The Copernican revolution - University of Florida Astronomy
... (published 1543). This idea was proposed by Aristarchus about 1700 years earlier. • Used model to determine layout of solar system (planetary distances in AU) ...
... (published 1543). This idea was proposed by Aristarchus about 1700 years earlier. • Used model to determine layout of solar system (planetary distances in AU) ...
Celestial Motions
... shadow, and its appearance to us is determined by the relative positions of Sun, Moon, and Earth. • What causes eclipses? – Lunar eclipse: Earth’s shadow on the Moon – Solar eclipse: Moon’s shadow on Earth – Tilt of Moon’s orbit means eclipses occur during two periods each year. © 2010 Pearson Educa ...
... shadow, and its appearance to us is determined by the relative positions of Sun, Moon, and Earth. • What causes eclipses? – Lunar eclipse: Earth’s shadow on the Moon – Solar eclipse: Moon’s shadow on Earth – Tilt of Moon’s orbit means eclipses occur during two periods each year. © 2010 Pearson Educa ...
Chapter 1 Clicker Questions
... False, but it would be a good idea to do so. False, even a spacecraft that moved close to the speed of light would take tens of thousands of years to get to a good vantage point. False, as the Sun and Earth move through the galaxy, we will be able to take a photograph from a different perspective. F ...
... False, but it would be a good idea to do so. False, even a spacecraft that moved close to the speed of light would take tens of thousands of years to get to a good vantage point. False, as the Sun and Earth move through the galaxy, we will be able to take a photograph from a different perspective. F ...
Asteroids
... (NEA) or Earth-Approaching asteroids. These asteroids probably came from the main Eros, Asteroid asteroid belt, but were jolted from the belt by #433, is an collisions or by interactions with other elongated Nearobjects' gravitational fields (primarily Earth Asteroid Jupiter). which is 21 by 8 by 8 ...
... (NEA) or Earth-Approaching asteroids. These asteroids probably came from the main Eros, Asteroid asteroid belt, but were jolted from the belt by #433, is an collisions or by interactions with other elongated Nearobjects' gravitational fields (primarily Earth Asteroid Jupiter). which is 21 by 8 by 8 ...
Motions in the Night Sky and the Celestial Sphere
... (a celestial sphere, a planetarium or planetarium software) and examines the usefulness of these models while identifying the model’s shortcomings. Introduction: A scientific model is one that is based on scientific observations and represents a physical system that accurately reflects at least one ...
... (a celestial sphere, a planetarium or planetarium software) and examines the usefulness of these models while identifying the model’s shortcomings. Introduction: A scientific model is one that is based on scientific observations and represents a physical system that accurately reflects at least one ...
The Night Sky - University of Saskatchewan
... 1. Discuss with the class appropriate ways to approach and interview old people, some of whom may be Elders, giving special attention to showing respect for their knowledge about the night sky. a. Discuss the protocol of giving gifts to Elders. In La Loche, a basket of treats is appropriate. The bas ...
... 1. Discuss with the class appropriate ways to approach and interview old people, some of whom may be Elders, giving special attention to showing respect for their knowledge about the night sky. a. Discuss the protocol of giving gifts to Elders. In La Loche, a basket of treats is appropriate. The bas ...
Pluto and definition of planet
... km) form Sun and when farthest he is 49.3 AU from Sun. Consequences of this are large variation of average temperature on surface, from -240°C to 218°C. When going away from Sun, Pluto’s atmosphere, composed from nitrogen, gets frozen. Pluto’s period of rotation is 6 days and 9 hours and his axial t ...
... km) form Sun and when farthest he is 49.3 AU from Sun. Consequences of this are large variation of average temperature on surface, from -240°C to 218°C. When going away from Sun, Pluto’s atmosphere, composed from nitrogen, gets frozen. Pluto’s period of rotation is 6 days and 9 hours and his axial t ...
topics and terms - Rice Space Institute
... curve to the two foci are a constant. Is a “conic section” – a cut across a “right” cone (a cone with a vertical central axis). If the cut is perpendicular to the axis, the ellipse is a circle. If at an angle to the axis, the ellipse is elongated (eccentric). 31. major axis: long measurement of an e ...
