1. Introduction
... in two modes, in most cases identified as the fundamental and the first overtone of radial pulsation. While measurement of a single mode, as discussed above, provides a measure of the mean density of the star, two periods roughly speaking allow determination of its mass and radius. It is striking th ...
... in two modes, in most cases identified as the fundamental and the first overtone of radial pulsation. While measurement of a single mode, as discussed above, provides a measure of the mean density of the star, two periods roughly speaking allow determination of its mass and radius. It is striking th ...
ASTR 1B - Texas Tech University Departments
... studied, reviewed, and learned for this assessment. • Recognize the importance and uses of astronomy in civilization. • Know how civilizations such as the Egyptians, Aztecs, and Europeans used astronomy. • Know contributions of Ptolemy, Copernicus, Galileo, Tycho Brahe, Newton, and Einstein. • Expla ...
... studied, reviewed, and learned for this assessment. • Recognize the importance and uses of astronomy in civilization. • Know how civilizations such as the Egyptians, Aztecs, and Europeans used astronomy. • Know contributions of Ptolemy, Copernicus, Galileo, Tycho Brahe, Newton, and Einstein. • Expla ...
Comets, Meteors and Asteroids - 6th Grade Science with Mrs. Voris
... Astronomers have discovered more than 100,000 asteroids, and they are constantly finding more. Most asteroids are small—less than a kilometer in diameter. Only Ceres, Pallas, and Vesta are more than 300 kilometers across. At one time, scientists thought that asteroids were the remains of a shattered ...
... Astronomers have discovered more than 100,000 asteroids, and they are constantly finding more. Most asteroids are small—less than a kilometer in diameter. Only Ceres, Pallas, and Vesta are more than 300 kilometers across. At one time, scientists thought that asteroids were the remains of a shattered ...
Astronomy 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Sun will burn hydrogen into helium in its core. Assume that the Sun was initially entirely composed of hydrogen, and that the Sun's current mass was its mass before main-sequence burning. You will use some known properties of the Sun, and the knowledge that the Sun fuses hydrogen into helium. (i) Fr ...
... Sun will burn hydrogen into helium in its core. Assume that the Sun was initially entirely composed of hydrogen, and that the Sun's current mass was its mass before main-sequence burning. You will use some known properties of the Sun, and the knowledge that the Sun fuses hydrogen into helium. (i) Fr ...
Astronomy Powerpoint
... nuclei into the nucleus of a helium atom, releasing a tremendous amount of energy. • During nuclear fusion, energy is released because some matter is actually converted to energy. • It is thought that a star the size of the sun can exist in its present stable state for 10 billion years. As the sun i ...
... nuclei into the nucleus of a helium atom, releasing a tremendous amount of energy. • During nuclear fusion, energy is released because some matter is actually converted to energy. • It is thought that a star the size of the sun can exist in its present stable state for 10 billion years. As the sun i ...
Additional Exercises for Chapter 4 Computations of Copernicus and
... by the astronomer Clyde Tombaugh, was the last. In 1951, the astronomer Gerard Kuiper predicted that other small bodies would be found beyond the orbits of Neptune and Pluto. Indeed, a number of such objects have been found. (This fact that led to the expulsion of Pluto from the list of planets in ...
... by the astronomer Clyde Tombaugh, was the last. In 1951, the astronomer Gerard Kuiper predicted that other small bodies would be found beyond the orbits of Neptune and Pluto. Indeed, a number of such objects have been found. (This fact that led to the expulsion of Pluto from the list of planets in ...
Sections 5 - Columbia Physics
... (c) Calculate the linear response function χ = ∂ hLi /∂F showing how the length changes if a small tensile force is applied to the two ends of the chain as shown in the figure. ...
... (c) Calculate the linear response function χ = ∂ hLi /∂F showing how the length changes if a small tensile force is applied to the two ends of the chain as shown in the figure. ...
Exercise set five
... Using each pair of observations, calculate the length of the sidereal day. (Hint: start by calculating how much earlier, in seconds, the later occultation occurred, then divide that by the number of days between the observations. This gives you how many seconds shorter a sidereal day is than a solar ...
... Using each pair of observations, calculate the length of the sidereal day. (Hint: start by calculating how much earlier, in seconds, the later occultation occurred, then divide that by the number of days between the observations. This gives you how many seconds shorter a sidereal day is than a solar ...
April 2016
... year of the Round Tower and Tycho Brache Planetarium in Denmark. The Round Tower is actually the oldest functioning observatory in the world [1642], while the planetarium opened in 1989. He gave us an entertaining history of Tycho, who became famous, and then fell out of favor with Denmark’s rulers. ...
