- LSU Chemistry
... increase F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2. But decrease as one goes from C-C > Si-C > Ge-C > Sn-C > Pb-C. For most transition metal M-M single bonds the trend is fairly consistent: first row < second row < third row. But for M-M quadruple bonds one has: Cr-Cr << Mo-Mo > W-W. ...
... increase F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2. But decrease as one goes from C-C > Si-C > Ge-C > Sn-C > Pb-C. For most transition metal M-M single bonds the trend is fairly consistent: first row < second row < third row. But for M-M quadruple bonds one has: Cr-Cr << Mo-Mo > W-W. ...
Practice Exercise
... has an octahedral geometry. Like [Co(NH3)4Cl2 ]+ (Figure 24.1), it has four ligands of one type and two of another. Consequently, it possesses two isomers: one with the Cl – ligands across the metal from each other (trans-Fe(CO)4Cl2) and one with the Cl– ligands adjacent (cis-Fe(CO)4Cl2). In princip ...
... has an octahedral geometry. Like [Co(NH3)4Cl2 ]+ (Figure 24.1), it has four ligands of one type and two of another. Consequently, it possesses two isomers: one with the Cl – ligands across the metal from each other (trans-Fe(CO)4Cl2) and one with the Cl– ligands adjacent (cis-Fe(CO)4Cl2). In princip ...
Preparation of a Coordination Compound
... Many transition metal ions are coloured because the energies required for the electronic transitions within their partially-filled d-subshells lie in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. That is, visible light passing through their crystals or solutions is sufficiently energetic to ra ...
... Many transition metal ions are coloured because the energies required for the electronic transitions within their partially-filled d-subshells lie in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. That is, visible light passing through their crystals or solutions is sufficiently energetic to ra ...
Molecular Docking Using GOLD
... What is molecular docking? (2) • Difficult to predict • Parameters to be considered: – Hydrogen bonds, lipophilic properties, van der Waals interactions – Possible metal ions – Tensions of the ligand backbone Conformation ...
... What is molecular docking? (2) • Difficult to predict • Parameters to be considered: – Hydrogen bonds, lipophilic properties, van der Waals interactions – Possible metal ions – Tensions of the ligand backbone Conformation ...
RuP(OMe) 2
... Hemilabile ligands have been of great interest to chemists working toward the development of molecular sensors. Hemilabile coordination is found to occur amongst polydentate ligands that contain both chemically inert and labile sites bound to a metal center. In the presence of molecules with a stron ...
... Hemilabile ligands have been of great interest to chemists working toward the development of molecular sensors. Hemilabile coordination is found to occur amongst polydentate ligands that contain both chemically inert and labile sites bound to a metal center. In the presence of molecules with a stron ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... between metal ion and ligands. In metal ions all fixed orbitals have same energy.(degenerate orbitals) On the approach of ligands electrons in d orbitals will be repelled by electron of ligands. The repulsion will increase the energy of d orbitals. Since d orbitals have different orientation ...
... between metal ion and ligands. In metal ions all fixed orbitals have same energy.(degenerate orbitals) On the approach of ligands electrons in d orbitals will be repelled by electron of ligands. The repulsion will increase the energy of d orbitals. Since d orbitals have different orientation ...
spectroscopic and antimicrobial studies of mixed ligand complexes
... INTRODUCTION In chemistry, a complexs, also called a "coordination compounds" or "metal complex", is a structure consisting of a central atom or molecule connected to surrounding atoms or molecules. Originally, a complex implied a reversible association of molecules, atoms, or ions through weak chem ...
... INTRODUCTION In chemistry, a complexs, also called a "coordination compounds" or "metal complex", is a structure consisting of a central atom or molecule connected to surrounding atoms or molecules. Originally, a complex implied a reversible association of molecules, atoms, or ions through weak chem ...
Practice final
... 22. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE ? A. The wavefunction, ψ, is a solution to the Schrodinger equation B. The square of the wavefunction, ψ 2, is the total probability of finding the electron in a spherical shell at distance r from the nucleus C. Orbitals with the same n cannot overla ...
... 22. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE ? A. The wavefunction, ψ, is a solution to the Schrodinger equation B. The square of the wavefunction, ψ 2, is the total probability of finding the electron in a spherical shell at distance r from the nucleus C. Orbitals with the same n cannot overla ...
Self-Study_Worksheet II_Basis for Color_ANSWERS
... b) Explain briefly the difference between this diagram and the one that you drew in Exercise 1 (other than the fact that there are no arrows). Why do you think it is called a “splitting” diagram? When does splitting occur? (Answer: When there are __ligands present) Initially all five d orbitals have ...
... b) Explain briefly the difference between this diagram and the one that you drew in Exercise 1 (other than the fact that there are no arrows). Why do you think it is called a “splitting” diagram? When does splitting occur? (Answer: When there are __ligands present) Initially all five d orbitals have ...
