Ch.11 #1 - Academic Program Pages
... The resistance is a property of the wires. How can we reduce R? Ch.11 #1 For a given length of wire, resistance is inversely proportional to the wire’s cross-sectional area. A utility is replacing a 115-kV transmission line with one using wire whose diameter is half that of the line it’s replacing. ...
... The resistance is a property of the wires. How can we reduce R? Ch.11 #1 For a given length of wire, resistance is inversely proportional to the wire’s cross-sectional area. A utility is replacing a 115-kV transmission line with one using wire whose diameter is half that of the line it’s replacing. ...
PPT Format - HubbleSOURCE
... a system of two objects in space (usually stars), which are so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
... a system of two objects in space (usually stars), which are so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
How we know the Earth moves - Michael Beeson
... If the Earth moves around the sun, then this motion should produce an apparent motion of the stars as seen from the Earth. To see this, imagine two stars, A and B, which are in line when viewed from the sun, with A farther away. Then when the Earth is at one side, A will appear to the left of B, and ...
... If the Earth moves around the sun, then this motion should produce an apparent motion of the stars as seen from the Earth. To see this, imagine two stars, A and B, which are in line when viewed from the sun, with A farther away. Then when the Earth is at one side, A will appear to the left of B, and ...
Astronomy Unit BM study guide
... light from the nearest large galaxy, Andromeda, was emitted 2.5 million years ago. Therefore, the images we see of these objects are how they looked at the time in the past when their light left them. The further away an object is, the older the light is that we are receiving from it. The shapes of ...
... light from the nearest large galaxy, Andromeda, was emitted 2.5 million years ago. Therefore, the images we see of these objects are how they looked at the time in the past when their light left them. The further away an object is, the older the light is that we are receiving from it. The shapes of ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... proportions for the Local Super Cluster and Visible Universe yields the following. The Local Super cluster would have a radius of 20 meters and the visible universe would have a radius of about 5.5 km. This last answer is worth discussing briefly. If the Milky Way galaxy were a nickel, then the dist ...
... proportions for the Local Super Cluster and Visible Universe yields the following. The Local Super cluster would have a radius of 20 meters and the visible universe would have a radius of about 5.5 km. This last answer is worth discussing briefly. If the Milky Way galaxy were a nickel, then the dist ...
Stellar Parallax Problems
... B. The Milky Way galaxy has a diameter of about100,000 light years and we are about 28,000 light years from the center. In a sentence describe how much of the galaxy this hypothetical Gaia-copy mission could see (ignoring other factors like obscuration due to interstellar dust)? ...
... B. The Milky Way galaxy has a diameter of about100,000 light years and we are about 28,000 light years from the center. In a sentence describe how much of the galaxy this hypothetical Gaia-copy mission could see (ignoring other factors like obscuration due to interstellar dust)? ...
Astronomical Distances
... “the distance from the Sun to a hypothetical astronomical object which has a parallax angle of 1 arcsecond”. So what on earth does that mean? First of all parallax; close one eye then hold a pencil out in front of you at arm’s length. Then keeping your arm still, change which eye you are looking thr ...
... “the distance from the Sun to a hypothetical astronomical object which has a parallax angle of 1 arcsecond”. So what on earth does that mean? First of all parallax; close one eye then hold a pencil out in front of you at arm’s length. Then keeping your arm still, change which eye you are looking thr ...
Article on Pluto (for 1st science news)
... the solar system--or that a new type of body even existed in the region--they assumed that designating the new discovery as the ninth planet was a scientifically accurate decision.. It has an eccentric orbit that crosses the path of Neptune and also takes it well above and below the main plane of th ...
... the solar system--or that a new type of body even existed in the region--they assumed that designating the new discovery as the ninth planet was a scientifically accurate decision.. It has an eccentric orbit that crosses the path of Neptune and also takes it well above and below the main plane of th ...