... year of the Round Tower and Tycho Brache Planetarium in Denmark. The Round Tower is actually the oldest functioning observatory in the world [1642], while the planetarium opened in 1989. He gave us an entertaining history of Tycho, who became famous, and then fell out of favor with Denmark’s rulers. ...
Reading the Heavens - The Esoteric Quarterly
... 0° (degrees) of Aries, the direction of the planetary soul (the cornerstone of The origin or starting point of the 12 the vision defined as tropical). sacred sectors/petals on the ecliptic is also identified with the alignment be The human Heart at the center, identitween the Sun and the Galactic ...
... 0° (degrees) of Aries, the direction of the planetary soul (the cornerstone of The origin or starting point of the 12 the vision defined as tropical). sacred sectors/petals on the ecliptic is also identified with the alignment be The human Heart at the center, identitween the Sun and the Galactic ...
Astro 4 Practice Test 1
... b. The diurnal motion means that the sky seems to rotate westward once per day, while the Sun seems to move eastward relative to the stars, maing one eastward circuit per year. c. The diurnal motion means that the sky seems to rotate eastward once per day, while the Sun seems to move westward relati ...
... b. The diurnal motion means that the sky seems to rotate westward once per day, while the Sun seems to move eastward relative to the stars, maing one eastward circuit per year. c. The diurnal motion means that the sky seems to rotate eastward once per day, while the Sun seems to move westward relati ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 3
... If one can determine the luminosity of a star WITHOUT knowing d, then a measurement of the flux F on Earth can be inverted to find d. That is: (i) extract L from some observable characteristic of the star (ii) measure F on Earth (iii) use F = L / 4πd2 to solve for d. The problem with this approach i ...
... If one can determine the luminosity of a star WITHOUT knowing d, then a measurement of the flux F on Earth can be inverted to find d. That is: (i) extract L from some observable characteristic of the star (ii) measure F on Earth (iii) use F = L / 4πd2 to solve for d. The problem with this approach i ...
The Motion of Celestial Bodies
... L. Lagrange (1736-1812), P. S. Laplace (1749-1827), U. J. Leverrier (1811-1877), F. Tisserand (1845-1896) and H. Poincaré (1854-1912). Laplace had a very deterministic view of the Solar System, believing that if the positions and velocities of the celestial bodies could be specified at some instant, ...
... L. Lagrange (1736-1812), P. S. Laplace (1749-1827), U. J. Leverrier (1811-1877), F. Tisserand (1845-1896) and H. Poincaré (1854-1912). Laplace had a very deterministic view of the Solar System, believing that if the positions and velocities of the celestial bodies could be specified at some instant, ...
2. Stellar Physics
... With this definition: • planets are not stars - no nuclear fusion • objects in which release of gravitational potential energy is always greater than fusion are not stars either - these are called brown dwarfs Distinction between brown dwarfs and planets is less clear, most people reserve `planet’ ...
... With this definition: • planets are not stars - no nuclear fusion • objects in which release of gravitational potential energy is always greater than fusion are not stars either - these are called brown dwarfs Distinction between brown dwarfs and planets is less clear, most people reserve `planet’ ...
Heliocentric Models and Modern Astronomy
... Law III : Planet moves around Sun such that they obey the relationship (Period P in years)2 = (Semi-major aixs a in AU) 3 planet moves slower when it is farther from Sun can use observed Period P infer a, and hence mean orbital speed in km/s ...
... Law III : Planet moves around Sun such that they obey the relationship (Period P in years)2 = (Semi-major aixs a in AU) 3 planet moves slower when it is farther from Sun can use observed Period P infer a, and hence mean orbital speed in km/s ...
Big idea # 5 * Earth in space in time
... frequency, use, and hazards and recognize its application to an understanding of planetary images and satellite photographs. SC.8.E.5.12 Summarize the effects of space exploration on the economy and culture of Florida. ...
... frequency, use, and hazards and recognize its application to an understanding of planetary images and satellite photographs. SC.8.E.5.12 Summarize the effects of space exploration on the economy and culture of Florida. ...
Prep/Review Questions - Faculty Web Sites at the University
... to move from one day to the next? A) north; B) south; C) east; D) west. To add visual interest, stage productions and movies often show a full Moon near the horizon, regardless of the ostensible time of night. At what times of night can this happen in real life? In a new Tom Hanks "Castaway" sequel, ...
... to move from one day to the next? A) north; B) south; C) east; D) west. To add visual interest, stage productions and movies often show a full Moon near the horizon, regardless of the ostensible time of night. At what times of night can this happen in real life? In a new Tom Hanks "Castaway" sequel, ...
