On Sunspot and Starspot Lifetimes - Patrick M. Hartigan
... brightness contrast between spot regions and the surrounding photosphere on hotter stars, which suggests that the temperature difference between them increases with stellar temperature. The temperature difference is about 2000 K in stars of spectral type G0 and only 200 K in stars of type M4. This p ...
... brightness contrast between spot regions and the surrounding photosphere on hotter stars, which suggests that the temperature difference between them increases with stellar temperature. The temperature difference is about 2000 K in stars of spectral type G0 and only 200 K in stars of type M4. This p ...
Selected topics in the evolution of low
... From a physical perspective, the situation immediately reminds one of that which was encountered a few decades ago in the field of stellar pulsation, with a persistent disagreement between computed and observed period ratios of double-mode (or “bump”) Cepheids. Simon [77] realized that the problem c ...
... From a physical perspective, the situation immediately reminds one of that which was encountered a few decades ago in the field of stellar pulsation, with a persistent disagreement between computed and observed period ratios of double-mode (or “bump”) Cepheids. Simon [77] realized that the problem c ...
fundamental concepts of physics
... It is likely that the problem of explaining the motion of planets in the night sky is one of the oldest to which humanity gave any attention. Ancient civilizations gave much thought to the problem of the objects wandering through the heavens and arrived at a wide variety of explanations for the obse ...
... It is likely that the problem of explaining the motion of planets in the night sky is one of the oldest to which humanity gave any attention. Ancient civilizations gave much thought to the problem of the objects wandering through the heavens and arrived at a wide variety of explanations for the obse ...
Preview Sample 3 - Test Bank, Manual Solution, Solution Manual
... 10. The summer solstice is the day when the Northern Hemisphere gets the most direct sunlight and the southern hemisphere the least direct. Also, on the summer solstice the Sun is as far north as it ever appears on the celestial sphere. On the winter solstice, the situation is exactly reversed: The ...
... 10. The summer solstice is the day when the Northern Hemisphere gets the most direct sunlight and the southern hemisphere the least direct. Also, on the summer solstice the Sun is as far north as it ever appears on the celestial sphere. On the winter solstice, the situation is exactly reversed: The ...
Astronomy and the Quran
... know, only Allah’s apostle can say better.’ Then Prophet (SA) replied, ‘After setting, the sun remains prostrated under Allah’s Aro’sh (Allah’s throne) and waits for Allah’s command for rising again in the East. Day will come when sun will not get any more permission from Allah to rise again and Qey ...
... know, only Allah’s apostle can say better.’ Then Prophet (SA) replied, ‘After setting, the sun remains prostrated under Allah’s Aro’sh (Allah’s throne) and waits for Allah’s command for rising again in the East. Day will come when sun will not get any more permission from Allah to rise again and Qey ...
Brown spots mark impact sites of Comet Shoemaker–Levy on
... The streams of dust and gas each form their own distinct tail, pointing in slightly different directions. The tail of dust is left behind in the comet's orbit in such a manner that it often forms a curved tail called the type II or dust tail. At the same time, the ion or type I tail, made of gases, ...
... The streams of dust and gas each form their own distinct tail, pointing in slightly different directions. The tail of dust is left behind in the comet's orbit in such a manner that it often forms a curved tail called the type II or dust tail. At the same time, the ion or type I tail, made of gases, ...
Zodiac Party Game - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... o PRECESSION--The very slow wobbling motion of the Earth on its axis. This motion has two effects: 1. It shifts the celestial sphere toward the east by one constellation every 2,200 years. 2. It alters which star, if any, is the North Star. A north star is a star that appears to be located directly ...
... o PRECESSION--The very slow wobbling motion of the Earth on its axis. This motion has two effects: 1. It shifts the celestial sphere toward the east by one constellation every 2,200 years. 2. It alters which star, if any, is the North Star. A north star is a star that appears to be located directly ...
The Star of Bethlehem: a Type Ia/Ic Supernova in the Andromeda
... Star in the east can also be translated at helical rising (in the first rays of dawn), as pointed out by Hughes[14] . I suggest that both interpretations are appropriate. Andromeda appears in the eastern sky only in the late winter and early spring months in the first decade B.C. We would expect nak ...
