Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... reaction is the formation of the cation intermediate Electron-donating substituents increase the rate of the substitution reactions by stabilizing the carbocation intermediate and the transition state leading to its formation ...
... reaction is the formation of the cation intermediate Electron-donating substituents increase the rate of the substitution reactions by stabilizing the carbocation intermediate and the transition state leading to its formation ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... In the haloform reaction, there is an -substitution whereby the methyl ketone is trihalogenated at the position. The trihalomethyl group is displaced by –OH. This reaction is used as a test for methyl ketones. + reactions would come from reactions a, and b; while – reactions would come from c, d, ...
... In the haloform reaction, there is an -substitution whereby the methyl ketone is trihalogenated at the position. The trihalomethyl group is displaced by –OH. This reaction is used as a test for methyl ketones. + reactions would come from reactions a, and b; while – reactions would come from c, d, ...
Organometallic Catalysts
... Generally far more selective for a single product far more easily studied from chemical & mechanistic aspects far more active ...
... Generally far more selective for a single product far more easily studied from chemical & mechanistic aspects far more active ...
Nucleophilic
... Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic chart. Thus, sulfur nucleophiles are more reactive than oxygen nucleophiles. Halides: I– > Br– > Cl– > F–. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than ...
... Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic chart. Thus, sulfur nucleophiles are more reactive than oxygen nucleophiles. Halides: I– > Br– > Cl– > F–. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than ...
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
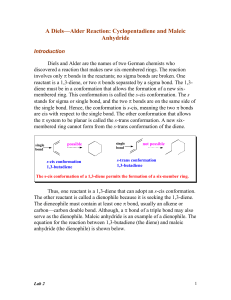
... Typical Dienophiles for Diels-Alder Reactions How does one recognize a Diels-Alder reaction? These reactions are easy to spot, because they involve two organic reactants and only heat as a reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the die ...
... Typical Dienophiles for Diels-Alder Reactions How does one recognize a Diels-Alder reaction? These reactions are easy to spot, because they involve two organic reactants and only heat as a reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the die ...
Carolina Aguirre, Rosa Arrieta, Soledad Anjarí, Andrés Illanes
... thermodynamically or kinetically controlled synthesis using enzymes. Kinetically controlled synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics, although requiring activated acyl donors, is usually a better strategy when product yield is a main issue (17) as is the case for antibiotic production (18), since it is not ...
... thermodynamically or kinetically controlled synthesis using enzymes. Kinetically controlled synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics, although requiring activated acyl donors, is usually a better strategy when product yield is a main issue (17) as is the case for antibiotic production (18), since it is not ...
Aldehydes and Ketones-12c - TAMU
... almost instantaneously. Aromatic aldehydes and ketones will give the color change at a much slower rate. ...
... almost instantaneously. Aromatic aldehydes and ketones will give the color change at a much slower rate. ...
Chapter 13 Silicon reagents
... •Silicon is directly below carbon in the periodic table, and shows some similarity in bonding. It forms 4 bonds in neutral molecules and is tetrahedral. • Silicon does not form very stable multiple bonds, as the large 3p orbital on silicon does not overlap well with the 2p orbital on carbon, oxygen ...
... •Silicon is directly below carbon in the periodic table, and shows some similarity in bonding. It forms 4 bonds in neutral molecules and is tetrahedral. • Silicon does not form very stable multiple bonds, as the large 3p orbital on silicon does not overlap well with the 2p orbital on carbon, oxygen ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion - Towson University
... bond due to the overlap of a p orbital on the substituent with a p orbital on the aromatic ring. C=O, CN, and NO2 substituents withdraw electrons from the aromatic ring by resonance, i.e. the electrons flow from the rings to the ...
... bond due to the overlap of a p orbital on the substituent with a p orbital on the aromatic ring. C=O, CN, and NO2 substituents withdraw electrons from the aromatic ring by resonance, i.e. the electrons flow from the rings to the ...