... curve to the two foci are a constant. Is a “conic section” – a cut across a “right” cone (a cone with a vertical central axis). If the cut is perpendicular to the axis, the ellipse is a circle. If at an angle to the axis, the ellipse is elongated (eccentric). 31. major axis: long measurement of an e ...
Asteroids and Comets - Wayne State University
... Scientific study of comets dates back to Newton who first recognized their orbits are elongated ellipses Edmund Halley (a contemporary of Newton) in 1705 calculated/published 24 cometary orbits Noted that the orbits of bright comets seen in 1531, 1607, and 1682 were quite similar — and could belong ...
... Scientific study of comets dates back to Newton who first recognized their orbits are elongated ellipses Edmund Halley (a contemporary of Newton) in 1705 calculated/published 24 cometary orbits Noted that the orbits of bright comets seen in 1531, 1607, and 1682 were quite similar — and could belong ...
PPT
... • A celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces, so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. ...
... • A celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces, so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. ...
Reference PDF document
... Transits of Venus are an extraordinarily rare phenomenon, since on average there are only two per century. These two transits are separated by 8 years and the interval between pairs of transits alternates between 105,5 and 121,5 years. Sometimes, as it happened in 1388, one of the transits of the pa ...
... Transits of Venus are an extraordinarily rare phenomenon, since on average there are only two per century. These two transits are separated by 8 years and the interval between pairs of transits alternates between 105,5 and 121,5 years. Sometimes, as it happened in 1388, one of the transits of the pa ...
Venus will be too far north to transit the Sun.
... It is well known that this distance of the sun from the earth, is supposed different by different astronomers. Ptolemy and his followers, as also Copernicus and Tycho Brahe, have computed it at 1200 semi-diameters of the earth, and Kepler at almost 3500; Riccioli doubles this last distance, and Heve ...
... It is well known that this distance of the sun from the earth, is supposed different by different astronomers. Ptolemy and his followers, as also Copernicus and Tycho Brahe, have computed it at 1200 semi-diameters of the earth, and Kepler at almost 3500; Riccioli doubles this last distance, and Heve ...
P2_5 The Apparent Magnitude of α Orionis Supernova
... radiate far more light and will become brighter in the night sky. This paper contains an investigation into the prospect of being able to see the supernova during the daytime. Analysis To see if the supernova is visible during the day, its apparent magnitude must be compared to that of the sun. Appa ...
... radiate far more light and will become brighter in the night sky. This paper contains an investigation into the prospect of being able to see the supernova during the daytime. Analysis To see if the supernova is visible during the day, its apparent magnitude must be compared to that of the sun. Appa ...
Notes (PowerPoint)
... • Celestial (heavenly) domain is perfect • Perfectly circular motion, but retrograde motion didn’t fit in • Normally counter-clockwise from above north pole • All planets exhibited this sometimes • Plato’s theory had extra spheres and features to handle retrograde motion ...
... • Celestial (heavenly) domain is perfect • Perfectly circular motion, but retrograde motion didn’t fit in • Normally counter-clockwise from above north pole • All planets exhibited this sometimes • Plato’s theory had extra spheres and features to handle retrograde motion ...
Lecture 4
... Work originally started by Henry Draper, continued by Annie Jump Cannon in 1910s, results published in the Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spectra are dominated by lines of Hydrogen and Helium and s ...
... Work originally started by Henry Draper, continued by Annie Jump Cannon in 1910s, results published in the Henry Draper Catalogue. Extended version of HD catalogue contains spectra of 225,000 stars down to 9th magnitude. Annie Jump Cannon – spectra are dominated by lines of Hydrogen and Helium and s ...
Stars Part 1
... Two 3He nuclei may eventually (within ten thousand years) find each other. 3He ...
... Two 3He nuclei may eventually (within ten thousand years) find each other. 3He ...