... Star in the east can also be translated at helical rising (in the first rays of dawn), as pointed out by Hughes[14] . I suggest that both interpretations are appropriate. Andromeda appears in the eastern sky only in the late winter and early spring months in the first decade B.C. We would expect nak ...
Entering the Universe of Vedic Astrology
... One of America’s leading jyotishis describes the fundamentals of the Vedic “Science of Light.” Like many of you, I am deeply grateful for the opportunity to expand my knowledge of myself and others, and of the nature of life itself, through the study of Vedic astrology. I consider myself fortunate i ...
... One of America’s leading jyotishis describes the fundamentals of the Vedic “Science of Light.” Like many of you, I am deeply grateful for the opportunity to expand my knowledge of myself and others, and of the nature of life itself, through the study of Vedic astrology. I consider myself fortunate i ...
The Emerald Tablet of Hermes
... This remaining polarity in the sphere of Sophia is what the double eagle points to. Although the consciousness, symbolized by the circle, is a self-contained unity, it shows itself in its passive-female (moon-silver-devotion) and male-active aspect (Mars-redself). Thus the white eagle expresses the ...
... This remaining polarity in the sphere of Sophia is what the double eagle points to. Although the consciousness, symbolized by the circle, is a self-contained unity, it shows itself in its passive-female (moon-silver-devotion) and male-active aspect (Mars-redself). Thus the white eagle expresses the ...
Journey to the Stars Educator`s Guide
... time, gravity causes the cloud to contract, drawing the gas closer and closer together. As more gas accumulates at the center, it becomes denser and pressure increases. This causes it to heat up and begin to glow. Its gravity continues to pull in gas and dust, further increasing its mass, and thus i ...
... time, gravity causes the cloud to contract, drawing the gas closer and closer together. As more gas accumulates at the center, it becomes denser and pressure increases. This causes it to heat up and begin to glow. Its gravity continues to pull in gas and dust, further increasing its mass, and thus i ...
Meteroroids! Asteroids! Comets!
... material formed into planets. • An Asteroid is smaller than a planet but larger than a meteoroid ...
... material formed into planets. • An Asteroid is smaller than a planet but larger than a meteoroid ...
Meteroroids! Asteroids! Comets!
... material formed into planets. • An Asteroid is smaller than a planet but larger than a meteoroid ...
... material formed into planets. • An Asteroid is smaller than a planet but larger than a meteoroid ...
pdf - at www.arxiv.org.
... The movement of the Sun around the barycentre is a consequence of the N-body dynamics operating in the Solar System. This gravitational motion of the Sun’s centre of mass produces a complex orbit which, due to the massive planet Jupiter (which has a mass ≈ 10-3 Ms, Ms = 1 solar mass, approximately 7 ...
... The movement of the Sun around the barycentre is a consequence of the N-body dynamics operating in the Solar System. This gravitational motion of the Sun’s centre of mass produces a complex orbit which, due to the massive planet Jupiter (which has a mass ≈ 10-3 Ms, Ms = 1 solar mass, approximately 7 ...
Slide 1
... Astronomical abundance scale: normalized to H, the most-abundant element in universe eH = 1012 atoms converted to log scale: A(H) = log eH = 12 abundances are measured relative to H, e.g., N(Fe)/N(H) log eFe = log { N(Fe)/N(H) } + 12 used for H-rich systems: stars, ISM Cosmochemical abundance scale: ...
... Astronomical abundance scale: normalized to H, the most-abundant element in universe eH = 1012 atoms converted to log scale: A(H) = log eH = 12 abundances are measured relative to H, e.g., N(Fe)/N(H) log eFe = log { N(Fe)/N(H) } + 12 used for H-rich systems: stars, ISM Cosmochemical abundance scale: ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
3 - Celestial Sphere
... The celestial sphere is a model you can use to describe, explain, and predict the motion of the Sun and the stars in the sky. It models how the sky looks from Earth. Identify the underlined concepts on your celestial sphere: 1) There are imaginary points such as the North and South Celestial Poles ( ...
