Ethers, Epoxides and Sulfides
... ethers as alkoxide ion is a poor leaving group. ¾ Epoxide’s high ring strain makes it susceptible to nucleophilic attack. ...
... ethers as alkoxide ion is a poor leaving group. ¾ Epoxide’s high ring strain makes it susceptible to nucleophilic attack. ...
Organic Chemistry
... • the carbon skeleton: how can we put it together. Our only method to date for forming new a C-C bond is the alkylation of alkyne anions (Section 7.5) • the functional groups: what are they, how can they be used in forming the carbon-skeleton of the target molecule, and how can they be changed to gi ...
... • the carbon skeleton: how can we put it together. Our only method to date for forming new a C-C bond is the alkylation of alkyne anions (Section 7.5) • the functional groups: what are they, how can they be used in forming the carbon-skeleton of the target molecule, and how can they be changed to gi ...
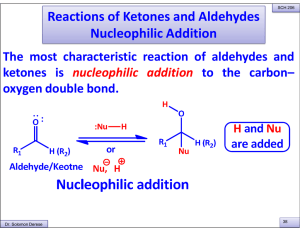
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
... If the cassava is crushed with water and allowed to stand (‘ferment’), enzymes in the cassava will do the same job and then the HCN can be washed out before the cassava is cooked and eaten. The cassava is now safe to eat but it still contains some glucoside. Some diseases found in eastern Nigeria ca ...
... If the cassava is crushed with water and allowed to stand (‘ferment’), enzymes in the cassava will do the same job and then the HCN can be washed out before the cassava is cooked and eaten. The cassava is now safe to eat but it still contains some glucoside. Some diseases found in eastern Nigeria ca ...
Reaction Rates
... reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transfe ...
... reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transfe ...
Chapter 16: Reaction Rates
... to reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 16.4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is t ...
... to reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 16.4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is t ...
File - Chemistry Workshop
... A tertiary carbon is directly bonded to three other C’s. Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
... A tertiary carbon is directly bonded to three other C’s. Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
Project Overview
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
Organic Chemistry II Introduction
... • The one -step mechanisms is E2 reaction and two step reaction mechanism is called E1 reaction, respectively. Dr Seemal Jelani ...
... • The one -step mechanisms is E2 reaction and two step reaction mechanism is called E1 reaction, respectively. Dr Seemal Jelani ...
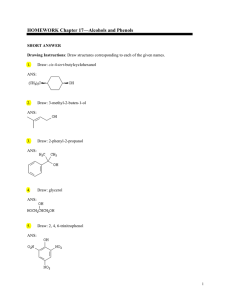
HOMEWORK Chapter 17—Alcohols and Phenols
... In E2 elimination, dehydration proceeds most readily when the two groups to be eliminated have a trans-diaxial relationship. In this compound, the only hydrogen with the proper geometric relationship to the −OH group is at C6 so the major product of this reaction is 3methylcyclohexene. ...
... In E2 elimination, dehydration proceeds most readily when the two groups to be eliminated have a trans-diaxial relationship. In this compound, the only hydrogen with the proper geometric relationship to the −OH group is at C6 so the major product of this reaction is 3methylcyclohexene. ...
Chemical Reactivity and Biological Activity of Diketene
... The alkylating potential of diketene (4-methylene-2-oxetanone), the basic unit of many derivatives of pesticides, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs, was investigated kinetically. The nucleophile 4-(pnitrobenzyl)pyridine (NBP), a trap for alkylating agents with nucleophilic characteristics si ...
... The alkylating potential of diketene (4-methylene-2-oxetanone), the basic unit of many derivatives of pesticides, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs, was investigated kinetically. The nucleophile 4-(pnitrobenzyl)pyridine (NBP), a trap for alkylating agents with nucleophilic characteristics si ...
Chemistry 360 - Athabasca University
... needs of Athabasca University students in mind. The format of this Report Book have been checked in our Athabasca laboratories by Dr. Lawton Shaw, Klaus Thomson, Nyron Jaleel, and Robert Carmichael. Special thanks to Ms. Aimee Caouette for her help on the Infrared Tutorial (Summer 1999). Also thanks ...
