, naphtha, and again yields LPG.