... The celestial sphere is a model you can use to describe, explain, and predict the motion of the Sun and the stars in the sky. It models how the sky looks from Earth. Identify the underlined concepts on your celestial sphere: 1) There are imaginary points such as the North and South Celestial Poles ( ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
03_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... 30) When did Copernicus live? A) about 5000 years ago B) about 2000 years ago C) about 1000 years ago D) about 500 years ago E) about 100 years ago Answer: D 31) Which of the following was not observed by Galileo? A) craters on the Moon B) stellar parallax C) sunspots D) Jupiter's moons E) phases o ...
... 30) When did Copernicus live? A) about 5000 years ago B) about 2000 years ago C) about 1000 years ago D) about 500 years ago E) about 100 years ago Answer: D 31) Which of the following was not observed by Galileo? A) craters on the Moon B) stellar parallax C) sunspots D) Jupiter's moons E) phases o ...
The Science of Astronomy
... detailed records. The Chinese, for example, began recording astronomical observations at least 5000 years ago, allowing ancient Chinese astronomers to make many important discoveries. Other cultures either did not leave such clear written records or had records that were lost or destroyed, so we mus ...
... detailed records. The Chinese, for example, began recording astronomical observations at least 5000 years ago, allowing ancient Chinese astronomers to make many important discoveries. Other cultures either did not leave such clear written records or had records that were lost or destroyed, so we mus ...
A Brief History of the Solar System
... philosophy, there was no taker of his finding. But this was the first attempt to understand that the world is actually heliocentric and not geocentric. During the second century AD, Klaudios Ptolemaios (85–165 AD), best known as Ptolemy, provided a detailed and complicated mathematical version of Ar ...
... philosophy, there was no taker of his finding. But this was the first attempt to understand that the world is actually heliocentric and not geocentric. During the second century AD, Klaudios Ptolemaios (85–165 AD), best known as Ptolemy, provided a detailed and complicated mathematical version of Ar ...
Preview Sample 2
... 4) Suppose that you live in Sydney, Australia (latitude 34°S). Describe the path of the Sun through your sky for each of the following days: a. the day of the spring equinox b. the day of the summer solstice c. the day of the winter solstice Answer: a. On the vernal equinox, the Sun rises due east, ...
... 4) Suppose that you live in Sydney, Australia (latitude 34°S). Describe the path of the Sun through your sky for each of the following days: a. the day of the spring equinox b. the day of the summer solstice c. the day of the winter solstice Answer: a. On the vernal equinox, the Sun rises due east, ...
Space astrometry 2: Scientific results from Hipparcos
... • monitoring Sun-like stars within 60 pc probes activity versus age (Wright 2004, 2006) (3) Various other studies of Sun’s orbit, spiral arm + Galactic plane passages (vertical oscillation period ~ 82 Myr), cratering records, geological crustal features, and relation between cosmic ray production an ...
... • monitoring Sun-like stars within 60 pc probes activity versus age (Wright 2004, 2006) (3) Various other studies of Sun’s orbit, spiral arm + Galactic plane passages (vertical oscillation period ~ 82 Myr), cratering records, geological crustal features, and relation between cosmic ray production an ...
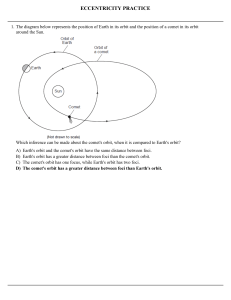
ECCENTRICITY PRACTICE
... 28. If the average distance between Earth and the Sun were doubled, what changes would occur in the Sun's gravitational pull on Earth and Earth's period of revolution? A) Gravitational pull would decrease and period of revolution would increase. B) Gravitational pull would decrease and period of rev ...
... 28. If the average distance between Earth and the Sun were doubled, what changes would occur in the Sun's gravitational pull on Earth and Earth's period of revolution? A) Gravitational pull would decrease and period of revolution would increase. B) Gravitational pull would decrease and period of rev ...
Solutions to End-of-Chapter Problems (Chapter 2)
... 4. The local sky looks like a dome because we see half of the full celestial sphere at any one time. Horizon—The boundary line dividing the ground and the sky. Zenith—The highest point in the sky, directly overhead. Meridian—The semicircle extending from the horizon due north to the zenith to the ho ...
... 4. The local sky looks like a dome because we see half of the full celestial sphere at any one time. Horizon—The boundary line dividing the ground and the sky. Zenith—The highest point in the sky, directly overhead. Meridian—The semicircle extending from the horizon due north to the zenith to the ho ...