... needs of Athabasca University students in mind. The format of this Report Book have been checked in our Athabasca laboratories by Dr. Lawton Shaw, Klaus Thomson, Nyron Jaleel, and Robert Carmichael. Special thanks to Ms. Aimee Caouette for her help on the Infrared Tutorial (Summer 1999). Also thanks ...
19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
... selective than LiAlH4 • LiAlH4 reacts with alkyl halides, alkyl tosylates, and nitro groups, but NaBH4 does not ...
... selective than LiAlH4 • LiAlH4 reacts with alkyl halides, alkyl tosylates, and nitro groups, but NaBH4 does not ...
Rhenium- and molybdenum-catalyzed dehydration reactions
... ratio close to one and are highly functionalized with hydroxyl groups. Therefore a completely different type of chemistry is required to acquire building blocks from lignocellulosic biomass suitable for the chemical industry: while in the case of fossil feedstocks functionality must be added, functi ...
... ratio close to one and are highly functionalized with hydroxyl groups. Therefore a completely different type of chemistry is required to acquire building blocks from lignocellulosic biomass suitable for the chemical industry: while in the case of fossil feedstocks functionality must be added, functi ...
Synthesis of alternating hydroxy-and methyl
... Potential problems such as epoxide formation and solvolysis in the oxymercuration of conformationally flexible cyclopropylcarbinols do not interfere with this transformation. Oxymercuration of acyclic cyclopropanes 6-9 followed by reduction provided diols 15-18. Although both mercuric nitrate and ac ...
... Potential problems such as epoxide formation and solvolysis in the oxymercuration of conformationally flexible cyclopropylcarbinols do not interfere with this transformation. Oxymercuration of acyclic cyclopropanes 6-9 followed by reduction provided diols 15-18. Although both mercuric nitrate and ac ...
Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions
... The second step of the mechanism is the same kind of rapid carbocation–anion combination that we saw earlier as the last step in the mechanism of the reaction of alcohols with hydrogen halides (Section 4.8). This general mechanism is called electrophilic addition. It is triggered by the acid acting ...
... The second step of the mechanism is the same kind of rapid carbocation–anion combination that we saw earlier as the last step in the mechanism of the reaction of alcohols with hydrogen halides (Section 4.8). This general mechanism is called electrophilic addition. It is triggered by the acid acting ...
Transition Metal Reagents and Catalysts
... important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were selected from a much larger number which I have collected over the years. I wanted to ...
... important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were selected from a much larger number which I have collected over the years. I wanted to ...
Handout VI
... form cyclic acetals (Scheme 10). The fact that the reaction can be made to go with 1,2diols but not with simple alcohols (ROH) is due to the entropy factor for the former being more favourable than that for the latter, which involves a decrease in the number of molecules on going from starting mater ...
... form cyclic acetals (Scheme 10). The fact that the reaction can be made to go with 1,2diols but not with simple alcohols (ROH) is due to the entropy factor for the former being more favourable than that for the latter, which involves a decrease in the number of molecules on going from starting mater ...
C−C, C−O, C−N Bond Formation on sp2 Carbon by Pd(II)
... with π-nucleophiles such as olefins, alkynes, and arenes. The mechanisms of these processes have been extensively studied. A typical reaction with alkenes starts with the complexation of the olefin by the Pd(II) salt, as shown in Scheme 1, left-hand side. The resulting π-olefin complex A can undergo ...
... with π-nucleophiles such as olefins, alkynes, and arenes. The mechanisms of these processes have been extensively studied. A typical reaction with alkenes starts with the complexation of the olefin by the Pd(II) salt, as shown in Scheme 1, left-hand side. The resulting π-olefin complex A can undergo ...
Synthesis of Nitrogen-, Oxygen- and Sulphur
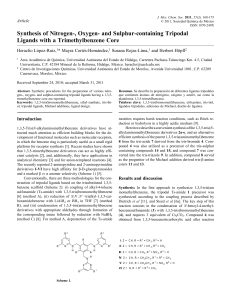
... ditionally, we prepared 1,3,5-tris((4-phenyl-1-H-1,2,3-triazol1-yl)methyl)benzene (9) by addition of three equivalents of phenylacetylene to 7 in the presence of a catalytic amount of CuI (Scheme 5) [13]. Examination of the reactivity of compound 8 in Michael addition reactions revealed that the exp ...