1 Chapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group
... Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic chart. Thus, sulfur nucleophiles are more reactive than oxygen nucleophiles. Halides: I– > Br– > Cl– > F–. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than ...
... Nucleophilicity usually increases going down a column of the periodic chart. Thus, sulfur nucleophiles are more reactive than oxygen nucleophiles. Halides: I– > Br– > Cl– > F–. Negatively charged nucleophiles are usually more reactive than ...
Barton Deoxygenation
... Hydrogenation: anti addition – Synthesis of trans-alkenes A dissolving metal reaction which uses lithium or sodium metal in low temperature ammonia or amine solvent produces trans-alkenes. This dissolving metal reduction process is different than other catalytic hydrogenation process. In this reacti ...
... Hydrogenation: anti addition – Synthesis of trans-alkenes A dissolving metal reaction which uses lithium or sodium metal in low temperature ammonia or amine solvent produces trans-alkenes. This dissolving metal reduction process is different than other catalytic hydrogenation process. In this reacti ...
Palladium Nanoparticles Entrapped in Aluminum Hydroxide: Dual
... To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of such a catalyst that consecutively performs the two reactions in one pot. Furthermore, the catalyst is recyclable and amphiphilic, active in both water and common organic solvents. Palladium nanoparticles have proved to be attractive catalyst ...
... To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of such a catalyst that consecutively performs the two reactions in one pot. Furthermore, the catalyst is recyclable and amphiphilic, active in both water and common organic solvents. Palladium nanoparticles have proved to be attractive catalyst ...
Enantioselective Henry Reactions under Dual Lewis Acid/Amine
... Claudio Palomo,* Mikel Oiarbide, and Antonio Laso There is increasing interest in developing catalytic asymmetric C C bond-forming processes.[1] In this endeavor the Henry reaction[2] is prominent because of the versatile chemistry of the nitro group.[3] Remarkably, however, while this reaction is c ...
... Claudio Palomo,* Mikel Oiarbide, and Antonio Laso There is increasing interest in developing catalytic asymmetric C C bond-forming processes.[1] In this endeavor the Henry reaction[2] is prominent because of the versatile chemistry of the nitro group.[3] Remarkably, however, while this reaction is c ...
Preparation of Alkyl Halides
... Victor Grignard discovered that a dry alkyl halide will react with dry magnesium metal in a dry ether solvent to produce an organometallic compound with that behaves as if it has the structure R-Mg-X It is now called an alkylmagnesium halide or Grignard reagent: ...
... Victor Grignard discovered that a dry alkyl halide will react with dry magnesium metal in a dry ether solvent to produce an organometallic compound with that behaves as if it has the structure R-Mg-X It is now called an alkylmagnesium halide or Grignard reagent: ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... Chemists synthesize compounds in just about every organic chemistry laboratory in the world. Industrial chemists synthesize pharmaceuticals, polymers (plastics), pesticides, dye stuffs, food colorings and flavorings, perfumes, detergents and disinfectants. Research chemists synthesize natural produc ...
... Chemists synthesize compounds in just about every organic chemistry laboratory in the world. Industrial chemists synthesize pharmaceuticals, polymers (plastics), pesticides, dye stuffs, food colorings and flavorings, perfumes, detergents and disinfectants. Research chemists synthesize natural produc ...
Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing a Pyridyl-Supported Pyrazolyl
... obtained by Claisen condensation of 4 with 3,3-dimethyl-2butone followed by reacting with hydrazine hydrate. The ligand precursor 6 was efficiently prepared by the reaction of 5 with 1-iodobutane in refluxing acetonitrile. When the tert-butyl group in 5 was substituted by a methyl group, the corresp ...
... obtained by Claisen condensation of 4 with 3,3-dimethyl-2butone followed by reacting with hydrazine hydrate. The ligand precursor 6 was efficiently prepared by the reaction of 5 with 1-iodobutane in refluxing acetonitrile. When the tert-butyl group in 5 was substituted by a methyl group, the corresp ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... Research chemists synthesize natural products whose structure is uncertain, compounds for mechanistic investigations, possible intermediate in chemical and biological processes, thousands of potential drugs for everyone which is used in medical practice, and even compounds which might themselves be ...