A Walk through the Universe
... [Get your volunteers to stand there for a while so the audience has a chance to take it in. This is a photo-opportunity: teachers often want to take pictures.] OK, that was great, thank you. Can I have my planets back please? Slide 9: The Solar System So now we see that the Sun is by far the biggest ...
... [Get your volunteers to stand there for a while so the audience has a chance to take it in. This is a photo-opportunity: teachers often want to take pictures.] OK, that was great, thank you. Can I have my planets back please? Slide 9: The Solar System So now we see that the Sun is by far the biggest ...
Untitled - Dommelroute
... of growing from the size of a large pinhead to a mountain may have taken one hundred thousand years or so. Then the process began to slow down. The original dust and gas had been used up, and the cloud thinned. Several stars—such as Beta Pictoris—have been observed with large, thin disks of dust sur ...
... of growing from the size of a large pinhead to a mountain may have taken one hundred thousand years or so. Then the process began to slow down. The original dust and gas had been used up, and the cloud thinned. Several stars—such as Beta Pictoris—have been observed with large, thin disks of dust sur ...
Sidereal Time and Celestial Coordinates
... Sidereal day – time it takes a star at the meridian to return to the meridian. – 23 hours 56 min 4 sec Solar day – time it takes the Sun at meridian (noon) to return to the meridian. – noon to noon or 24 hours Why the 4-minute difference? – as it rotates, the Earth also orbits the Sun – Earth must r ...
... Sidereal day – time it takes a star at the meridian to return to the meridian. – 23 hours 56 min 4 sec Solar day – time it takes the Sun at meridian (noon) to return to the meridian. – noon to noon or 24 hours Why the 4-minute difference? – as it rotates, the Earth also orbits the Sun – Earth must r ...
23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System
... Occasionally, meteor sightings can reach 60 or more an hour. These displays, called meteor showers, result when Earth encounters a swarm of meteoroids travelling in the same direction and at nearly the same speed as Earth. Some meteor showers are closely associated with the orbits of some comets. Th ...
... Occasionally, meteor sightings can reach 60 or more an hour. These displays, called meteor showers, result when Earth encounters a swarm of meteoroids travelling in the same direction and at nearly the same speed as Earth. Some meteor showers are closely associated with the orbits of some comets. Th ...
scale_moon
... Do you know what the phases of the moon are? Does the moon look the same every night? (different shapes that the moon takes on at night) What causes the phases? (write these ideas down on the board – probably will say things like earth’s shadow, clouds, etc.) Have all kids stand around in a circle a ...
... Do you know what the phases of the moon are? Does the moon look the same every night? (different shapes that the moon takes on at night) What causes the phases? (write these ideas down on the board – probably will say things like earth’s shadow, clouds, etc.) Have all kids stand around in a circle a ...
Objects in the Sky STair
... The Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours. As Earth rotates, it gives the appearance that the sun “rises in the sky” every morning and “sets or goes down in the sky” every night When it rises here, it is setting on the other side of Earth and when it is setting here, it is rising on the other sid ...
... The Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours. As Earth rotates, it gives the appearance that the sun “rises in the sky” every morning and “sets or goes down in the sky” every night When it rises here, it is setting on the other side of Earth and when it is setting here, it is rising on the other sid ...
Chapter 3
... year (at 0:00 and 12:00 GMT) are given in the Nautical Almanac (grey background indicates negative EoT). EoT is needed when calculating times of sunrise and sunset, or determining a noon longitude (see chapter 6). Formulas for the calculation of EoT are given in chapter 15. Due to the rapid change o ...
... year (at 0:00 and 12:00 GMT) are given in the Nautical Almanac (grey background indicates negative EoT). EoT is needed when calculating times of sunrise and sunset, or determining a noon longitude (see chapter 6). Formulas for the calculation of EoT are given in chapter 15. Due to the rapid change o ...
