CHE 322
... 3. (8) Give the complete mechanism that shows why the reaction of butanal with a cyclic 2° amine followed by heating with acid produces an enamine that is nucleophilic at butanal’s former α-carbon. ...
... 3. (8) Give the complete mechanism that shows why the reaction of butanal with a cyclic 2° amine followed by heating with acid produces an enamine that is nucleophilic at butanal’s former α-carbon. ...
Johnson Group Research
... rhodium complexes to catalyze the cleavage of Csp2-Csp3 single bonds adjacent to ketones, ultimately allowing for the exchange of ketone substituents. This reaction can also be viewed as alkene ‘hydroacylation’, the addition of a hydrogen and an acyl group across a double bond. Our initial research ...
... rhodium complexes to catalyze the cleavage of Csp2-Csp3 single bonds adjacent to ketones, ultimately allowing for the exchange of ketone substituents. This reaction can also be viewed as alkene ‘hydroacylation’, the addition of a hydrogen and an acyl group across a double bond. Our initial research ...
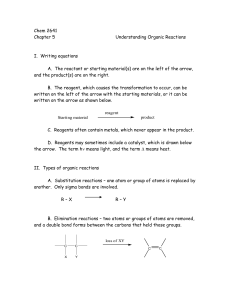
Chem 2641 Chapter 5 Understanding Organic Reactions I. Writing
... The initiation stage – Cl2 reacts with the uv light to form Cl. Propagation stage – The Cl. reacts with CH4 to form CH3. and HCl The CH3. reacts with Cl2 to form CH3Cl and Cl. Termination stage – any two radicals can combine to form a stable product. ...
... The initiation stage – Cl2 reacts with the uv light to form Cl. Propagation stage – The Cl. reacts with CH4 to form CH3. and HCl The CH3. reacts with Cl2 to form CH3Cl and Cl. Termination stage – any two radicals can combine to form a stable product. ...
Slide 1
... presence of base or by heating a mixture of the reactants at high temperatures ranging from 150-220°C in the absence of catalyst.(1) ...
... presence of base or by heating a mixture of the reactants at high temperatures ranging from 150-220°C in the absence of catalyst.(1) ...
CH 10
... • Reactions involving organohalides are less frequently encountered than other organic compounds, but reactions such as nucleophilic substitutions/eliminations that they undergo will be encountered • Alkyl halide chemistry is model for mechanistically similar but more complex ...
... • Reactions involving organohalides are less frequently encountered than other organic compounds, but reactions such as nucleophilic substitutions/eliminations that they undergo will be encountered • Alkyl halide chemistry is model for mechanistically similar but more complex ...
lect3
... elements are very reactive. Those of less electropositive metals are less so (but react more selectively) ...
... elements are very reactive. Those of less electropositive metals are less so (but react more selectively) ...
Oxacyclopropane (Epoxide) Synthesis: Epoxidation by
... Catalytic amounts of osmium tetroxide in the presence of an oxidizing agent (H2O2) to regenerate the spent osmium tetroxide are often used, due to the expense and toxicity of OsO4. ...
... Catalytic amounts of osmium tetroxide in the presence of an oxidizing agent (H2O2) to regenerate the spent osmium tetroxide are often used, due to the expense and toxicity of OsO4. ...
Dess-Martin Oxidation
... • Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP) is a chemical reagent used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones ...
... • Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP) is a chemical reagent used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alkynes, either on heating or treatment with organolithium reagents. Highly reactive cycloalkynes are prepara ...
... Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alkynes, either on heating or treatment with organolithium reagents. Highly reactive cycloalkynes are prepara ...
Chapter 8_part 1
... double bond, the positive portion of the adding reagent attaches itself to a carbon of the double bond so as to yield the more stable carbocation as intermediate ...
... double bond, the positive portion of the adding reagent attaches itself to a carbon of the double bond so as to yield the more stable carbocation as intermediate ...
