Chemistry to Remember
... in barometric pressure and gas pressure electronically. Temperature is measured by two different scales: degree Fahrenheit (˚F) and degree Centigrade (˚C). A thermometer is a column of mercury in a vacuum that expands and contracts depending on the thermometric activity of the substance surrounding ...
... in barometric pressure and gas pressure electronically. Temperature is measured by two different scales: degree Fahrenheit (˚F) and degree Centigrade (˚C). A thermometer is a column of mercury in a vacuum that expands and contracts depending on the thermometric activity of the substance surrounding ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... formation of a covalent bond.) Continue doing this until each atom has an octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if ...
... formation of a covalent bond.) Continue doing this until each atom has an octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if ...
Document
... together the active site where electron and atom transfer to the pretreated substrate molecule(s) occurs. So, instead of the traditional synthetic procedures, it has been conceived that bidentate ligands may also be obtained by self-assembly of monodentate ones. Construction of complex structures fr ...
... together the active site where electron and atom transfer to the pretreated substrate molecule(s) occurs. So, instead of the traditional synthetic procedures, it has been conceived that bidentate ligands may also be obtained by self-assembly of monodentate ones. Construction of complex structures fr ...
Ch. 2 Chemistry
... In some cases, atoms strip electrons away from their bonding partners Electron transfer between two atoms creates ions Ions • Are atoms with more or fewer electrons than usual (charged atoms) • Such as Na+, Cl-, K+, PO43- ...
... In some cases, atoms strip electrons away from their bonding partners Electron transfer between two atoms creates ions Ions • Are atoms with more or fewer electrons than usual (charged atoms) • Such as Na+, Cl-, K+, PO43- ...
Clusters and Polynuclear Compounds
... designate a finite group of metal atoms held together mainly, or at least to a significant extent, by metal-metal bonds. That was necessary in order to differentiate this emerging class of compounds from polynuclear complexes in which the metal centers are held together exclusively or mainly by brid ...
... designate a finite group of metal atoms held together mainly, or at least to a significant extent, by metal-metal bonds. That was necessary in order to differentiate this emerging class of compounds from polynuclear complexes in which the metal centers are held together exclusively or mainly by brid ...
as a PDF
... (III in Fig. 2) leads to an intervalence transfer excited state which initiates the redox reaction. This photoredox reaction is simply a special case of the photochemistry of aqueous Co(III) complex ammines which generally undergo redox reactions under formation of C o ...
... (III in Fig. 2) leads to an intervalence transfer excited state which initiates the redox reaction. This photoredox reaction is simply a special case of the photochemistry of aqueous Co(III) complex ammines which generally undergo redox reactions under formation of C o ...
Look at the reaction coordinate diagram…
... When hydrogen is bonded to another atom (F, O, N, Cl) such that the bond is polar the H atom bears a partial positive charge and the more electronegative atom bears a negative charge. This results in an interaction between molecules Details of these interactions are disputed but they are generally a ...
... When hydrogen is bonded to another atom (F, O, N, Cl) such that the bond is polar the H atom bears a partial positive charge and the more electronegative atom bears a negative charge. This results in an interaction between molecules Details of these interactions are disputed but they are generally a ...
1. (a) Write the electronic structure of a manganese atom and a Mn
... The addition of excess aqueous silver nitrate to aqueous solutions of either of these two salts produces a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. ...
... The addition of excess aqueous silver nitrate to aqueous solutions of either of these two salts produces a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. ...
Rembrandt: The Late Works - Science Teachers Word Bank
... A solvent is a substance that dissolves a soluble material (or solute). For example, varnish is insoluble in water but might dissolve in propanone or acetone. The solubility of a substance depends on many factors, but a solute will dissolve in a solvent that has a similar polarity (‘like-dissolves-l ...
... A solvent is a substance that dissolves a soluble material (or solute). For example, varnish is insoluble in water but might dissolve in propanone or acetone. The solubility of a substance depends on many factors, but a solute will dissolve in a solvent that has a similar polarity (‘like-dissolves-l ...
Feasibility Study of using FAIMS to Detect Carbonyl Sulfide in Propane
... Sample preparation and introduction FAIMS can be used to detect volatiles in aqueous, solid and gaseous matrices and can consequently be used for a wide variety of applications. The user requirements and sample matrix for each application define the sample preparation and introduction steps required ...
... Sample preparation and introduction FAIMS can be used to detect volatiles in aqueous, solid and gaseous matrices and can consequently be used for a wide variety of applications. The user requirements and sample matrix for each application define the sample preparation and introduction steps required ...