The Search for Planet X
... Earth (super Earths are planets up to roughly 10 times more massive than Earth). If such a hidden object—sometimes whimsically called “Planet X”—exists, it would orbit at least 10 times farther from the sun than Neptune—too distant and too faint to have been spotted by any telescope to date. Yet it ...
... Earth (super Earths are planets up to roughly 10 times more massive than Earth). If such a hidden object—sometimes whimsically called “Planet X”—exists, it would orbit at least 10 times farther from the sun than Neptune—too distant and too faint to have been spotted by any telescope to date. Yet it ...
Star and Planet Formation - Homepages of UvA/FNWI staff
... the third one is true, but the effect of parallax is Pluto, some asteroids, and a comet. so small that it could not be observed at that time with the naked eye. In the 16th century, Nicholas Copernicus (1473-1543) was the first to advance the model that all planets orbit the Sun. This change of para ...
... the third one is true, but the effect of parallax is Pluto, some asteroids, and a comet. so small that it could not be observed at that time with the naked eye. In the 16th century, Nicholas Copernicus (1473-1543) was the first to advance the model that all planets orbit the Sun. This change of para ...
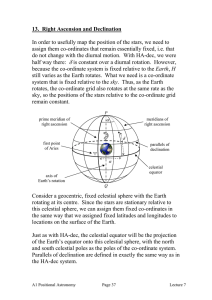
13. Right Ascension and Declination
... With declination δ as the equivalent of terrestrial latitude, we also need an analogue for terrestrial longitude: this is the right ascension, α. Great half-circles passing through the north and south celestial poles form the meridians of right ascension. Just as we use the Greenwich meridian as th ...
... With declination δ as the equivalent of terrestrial latitude, we also need an analogue for terrestrial longitude: this is the right ascension, α. Great half-circles passing through the north and south celestial poles form the meridians of right ascension. Just as we use the Greenwich meridian as th ...
The Motion of Celestial Bodies
... L. Lagrange (1736-1812), P. S. Laplace (1749-1827), U. J. Leverrier (1811-1877), F. Tisserand (1845-1896) and H. Poincaré (1854-1912). Laplace had a very deterministic view of the Solar System, believing that if the positions and velocities of the celestial bodies could be specified at some instant, ...
... L. Lagrange (1736-1812), P. S. Laplace (1749-1827), U. J. Leverrier (1811-1877), F. Tisserand (1845-1896) and H. Poincaré (1854-1912). Laplace had a very deterministic view of the Solar System, believing that if the positions and velocities of the celestial bodies could be specified at some instant, ...
Brightness Luminosity and Inverse Square Law
... Sun as viewed from Earth is 1362 W/m2 We also know that Saturn is 9.7 times further away from our Sun than the Earth. If b α 1/d2 , then as viewed from Saturn, the sun would appear 1/(9.7)2 or 1/94th as bright. The brightness would then be 1362 W/m2(1/94) = 14.5 W/m2 ...
... Sun as viewed from Earth is 1362 W/m2 We also know that Saturn is 9.7 times further away from our Sun than the Earth. If b α 1/d2 , then as viewed from Saturn, the sun would appear 1/(9.7)2 or 1/94th as bright. The brightness would then be 1362 W/m2(1/94) = 14.5 W/m2 ...
2 Periodic Events I - Journigan-wiki
... Around the year 130 BC, Hipparchus compared ancient observations to his own and concluded that in the preceding 169 years heavenly bodies had moved by 2 degrees. How could Hipparchus know the position of the Sun among the stars so exactly, when stars are not visible in the daytime? By using not the ...
... Around the year 130 BC, Hipparchus compared ancient observations to his own and concluded that in the preceding 169 years heavenly bodies had moved by 2 degrees. How could Hipparchus know the position of the Sun among the stars so exactly, when stars are not visible in the daytime? By using not the ...
How much Sugar in Gum
... Background and Misconceptions: Since the distances are vast in the solar system and between stars, astronomers have created various units to represent these large distances. They use them only because they are easier to use and they are agreed upon quantities. The common units are: ...
... Background and Misconceptions: Since the distances are vast in the solar system and between stars, astronomers have created various units to represent these large distances. They use them only because they are easier to use and they are agreed upon quantities. The common units are: ...
The Oort Cloud
... • Distance between Oort Cloud Comets: 50-500 million km (0.33-3.33 AU) • Surface temp. in Oort Cloud ~5-6 K (Kuiper belt 30-60 K) • Named after Jan Oort ...
... • Distance between Oort Cloud Comets: 50-500 million km (0.33-3.33 AU) • Surface temp. in Oort Cloud ~5-6 K (Kuiper belt 30-60 K) • Named after Jan Oort ...