Organo halides
... What Is an Alkylhlaide An organic compound containing at least one carbon-halogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
... What Is an Alkylhlaide An organic compound containing at least one carbon-halogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
Topic 3 – Chemical Structure and Bonding
... o Nitration of benzene followed by reduction using Sn/HCl o Substitution of a halogen by CN- to lengthen a carbon chain o Acylation of a benzene ring followed by reduction using LiAlH4 to give an alcohol ...
... o Nitration of benzene followed by reduction using Sn/HCl o Substitution of a halogen by CN- to lengthen a carbon chain o Acylation of a benzene ring followed by reduction using LiAlH4 to give an alcohol ...
Ch 26 C-C bond formation
... • To form the carbon skeletons of complex molecules, organic chemists need an extensive repertoire of carbon–carbon bond forming reactions. • We have earlier looked at reactions of organometallic reagents such as Grignard, organolithium and organocuprate reagents with carbonyl and other substrates t ...
... • To form the carbon skeletons of complex molecules, organic chemists need an extensive repertoire of carbon–carbon bond forming reactions. • We have earlier looked at reactions of organometallic reagents such as Grignard, organolithium and organocuprate reagents with carbonyl and other substrates t ...
18 Important and sometimes forgotten) organic transformations
... •Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination (Chugaev reaction) •Thionoformates may be used to derivatise and deoxygenate tertiary alcohols without competing elimination ...
... •Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination (Chugaev reaction) •Thionoformates may be used to derivatise and deoxygenate tertiary alcohols without competing elimination ...
Applications of Phosphorus, Sulfur, Silicon and Boron Chemistry:
... outcome of the transformations. 10. Show how silyl ethers can be used as hydroxyl protecting groups in organic chemistry. These notes, self-study workbook problems with answers, and sample past exam paper questions (some with solutions) are available for download at: http://www.hull.ac.uk/php/chsanb ...
... outcome of the transformations. 10. Show how silyl ethers can be used as hydroxyl protecting groups in organic chemistry. These notes, self-study workbook problems with answers, and sample past exam paper questions (some with solutions) are available for download at: http://www.hull.ac.uk/php/chsanb ...
Notes 07 Organometallic Compounds
... Creation of new C-C bonds. ______________are best, otherwise an elimination reaction can occur. The R’ group in the halide can be ______________ The R group of the cuprate can be ______________ Although the mechanism looks like a _________ reaction, it is more complex and is not well understood. ...
... Creation of new C-C bonds. ______________are best, otherwise an elimination reaction can occur. The R’ group in the halide can be ______________ The R group of the cuprate can be ______________ Although the mechanism looks like a _________ reaction, it is more complex and is not well understood. ...
Synthesis of a Family of Chiral Asymmetric Schiff - Blogs at H-SC
... trial two. Deprotection yielded spectra that plausibly matched chemical shifts for the intended molecule, even though the product remained an oil. The initial target reaction was not straight out of literature but was rather inspired by work done by Hoveyda’s group. Thus, the target compound, under ...
... trial two. Deprotection yielded spectra that plausibly matched chemical shifts for the intended molecule, even though the product remained an oil. The initial target reaction was not straight out of literature but was rather inspired by work done by Hoveyda’s group. Thus, the target compound, under ...
10. Alkyl Halides
... Not defined as loss of electrons by an atom as in inorganic chemistry Oxidation is a reaction that results in loss of electron density at carbon (as more electronegative atoms replace hydrogen or carbon) Organic reduction is the opposite of oxidation Results in gain of electron density at ca ...
... Not defined as loss of electrons by an atom as in inorganic chemistry Oxidation is a reaction that results in loss of electron density at carbon (as more electronegative atoms replace hydrogen or carbon) Organic reduction is the opposite of oxidation Results in gain of electron density at ca ...
07.Chapter7.Alcohols and Related
... Nucleophilicity of halide ion is not strong enough for SN2 Please refer to page 219 ...