Molecular Symmetry
... • When two basis functions are shown in parenthesis these objects transform together and are degenerate – eg. (x,y) ...
... • When two basis functions are shown in parenthesis these objects transform together and are degenerate – eg. (x,y) ...
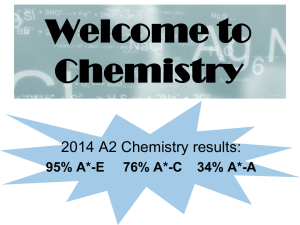
AS Chemistry - Crawshaw Academy
... be comfortable with the basic Chemistry from the GCSE course, most significantly: ‘Bonding and Structure’, ‘Periodicity’, ‘Chemical Formulae’, Chemistry Calculations’ and ‘Balancing Equations’. In order for you to settle into the course quickly it is essential that you do some background work on the ...
... be comfortable with the basic Chemistry from the GCSE course, most significantly: ‘Bonding and Structure’, ‘Periodicity’, ‘Chemical Formulae’, Chemistry Calculations’ and ‘Balancing Equations’. In order for you to settle into the course quickly it is essential that you do some background work on the ...
Substituent groups in aryl- and arylalkylphosphanes: effects on
... A coordination compound contains a metal center surrounded by a number of oppositely charged ions or neutral molecules (possessing lone pairs of electrons), which are known as ligands. The most straightforward way to affect the chemical behavior of a metal ion is through change in its ligands. It is ...
... A coordination compound contains a metal center surrounded by a number of oppositely charged ions or neutral molecules (possessing lone pairs of electrons), which are known as ligands. The most straightforward way to affect the chemical behavior of a metal ion is through change in its ligands. It is ...
Metal–dioxygen and metal–dinitrogen complexes: where are the
... through a second side-on interaction, and the resulting binding mode is described as m-h2 :h2 or “side-on/side-on” binding (Fig. 1). The most intense characterization of this binding mode for O2 complexes has come in m-h2 :h2 -peroxodicopper(II) complexes, because they are synthetic analogues for co ...
... through a second side-on interaction, and the resulting binding mode is described as m-h2 :h2 or “side-on/side-on” binding (Fig. 1). The most intense characterization of this binding mode for O2 complexes has come in m-h2 :h2 -peroxodicopper(II) complexes, because they are synthetic analogues for co ...
Chemical Equilibrium – Le Chatelier`s Principle
... What is the color of methyl violet in water ? What reagent causes a color change? What reagent causes a shift back to the original color? In terms of equilibrium of reaction (2), explain why the reagents for Steps 2 and 3 worked. Part B. Solubility Equilibrium; Finding a Value for Ksp Calculate the ...
... What is the color of methyl violet in water ? What reagent causes a color change? What reagent causes a shift back to the original color? In terms of equilibrium of reaction (2), explain why the reagents for Steps 2 and 3 worked. Part B. Solubility Equilibrium; Finding a Value for Ksp Calculate the ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... If the two elements in a binary compound are both nonmetals the compound is a molecular compound The method of naming these compound is similar just discussed. Usually write the positive OS element first. HCl: hydrogen chloride Some pairs of nonmetals form more than one compound, we need to ...
... If the two elements in a binary compound are both nonmetals the compound is a molecular compound The method of naming these compound is similar just discussed. Usually write the positive OS element first. HCl: hydrogen chloride Some pairs of nonmetals form more than one compound, we need to ...
ENERGY LEVELS OF TRANSITION METAL IONS IN LASER
... the fourth period of the periodic table, lose the outer 4s electrons and possible some 3d electrons in forming ionic bonds; their resulting electronic configurations are 1s22s22p63s23p63dn where n<10. Ions with incomplete 3d shells have a number of low lying energy levels between which optical trans ...
... the fourth period of the periodic table, lose the outer 4s electrons and possible some 3d electrons in forming ionic bonds; their resulting electronic configurations are 1s22s22p63s23p63dn where n<10. Ions with incomplete 3d shells have a number of low lying energy levels between which optical trans ...
VVV
... c) NO d) Ne e) NF3 25. (2) The normal boiling point of a liquid a) Is the temperature at which liquid and vapor are in equilibrium b) Varies with the atmospheric pressure c) Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure is 1 atm. d) Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals external pre ...
... c) NO d) Ne e) NF3 25. (2) The normal boiling point of a liquid a) Is the temperature at which liquid and vapor are in equilibrium b) Varies with the atmospheric pressure c) Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure is 1 atm. d) Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals external pre ...
Chapter8
... Octet rule, atoms tend to combine in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shells, giving them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The ...
... Octet rule, atoms tend to combine in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shells, giving them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.