Mixed ligand complexes of essential metal ions with L
... ML second one. Hence, the order of stability K M ML >K ML2 holds well. This leads to the natural expectation for Δ log K to be negative, although several exceptions have been found.26,30 The statistical values of Δ log K for bidentate L and X are –0.4 and –0.6 for octahedral and square planar comple ...
... ML second one. Hence, the order of stability K M ML >K ML2 holds well. This leads to the natural expectation for Δ log K to be negative, although several exceptions have been found.26,30 The statistical values of Δ log K for bidentate L and X are –0.4 and –0.6 for octahedral and square planar comple ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry!
... I hope you are ready for a fun, yet challenging year. You already have a solid background in basic chemistry from your first year Chem class, and this is critical to success in AP Chem. As the year progresses and you develop your skills for making connections and problem solving as we delve into gre ...
... I hope you are ready for a fun, yet challenging year. You already have a solid background in basic chemistry from your first year Chem class, and this is critical to success in AP Chem. As the year progresses and you develop your skills for making connections and problem solving as we delve into gre ...
FREE Sample Here
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
CHM 423 Coordination Chemistry
... compounds is restricted to compounds in which the Lewis acid is a transition metal or dblock elements. A molecule can function as a Lewis base provided it has heteroatom(s) with lone pair(s) on them. Examples of such molecules are H2O, NH3, CO etc, anions such as halides (F-, Cl-, Br), cyanide (CN-) ...
... compounds is restricted to compounds in which the Lewis acid is a transition metal or dblock elements. A molecule can function as a Lewis base provided it has heteroatom(s) with lone pair(s) on them. Examples of such molecules are H2O, NH3, CO etc, anions such as halides (F-, Cl-, Br), cyanide (CN-) ...
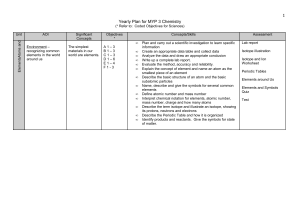
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an atom and the basic subatomic particles Name, describe and give the symbols for several common elements Define atomic number and mass number Interpret chemical notation for elements, ...
... Explain the concept of element and name an atom as the smallest piece of an element Describe the basic structure of an atom and the basic subatomic particles Name, describe and give the symbols for several common elements Define atomic number and mass number Interpret chemical notation for elements, ...
Comparison of structurally-related alkoxide, amine, and thiolate
... MeOH/Et2O solution (1:3). The solution was filtered and the precipitate was washed with additional ether (2 · 15 ml). The solid was further purified by triturating for 2 days in an Et2O/CH2Cl2 mixture (1:1). The residue was then filtered, washed with additional ether, and pumped dry under vacuum. Yi ...
... MeOH/Et2O solution (1:3). The solution was filtered and the precipitate was washed with additional ether (2 · 15 ml). The solid was further purified by triturating for 2 days in an Et2O/CH2Cl2 mixture (1:1). The residue was then filtered, washed with additional ether, and pumped dry under vacuum. Yi ...
ZnSo4 CuSo4 Zn Cu
... Write its oxidizing action with (i) H2S. (ii) Iron(II) sulphate solution. (2) (b)Lists of transition metal ions are given. Ti2+, Cr2+, Mn2+. i. Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in them. (1½) ii. Select the ion having most magnetic moment. (1/2 ) 9. a) IUPAC recommended rules for naming a c ...
... Write its oxidizing action with (i) H2S. (ii) Iron(II) sulphate solution. (2) (b)Lists of transition metal ions are given. Ti2+, Cr2+, Mn2+. i. Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in them. (1½) ii. Select the ion having most magnetic moment. (1/2 ) 9. a) IUPAC recommended rules for naming a c ...
TIPS for WRITING EQUATIONS The first step is to write the overall
... reaction. It remains as a solid (non-‐electrolyte) and is not written as ions. These are determined using the solubility rules. A list of common gases should be memorized. Molecules should be evide ...
... reaction. It remains as a solid (non-‐electrolyte) and is not written as ions. These are determined using the solubility rules. A list of common gases should be memorized. Molecules should be evide ...
vsepr_sushma - WordPress.com
... Steric number : The steric number of a molecule is the number of atoms bonded to the central atom of a molecule plus the number of lone pairs on the central atom. Valence Bond Theory : Valence bond theory explains the nature of a chemical bond in a molecule in terms of atomic valencies.[ Valence bon ...
... Steric number : The steric number of a molecule is the number of atoms bonded to the central atom of a molecule plus the number of lone pairs on the central atom. Valence Bond Theory : Valence bond theory explains the nature of a chemical bond in a molecule in terms of atomic valencies.[ Valence bon ...
1 Computer Experiment 15: Computational Coordination Chemistry
... (section Error! Reference source not found., page Error! Bookmark not defined.) but are weaker than the typical covalent bonds formed in organic chemistry. Consequently, the metal-‐ligand bonds are easier to ...
... (section Error! Reference source not found., page Error! Bookmark not defined.) but are weaker than the typical covalent bonds formed in organic chemistry. Consequently, the metal-‐ligand bonds are easier to ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... When one substance is oxidized, another is reduced. An oxidation-reduction reaction occurs. Or a redox reaction occurs. Oxidation: loss of electrons (more positive) Reduction: gain of electrons (less positive) ...