... Nucleophilicity of halide ion is not strong enough for SN2 Please refer to page 219 ...
Pd presentation
... Palladium can be used in a wide variety of reactions: •Stille- between organohalides & organotin compounds •Buchwald-Hartwig- between aryl halide & amine or aryl alcohol •Tsuji-Trost- between alkene & a nucleophile •Heck- between alkenes & alkyl halides This presentation was created as part of the r ...
... Palladium can be used in a wide variety of reactions: •Stille- between organohalides & organotin compounds •Buchwald-Hartwig- between aryl halide & amine or aryl alcohol •Tsuji-Trost- between alkene & a nucleophile •Heck- between alkenes & alkyl halides This presentation was created as part of the r ...
Elimination reactions under acidic conditions
... Alcohols may be dehydrated under acid catalyzed conditions to give alkenes. This is an example of an elimination reaction. The mechanism of the dehydration of an alcohol to form an alkene is exactly the opposite of the addition of water to an alkene to form an alcohol (microscopic reversibility) ...
... Alcohols may be dehydrated under acid catalyzed conditions to give alkenes. This is an example of an elimination reaction. The mechanism of the dehydration of an alcohol to form an alkene is exactly the opposite of the addition of water to an alkene to form an alcohol (microscopic reversibility) ...
Eliminations
... This is the same phenomenon (hyperconjugation) that stabilizes carbocations. In general, more electron density in a bond results in a stronger bond: a covalent bond is the sharing of two electrons; the ...
... This is the same phenomenon (hyperconjugation) that stabilizes carbocations. In general, more electron density in a bond results in a stronger bond: a covalent bond is the sharing of two electrons; the ...
Losing and Gaining Electrons
... (i.e., the solid angle) that the ligand occupies around the imaginary first coordination sphere. Both of these factors can be incorporated into the concept of the “% buried volume”, the volume of the ligand inside the coordination sphere. ...
... (i.e., the solid angle) that the ligand occupies around the imaginary first coordination sphere. Both of these factors can be incorporated into the concept of the “% buried volume”, the volume of the ligand inside the coordination sphere. ...
(Z)-Tamoxifen and Tetrasubstituted Alkenes and Dienes via a Regio
... π-orbitals in the addition component. Thus the poor result with the methylmagnesium chloride (entry 8) is due to the inefficiency of the carbometalation and not to the subsequent cross-coupling. The yield of the Grignard additions to propargyl alcohols can be enhanced, in some cases, by the addition ...
... π-orbitals in the addition component. Thus the poor result with the methylmagnesium chloride (entry 8) is due to the inefficiency of the carbometalation and not to the subsequent cross-coupling. The yield of the Grignard additions to propargyl alcohols can be enhanced, in some cases, by the addition ...
Stille reaction

The Stille reaction, or the Migita-Kosugi-Stille coupling, is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis which involves the coupling of an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes) with a variety of organic electrophiles via palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction.The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including alkenes, and aryl groups; however, conditions have been devised to incorporate both sp3-hybridized groups, such as allylic and benzylic substituents, and sp-hybridized alkynes. These organostannanes are also stable to both air and moisture, and many of these reagents are either commercially available or can be synthesized from literature precedent. However, these tin reagents tend to be highly toxic. X is typically a halide, such as Cl, Br, I, yet pseudohalides such as triflates and sulfonates and phosphates can also be used.The groundwork for the Stille reaction was laid by Colin Eaborn, Toshihiko Migita, and Masanori Kosugi in 1976 and 1977, who explored numerous palladium catalyzed couplings involving organotin reagents. John Stille and David Milstein developed a much milder and more broadly applicable procedure in 1978. Stille’s work on this area might have earned him a share of the 2010 Nobel Prize, which was awarded to Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki for their work on the Heck, Negishi, and Suzuki coupling reactions. However, Stille died in the plane crash of United Airlines Flight 232 in 1989.Several reviews have been published on the Stille reaction.