... Research chemists synthesize natural products whose structure is uncertain, compounds for mechanistic investigations, possible intermediate in chemical and biological processes, thousands of potential drugs for everyone which is used in medical practice, and even compounds which might themselves be ...
level three chemistry: organics
... paper. I can show understanding of the differences between aldehydes and ketones by explaining how to distinguish between them using Tollens, Benedicts or Fehlings reagents and describing any observations that would occur. I can show understanding of how acyl chlorides differ from other molecules by ...
... paper. I can show understanding of the differences between aldehydes and ketones by explaining how to distinguish between them using Tollens, Benedicts or Fehlings reagents and describing any observations that would occur. I can show understanding of how acyl chlorides differ from other molecules by ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
Perspective and prospects for pincer ligand chemistry
... Processes such as P−C cleavage of phosphines, undesirable ligand dissociation, and irreversible ligand oxidative addition are well documented with many catalysts. Some of the pincer systems developed to date appear to avoid these pitfalls, perhaps due to their restrictive environments, at least unti ...
... Processes such as P−C cleavage of phosphines, undesirable ligand dissociation, and irreversible ligand oxidative addition are well documented with many catalysts. Some of the pincer systems developed to date appear to avoid these pitfalls, perhaps due to their restrictive environments, at least unti ...
Abstract OXIDATIVE TRANSFORMATIONS AND CYCLIZATIONS
... Chapter III. Catalytic Oxidative Conversion of Alcohols, Aldehydes and Amines into Nitriles using KI/I2–TBHP system Nitriles are useful functional groups in synthetic organic chemistry as they are most important precursors for esters, amides, carboxylic acids, amines, and nitrogencontaining heterocy ...
... Chapter III. Catalytic Oxidative Conversion of Alcohols, Aldehydes and Amines into Nitriles using KI/I2–TBHP system Nitriles are useful functional groups in synthetic organic chemistry as they are most important precursors for esters, amides, carboxylic acids, amines, and nitrogencontaining heterocy ...
14_chapter 8
... separation has the advantage of isolating the product by simple extraction with organic solvent. It was observed that the benzyl bromides of unsubstituted, substituted with electron donating groups undergo the reaction in shorter duration with maximum yield of benzaldehydes (entry 1,2), ...
... separation has the advantage of isolating the product by simple extraction with organic solvent. It was observed that the benzyl bromides of unsubstituted, substituted with electron donating groups undergo the reaction in shorter duration with maximum yield of benzaldehydes (entry 1,2), ...
Stille reaction

The Stille reaction, or the Migita-Kosugi-Stille coupling, is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis which involves the coupling of an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes) with a variety of organic electrophiles via palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction.The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including alkenes, and aryl groups; however, conditions have been devised to incorporate both sp3-hybridized groups, such as allylic and benzylic substituents, and sp-hybridized alkynes. These organostannanes are also stable to both air and moisture, and many of these reagents are either commercially available or can be synthesized from literature precedent. However, these tin reagents tend to be highly toxic. X is typically a halide, such as Cl, Br, I, yet pseudohalides such as triflates and sulfonates and phosphates can also be used.The groundwork for the Stille reaction was laid by Colin Eaborn, Toshihiko Migita, and Masanori Kosugi in 1976 and 1977, who explored numerous palladium catalyzed couplings involving organotin reagents. John Stille and David Milstein developed a much milder and more broadly applicable procedure in 1978. Stille’s work on this area might have earned him a share of the 2010 Nobel Prize, which was awarded to Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki for their work on the Heck, Negishi, and Suzuki coupling reactions. However, Stille died in the plane crash of United Airlines Flight 232 in 1989.Several reviews have been published on the Stille reaction.