19-3 Esters and Anhydrides (PPT)
... With less basic nucleophiles, especially under acidic conditions, substitution through the addition-elimination mechanism may occur. In the esterification of a carboxylic acid, an alcohol and a carboxylic acid react in the presence of acid to form an ester and water. ...
... With less basic nucleophiles, especially under acidic conditions, substitution through the addition-elimination mechanism may occur. In the esterification of a carboxylic acid, an alcohol and a carboxylic acid react in the presence of acid to form an ester and water. ...
“If You Want to Make a Carbon
... If you want to make a carbon carbon bond, a bond Of organic chem. you must be awfully fond, quite fond You might want to use SN2, or Friedel Crafts could work for you Don’t forget Organometallic and Diels-Alder , and Wittig, and condensation, and substitution…of carbonyl compounds Why don’t we tell ...
... If you want to make a carbon carbon bond, a bond Of organic chem. you must be awfully fond, quite fond You might want to use SN2, or Friedel Crafts could work for you Don’t forget Organometallic and Diels-Alder , and Wittig, and condensation, and substitution…of carbonyl compounds Why don’t we tell ...
Alkanes - MsReenChemistry
... • Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. They contain all single carbon-carbon bonds. [Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain double or triple carbon-carbon bonds.] • Alkanes are also aliphatic, meaning the carbon atoms form open chains. [In contrast to aromatic compounds which contain benzene rings.] Alkane ...
... • Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. They contain all single carbon-carbon bonds. [Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain double or triple carbon-carbon bonds.] • Alkanes are also aliphatic, meaning the carbon atoms form open chains. [In contrast to aromatic compounds which contain benzene rings.] Alkane ...
notes fill in File
... The lower the number, the more _________ pH 7 = base The higher the number, the more _________ An indicator is used to determine pH (litmus paper/phenolphthalein…. Other indicators are pH paper, methyl orange, bromothymol blue, red cabbage juice, and tea The most accurate measurements are done wit ...
... The lower the number, the more _________ pH 7 = base The higher the number, the more _________ An indicator is used to determine pH (litmus paper/phenolphthalein…. Other indicators are pH paper, methyl orange, bromothymol blue, red cabbage juice, and tea The most accurate measurements are done wit ...
Organic Chemistry
... Alcohols are *substituted hydrocarbons in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced with a hydroxyl group (-OH). *Another element has replaced hydrogen. H ...
... Alcohols are *substituted hydrocarbons in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced with a hydroxyl group (-OH). *Another element has replaced hydrogen. H ...
Naming Substituted Hydrocarbons
... element other than hydrogen attached somewhere along the hydrocarbon chain. It is named in a similar fashion to a hydrocarbon. This can be illustrated with alcohols as an example. The compounds pictured to the lower left are alcohols. They look like alkanes with –OH at one end where a H hydrogen wou ...
... element other than hydrogen attached somewhere along the hydrocarbon chain. It is named in a similar fashion to a hydrocarbon. This can be illustrated with alcohols as an example. The compounds pictured to the lower left are alcohols. They look like alkanes with –OH at one end where a H hydrogen wou ...
Topic 3 – Chemical Structure and Bonding
... The pollutants produced by car engines include carbon, C, carbon monoxide, CO, sulphur dioxide, SO2, oxides of nitrogen, NOx and unburnt hydrocarbons Carbon monoxide and carbon come from the incomplete combustion of the hydrocarbons in petrol and are toxic. Carbon is also a respiratory irritant Sulp ...
... The pollutants produced by car engines include carbon, C, carbon monoxide, CO, sulphur dioxide, SO2, oxides of nitrogen, NOx and unburnt hydrocarbons Carbon monoxide and carbon come from the incomplete combustion of the hydrocarbons in petrol and are toxic. Carbon is also a respiratory irritant Sulp ...
National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions Unit 1 Chemical
... 2. a) How do catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction? b) Name the types of catalysts and describe how they differ from each other? 3. What is an enzyme and state the use of one. 4. Calculate the rate of reaction if 20cm3 of carbon dioxide gas is given off in the first 60 seconds of a reacti ...
... 2. a) How do catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction? b) Name the types of catalysts and describe how they differ from each other? 3. What is an enzyme and state the use of one. 4. Calculate the rate of reaction if 20cm3 of carbon dioxide gas is given off in the first 60 seconds of a reacti ...
Exam 3 Review
... What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more r ...
... What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more r ...
Practice exam 1 - Little Dumb doctor, homework solutions
... 3.(10) Draw the resonance structure for each of the species below using the arrows indicating the electron flow. O a) ...
... 3.(10) Draw the resonance structure for each of the species below using the arrows indicating the electron flow. O a) ...
Lecture 2 - Bonding in Organic Compounds
... tetrahedral shape, the hybridized orbital will be sp3. • Single bonds are sigma (S) • Double Bonds are Pi (P) • Triple Bonds are Sigma & Pi (S & P) • Alkenes and Alkynes are called unsaturated hydrocarbons (presence of ...