... ditionally, we prepared 1,3,5-tris((4-phenyl-1-H-1,2,3-triazol1-yl)methyl)benzene (9) by addition of three equivalents of phenylacetylene to 7 in the presence of a catalytic amount of CuI (Scheme 5) [13]. Examination of the reactivity of compound 8 in Michael addition reactions revealed that the exp ...
Forward
... As we’ll see later in this chapter and the next, aldehydes and ketones are involved in many of the most used reactions in synthetic organic chemistry. Where do aldehydes and ketones come from? Many occur naturally. In terms of both variety and quantity, aldehydes and ketones rank among the most comm ...
... As we’ll see later in this chapter and the next, aldehydes and ketones are involved in many of the most used reactions in synthetic organic chemistry. Where do aldehydes and ketones come from? Many occur naturally. In terms of both variety and quantity, aldehydes and ketones rank among the most comm ...
Chapter - FIU Faculty Websites
... • Like gem-diol formation, the synthesis of acetals is reversible, and often, the equilibrium favors the reactants. • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please ...
... • Like gem-diol formation, the synthesis of acetals is reversible, and often, the equilibrium favors the reactants. • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please ...
CHEM 203 Material
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
12_chemistry_impq_CH10_haloalkanes_and_haloarenes_02
... Ans. Nitration is an electrophilic substitution. The –OH group in phenol increases the electron density at ortho and para position as follows Since phenol has higher electron density due to electron releasing nature of -OH group , compared to benzene , therefore nitration is easy in phenol than benz ...
... Ans. Nitration is an electrophilic substitution. The –OH group in phenol increases the electron density at ortho and para position as follows Since phenol has higher electron density due to electron releasing nature of -OH group , compared to benzene , therefore nitration is easy in phenol than benz ...
organic chemistry - Sakshieducation.com
... 3. Explain the structure and chemical nature of ethers. Ans: Structure : In CH3OCH3, the central oxygen atom is sp3 hybridized with two completely filled sp3 orbitals having lone pair of electrons and two half filled sp3 hybridized orbitals. Also carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized and both the half fil ...
... 3. Explain the structure and chemical nature of ethers. Ans: Structure : In CH3OCH3, the central oxygen atom is sp3 hybridized with two completely filled sp3 orbitals having lone pair of electrons and two half filled sp3 hybridized orbitals. Also carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized and both the half fil ...
幻灯片 1
... Bonding in organic compounds at that time was thought to be of either the water type, as in alcohols, ROH, or of the radical type, as in ethers which would be given the formula RO. But Williamson, by his ether synthesis, showed that mixed ethers, with two different alkyl groups, could be prepared. ...
... Bonding in organic compounds at that time was thought to be of either the water type, as in alcohols, ROH, or of the radical type, as in ethers which would be given the formula RO. But Williamson, by his ether synthesis, showed that mixed ethers, with two different alkyl groups, could be prepared. ...
Stille reaction

The Stille reaction, or the Migita-Kosugi-Stille coupling, is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis which involves the coupling of an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes) with a variety of organic electrophiles via palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction.The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including alkenes, and aryl groups; however, conditions have been devised to incorporate both sp3-hybridized groups, such as allylic and benzylic substituents, and sp-hybridized alkynes. These organostannanes are also stable to both air and moisture, and many of these reagents are either commercially available or can be synthesized from literature precedent. However, these tin reagents tend to be highly toxic. X is typically a halide, such as Cl, Br, I, yet pseudohalides such as triflates and sulfonates and phosphates can also be used.The groundwork for the Stille reaction was laid by Colin Eaborn, Toshihiko Migita, and Masanori Kosugi in 1976 and 1977, who explored numerous palladium catalyzed couplings involving organotin reagents. John Stille and David Milstein developed a much milder and more broadly applicable procedure in 1978. Stille’s work on this area might have earned him a share of the 2010 Nobel Prize, which was awarded to Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki for their work on the Heck, Negishi, and Suzuki coupling reactions. However, Stille died in the plane crash of United Airlines Flight 232 in 1989.Several reviews have been published on the Stille reaction.