All contain a transition metal!! All are coordination compounds Many
... Legumes (nitrogen fixers) Radiopharmaceuticals (some) MRI contrast agents ...
... Legumes (nitrogen fixers) Radiopharmaceuticals (some) MRI contrast agents ...
chapter 24
... " A complex must have partially filled d subshell on metal to exhibit color " A complex with 0 or 10 d e-s is colorless ...
... " A complex must have partially filled d subshell on metal to exhibit color " A complex with 0 or 10 d e-s is colorless ...
Elements, basic principles, periodic table
... + ion smaller than the neutral atom b/c fewer e- feel the "pull" of the positively charged nucleus - ion is larger than the neutral atom Ions behave the same as atoms across the periodic table (row vs column Importance of the radius: molecules can only “fit” certain sizes ...
... + ion smaller than the neutral atom b/c fewer e- feel the "pull" of the positively charged nucleus - ion is larger than the neutral atom Ions behave the same as atoms across the periodic table (row vs column Importance of the radius: molecules can only “fit” certain sizes ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-ISSN: 2278-5736.
... finger printing agents2. Considerable attention has been paid in recent year on the investigation of the complex forming properties of potentially bidentate and tridentates ligands3-6.The metal complexes of pyrimidine bases are of prime biological importance as a model of nucleic acids ion interacti ...
... finger printing agents2. Considerable attention has been paid in recent year on the investigation of the complex forming properties of potentially bidentate and tridentates ligands3-6.The metal complexes of pyrimidine bases are of prime biological importance as a model of nucleic acids ion interacti ...
Crystal-Field Theory Ligand-Field or Molecular Orbital Theory
... Filled ns, np shells; chemistry defined by unoccupied nd-orbitals Number of d-electrons = Z – nearest noble gas e’s – charge e.g.: Fe(II) = 26 – 18 – 2 =6 ...
... Filled ns, np shells; chemistry defined by unoccupied nd-orbitals Number of d-electrons = Z – nearest noble gas e’s – charge e.g.: Fe(II) = 26 – 18 – 2 =6 ...
Problems - UCI Chemistry
... consistent with these observations. 10.21 a. Explain the effect on the d-orbital energies when an octahedral complex is compressed along the z axis. b. Explain the effect on the d-orbital energies when an octahedral complex is stretched along the z axis. In the limit, this results in a square-planar ...
... consistent with these observations. 10.21 a. Explain the effect on the d-orbital energies when an octahedral complex is compressed along the z axis. b. Explain the effect on the d-orbital energies when an octahedral complex is stretched along the z axis. In the limit, this results in a square-planar ...
STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL MIMIC OF
... or in living organisms. Beside this it allows the determination of the structural porperties of the active centre what is often impossible in the case of the native systems. These investigations are not only simpler and cheaper than those of the native macromolecules but provide also an opportunity ...
... or in living organisms. Beside this it allows the determination of the structural porperties of the active centre what is often impossible in the case of the native systems. These investigations are not only simpler and cheaper than those of the native macromolecules but provide also an opportunity ...
Crystal Field Theory
... Therefore, [Ti(en)6]3+ must have the shortest λ - tetrahedral and square planar complexes ...
... Therefore, [Ti(en)6]3+ must have the shortest λ - tetrahedral and square planar complexes ...
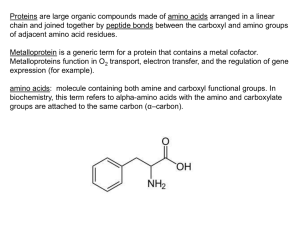
amino acids
... Cytochrome: Any of a class of iron-containing proteins important in cell respiration as catalysts of oxidation-reduction reactions. Cytochrome P450: one of a large group of iron-containing oyxgenases that utilize atmospheric dioxygen to functionalize molecules using cofactors such as flavins or NAD ...
... Cytochrome: Any of a class of iron-containing proteins important in cell respiration as catalysts of oxidation-reduction reactions. Cytochrome P450: one of a large group of iron-containing oyxgenases that utilize atmospheric dioxygen to functionalize molecules using cofactors such as flavins or NAD ...
Electronic Structure of Metals The “Sea of Electrons”
... Cr and Cu are exceptions to trend: both are 4s1 3dn Neutral TM: 3d and 4s orbitals similar in energy 3d orbitals for TM ions much less E than 4s, so 4s electrons leave first (1st row TM ions do not have 4s electrons) ...
... Cr and Cu are exceptions to trend: both are 4s1 3dn Neutral TM: 3d and 4s orbitals similar in energy 3d orbitals for TM ions much less E than 4s, so 4s electrons leave first (1st row TM ions do not have 4s electrons) ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.