... tetrahedral shape, the hybridized orbital will be sp3. • Single bonds are sigma (S) • Double Bonds are Pi (P) • Triple Bonds are Sigma & Pi (S & P) • Alkenes and Alkynes are called unsaturated hydrocarbons (presence of ...
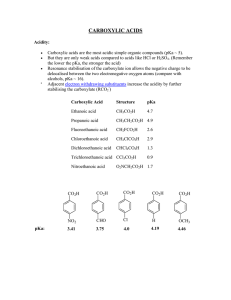
carboxylic acids - La Salle University
... NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION OF RMgX TO CARBON DIOXIDE Step 1: The nucleophilic C in the Grignard reagent adds to the electrophilic C in the polar carbonyl group, electrons from the C=O move to the electronegative O creating an intermediate magnesium carboxylate complex. ...
... NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION OF RMgX TO CARBON DIOXIDE Step 1: The nucleophilic C in the Grignard reagent adds to the electrophilic C in the polar carbonyl group, electrons from the C=O move to the electronegative O creating an intermediate magnesium carboxylate complex. ...
Johnson Group Research
... cleavage and functionalization of carbon-carbon bonds. While carbon-carbon single bonds are inert under a vast majority of standard reaction conditions, certain transition metal complexes promote the activation of these bonds. Research in the Johnson group will follow several avenues of study, inclu ...
... cleavage and functionalization of carbon-carbon bonds. While carbon-carbon single bonds are inert under a vast majority of standard reaction conditions, certain transition metal complexes promote the activation of these bonds. Research in the Johnson group will follow several avenues of study, inclu ...
ch 1: organic chemistry
... structure similar to water H-O-H and alcohols R-O-H only in ethers, structure is R-O-R (where R=alkyl groups) alkyl groups may be identical or different there are no OH bonds in ethers so they do not form hydrogen bonds C-O bonds are polar and the v-shape of the C-O-C group make ether molecu ...
... structure similar to water H-O-H and alcohols R-O-H only in ethers, structure is R-O-R (where R=alkyl groups) alkyl groups may be identical or different there are no OH bonds in ethers so they do not form hydrogen bonds C-O bonds are polar and the v-shape of the C-O-C group make ether molecu ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... In the haloform reaction, there is an -substitution whereby the methyl ketone is trihalogenated at the position. The trihalomethyl group is displaced by –OH. This reaction is used as a test for methyl ketones. + reactions would come from reactions a, and b; while – reactions would come from c, d, ...
... In the haloform reaction, there is an -substitution whereby the methyl ketone is trihalogenated at the position. The trihalomethyl group is displaced by –OH. This reaction is used as a test for methyl ketones. + reactions would come from reactions a, and b; while – reactions would come from c, d, ...
elements of chemistry unit
... Although all organic compounds contain carbon, and almost all of them contain hydrogen, most of them contain other elements as well. The most common extra elements in organic compounds are oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and the halogens (Group 17). HALOGENS Halogens resemble hydrogen because they form si ...
... Although all organic compounds contain carbon, and almost all of them contain hydrogen, most of them contain other elements as well. The most common extra elements in organic compounds are oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and the halogens (Group 17). HALOGENS Halogens resemble hydrogen because they form si ...
اســـم المـــدرس: د
... 2) Write the chemical and the reaction mechanism for the reaction of benzaldehyde with excess methanol and acid catalyst. ...
... 2) Write the chemical and the reaction mechanism for the reaction of benzaldehyde with excess methanol and acid catalyst. ...
IUBAC naming organic compounds
... Chlorine is called “chloro” Fluorine is called “ Fluoro” Bromine is called “bromo” Iodine is called “iodo ...
... Chlorine is called “chloro” Fluorine is called “ Fluoro” Bromine is called “bromo” Iodine is called “iodo ...
Chapter 22: HW questions 1. Alkanes have the general formula --
... 29. Esters are synthesized from two classes of organic compounds. Those two types of compounds are A) acids and bases. D) amines and alkenes. B) amines and alcohols. E) alkenes and bases. C) alcohols and acids. ...
... 29. Esters are synthesized from two classes of organic compounds. Those two types of compounds are A) acids and bases. D) amines and alkenes. B) amines and alcohols. E) alkenes and bases. C) alcohols and acids. ...
3.8 ADDITION OF WATER TO AN ALKENE H or enzyme + H-O
... Polymerization is the formation of extremely long molecules from small molecules called monomers. The plastics and rubber are examples of the most common polymers which are commonly used in both everyday life and in medical applications. The exact properties of polymers depends on a variety of chemi ...
... Polymerization is the formation of extremely long molecules from small molecules called monomers. The plastics and rubber are examples of the most common polymers which are commonly used in both everyday life and in medical applications. The exact properties of polymers depends on a variety of chemi ...
Carbon Compounds
... – If just one atom of another element is substituted for one hydrogen atom, a different compound is created!!!! ...
... – If just one atom of another element is substituted for one hydrogen atom, a different compound is created!!!! ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.