... When one substance is oxidized, another is reduced. An oxidation-reduction reaction occurs. Or a redox reaction occurs. Oxidation: loss of electrons (more positive) Reduction: gain of electrons (less positive) ...
Lecture 4
... Overlap with 3d is small (bonding dominated by overlap with 4s) Overlap improves down group so bond strengths increase 3d < 4d < 5d Contrast main group where bond strengths decrease 2p < 3p < 4p < 5p ...
... Overlap with 3d is small (bonding dominated by overlap with 4s) Overlap improves down group so bond strengths increase 3d < 4d < 5d Contrast main group where bond strengths decrease 2p < 3p < 4p < 5p ...
(b) Costes, J - Nanyang Technological University
... to discern the nature of the Co-Er interaction because, in the latter, two different interactions may occur: Co-Er and ErEr. Thus, the magnetic behavior of the latter species corresponds not only to the Co-Er interaction but also to the overall behavior of the molecule, including both interactions a ...
... to discern the nature of the Co-Er interaction because, in the latter, two different interactions may occur: Co-Er and ErEr. Thus, the magnetic behavior of the latter species corresponds not only to the Co-Er interaction but also to the overall behavior of the molecule, including both interactions a ...
Electronic Structures of Metal Hexacarbonyls
... and Re(CO)6+in solution at 300°K are reported with additional spectral measurements for V(CO)6- at 77°K. The transition assignments and discussion of electronic structures are based on calculated molecular orbital energy levels for the various hexacarbonyls. Abstract: ...
... and Re(CO)6+in solution at 300°K are reported with additional spectral measurements for V(CO)6- at 77°K. The transition assignments and discussion of electronic structures are based on calculated molecular orbital energy levels for the various hexacarbonyls. Abstract: ...
Complexes of Ethylenediaminetetracarboxylate Ligands
... of the supposed larger strain for the G glycinate rings compared to the corresponding R rings, the authors claimed it was reasonable to expect that the trans(O5O6) isomer (Figure 1, middle) with the larger (six-membered) chelate rings in the G plane should form preferentially relative to the corresp ...
... of the supposed larger strain for the G glycinate rings compared to the corresponding R rings, the authors claimed it was reasonable to expect that the trans(O5O6) isomer (Figure 1, middle) with the larger (six-membered) chelate rings in the G plane should form preferentially relative to the corresp ...
5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II
... only difference being an energy of stabilization of eδ for the Lδ orbital and the energy of de-stabilization of eδ for the δ metal-based orbitals. SML(δ) is small compared to SML(π) or SML(σ). Moreover, there are few ligands with δ orbital symmetry (if they exist, the δ symmetry arises from the pπ-s ...
... only difference being an energy of stabilization of eδ for the Lδ orbital and the energy of de-stabilization of eδ for the δ metal-based orbitals. SML(δ) is small compared to SML(π) or SML(σ). Moreover, there are few ligands with δ orbital symmetry (if they exist, the δ symmetry arises from the pπ-s ...
58 - American Chemical Society
... hcp/ccp arrangement as shown in Scheme I. The ccp moiety, formed by the three upper layers, is a 7/6/3 array of Td symmetry (i.e., a truncated supertetrahedron with four seven-atom faces). The hcp moiety, consisting of the three lower layers, is a 6/7/6 symmetry, which can be described as a centered ...
... hcp/ccp arrangement as shown in Scheme I. The ccp moiety, formed by the three upper layers, is a 7/6/3 array of Td symmetry (i.e., a truncated supertetrahedron with four seven-atom faces). The hcp moiety, consisting of the three lower layers, is a 6/7/6 symmetry, which can be described as a centered ...
Solids in contact with natural waters
... in various states of deprotonation, other complexes including those involving organic material, polynuclear species, ion exchange with clay solids, and interaction with gaseous carbon dioxide. In addition, the solubilities of a number of important metallic elements are markedly different in differen ...
... in various states of deprotonation, other complexes including those involving organic material, polynuclear species, ion exchange with clay solids, and interaction with gaseous carbon dioxide. In addition, the solubilities of a number of important metallic elements are markedly different in differen ...
this PDF file
... It was shown that PSA-MIP demonstrates highly specific recognition for template molecule in comparison with NIP and MIP-no metal ion coordination. Proteins may undergo conformational changes in the presence of monomers and crosslinkers due to its vulnerable nature. It was reported that for lysozyme ...
... It was shown that PSA-MIP demonstrates highly specific recognition for template molecule in comparison with NIP and MIP-no metal ion coordination. Proteins may undergo conformational changes in the presence of monomers and crosslinkers due to its vulnerable nature. It was reported that for lysozyme ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... • Halogens ... gases: F, Cl; liquid: Br; solid: I; highly reactive; F is the most reactive element; all quite toxic; not found in elemental form • Noble Gases ... all gases; largely unreactive, although Kr and Xe can form compounds; found in minute quantities in the atmosphere ...
... • Halogens ... gases: F, Cl; liquid: Br; solid: I; highly reactive; F is the most reactive element; all quite toxic; not found in elemental form • Noble Gases ... all gases; largely unreactive, although Kr and Xe can form compounds; found in minute quantities in the atmosphere ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.