Lecture 19 - Stellar Lifecycles
... • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The explosion is so energetic that it can outshine the combined light of a galaxy! • Heavy elements are formed in the material blown off the star. These elements a ...
... • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The explosion is so energetic that it can outshine the combined light of a galaxy! • Heavy elements are formed in the material blown off the star. These elements a ...
6th Grade Winter - Partnership for Effective Science Teaching and
... Objective 2: Describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky relative to Earth and how various cultures have understood and used them. a. Locate and identify stars that are grouped in patterns in the night sky. b. Identify ways people have historically grouped stars i ...
... Objective 2: Describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky relative to Earth and how various cultures have understood and used them. a. Locate and identify stars that are grouped in patterns in the night sky. b. Identify ways people have historically grouped stars i ...
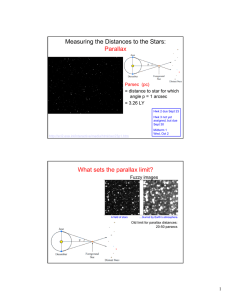
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
Lifetime of Stars/ Fusion powers the stars—11 Oct
... 19th Century “Energy Crisis” • Luminosity of sun L=41026Watt • Mass m=21030kg • How long will the sun last if the energy is produced by burning coal? C+O2→CO2 – Life time = m(E/m)/L – E/m=9MJ/kg – 1500 years ...
... 19th Century “Energy Crisis” • Luminosity of sun L=41026Watt • Mass m=21030kg • How long will the sun last if the energy is produced by burning coal? C+O2→CO2 – Life time = m(E/m)/L – E/m=9MJ/kg – 1500 years ...
Definition - SchoolNotes
... – These lines are marked in degrees – the equator being represented by 0o, and increasing in both directions as you move away from the equator line. ...
... – These lines are marked in degrees – the equator being represented by 0o, and increasing in both directions as you move away from the equator line. ...
DTU 8e Chap 5 Formation of the Solar System
... much later by stars and are cast into space when stars die. By mass, 98% of the observed matter in the universe is hydrogen and helium. The solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago from a swirling, disk-shaped cloud of gas, ice, and dust called the solar nebula. The planets and other debris in the ...
... much later by stars and are cast into space when stars die. By mass, 98% of the observed matter in the universe is hydrogen and helium. The solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago from a swirling, disk-shaped cloud of gas, ice, and dust called the solar nebula. The planets and other debris in the ...
3rd Grade Object in the Sky Assessment
... If the model Earth acts the same as the real Earth, what will happen as the students spin the model? A. Different parts of the model Earth will have different seasons. B. Some parts of the model Earth with have daytime and some will have night. C. A new year will start each time the model Earth make ...
... If the model Earth acts the same as the real Earth, what will happen as the students spin the model? A. Different parts of the model Earth will have different seasons. B. Some parts of the model Earth with have daytime and some will have night. C. A new year will start each time the model Earth make ...
C.4 The Period of Rotation of the Sun
... You will now analyze your data to determine the rotational period of the Sun. The computer will plot the data and you will use simple controls to obtain a best-fit line through your data points. The slope of this graph will be in degrees/day which you can use to determine the rotational period. 1. I ...
... You will now analyze your data to determine the rotational period of the Sun. The computer will plot the data and you will use simple controls to obtain a best-fit line through your data points. The slope of this graph will be in degrees/day which you can use to determine the rotational period. 1. I ...
Latitudes and Longitudes
... north and at other times in the south? • Find the Equator and the north-south axis on the globe. Light up the globe with a lamp and tilt the axis slightly towards the light so that the area around the North Pole, outlined by the Arctic Circle, is lit up. Place a pencil against the globe and move it ...
... north and at other times in the south? • Find the Equator and the north-south axis on the globe. Light up the globe with a lamp and tilt the axis slightly towards the light so that the area around the North Pole, outlined by the Arctic Circle, is lit up. Place a pencil against the globe and move it ...