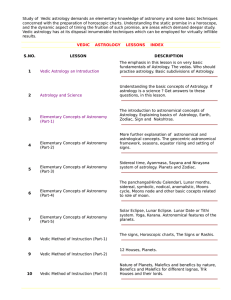
Study of Vedic Astrology by Acharya Aryabhatt
... appreciate that astrology is a cosmic science and not bound by the limitations of a laboratory. In physical sciences, there may be a gross cause or a subtle cause, producing a physically visible or gross effect. Gravitation, which is a subtle cause, produces a gross effect of attracting a physical b ...
... appreciate that astrology is a cosmic science and not bound by the limitations of a laboratory. In physical sciences, there may be a gross cause or a subtle cause, producing a physically visible or gross effect. Gravitation, which is a subtle cause, produces a gross effect of attracting a physical b ...
Planets in the Sky
... Which planets do show phases, and which of them show a full cycle of phases. Why isn’t Venus ever visible overhead or around midnight? What is the Morning star and the Evening star? What makes the observing Mercury so difficult? What is the phase of Venus when it is brightest? Why isn’t Venus bright ...
... Which planets do show phases, and which of them show a full cycle of phases. Why isn’t Venus ever visible overhead or around midnight? What is the Morning star and the Evening star? What makes the observing Mercury so difficult? What is the phase of Venus when it is brightest? Why isn’t Venus bright ...
Chapter 2
... 3. On a slow day in the lab, two graduate students made a bet about how many sunspots would occur 2 months later in spring semester, 2000. Chad estimated there would be 120 sunspots; Julie thought there would be 100. When the day rolled around, 163 sunspots were recorded. Does this mean that Chad an ...
... 3. On a slow day in the lab, two graduate students made a bet about how many sunspots would occur 2 months later in spring semester, 2000. Chad estimated there would be 120 sunspots; Julie thought there would be 100. When the day rolled around, 163 sunspots were recorded. Does this mean that Chad an ...
SDO Systems Retreat
... 2. Provide information about the global solar magnetic field, the active region evolution, small-scale features, and sources of irradiance variations. (Longitudinal and Vector Magnetic Field Images, Atmospheric Images, Spectral Irradiance Measurements) 3. Characterize the rapid evolution of plasma i ...
... 2. Provide information about the global solar magnetic field, the active region evolution, small-scale features, and sources of irradiance variations. (Longitudinal and Vector Magnetic Field Images, Atmospheric Images, Spectral Irradiance Measurements) 3. Characterize the rapid evolution of plasma i ...
Here - SDSU Astronomy Department and Mount Laguna Observatory
... poles related to Earth’s axis of rotation? 11. Why does the tilt of Earth’s axis relative to its orbit cause the seasons as Earth revolves around the Sun?... 15. Why is it warmer in the summer than in winter? 16. Why does the Moon exhibit phases? 23. At which phase(s) of the Moon does a solar eclips ...
... poles related to Earth’s axis of rotation? 11. Why does the tilt of Earth’s axis relative to its orbit cause the seasons as Earth revolves around the Sun?... 15. Why is it warmer in the summer than in winter? 16. Why does the Moon exhibit phases? 23. At which phase(s) of the Moon does a solar eclips ...
The Earth in the Solar System
... observe the life cycle of a single star, we can search through the current “snapshot” of our galaxy and find stars at all stages of evolution. Making an ensemble H-R plot reveals that many stars fall along a single line called the main sequence. Stars on the main sequence are in a relatively steady ...
... observe the life cycle of a single star, we can search through the current “snapshot” of our galaxy and find stars at all stages of evolution. Making an ensemble H-R plot reveals that many stars fall along a single line called the main sequence. Stars on the main sequence are in a relatively steady ...
Science Through Postcard
... It is not uncommon that at the end of a public lecture, I am surrounded by autograph-hunters, mostly students. Rather than oblige them with my signature, I decided to try out an experiment, on such occasions. I asked the typical autograph-aspirant to send me a question on a postcard. The question sh ...
... It is not uncommon that at the end of a public lecture, I am surrounded by autograph-hunters, mostly students. Rather than oblige them with my signature, I decided to try out an experiment, on such occasions. I asked the typical autograph-aspirant to send me a question on a postcard. The question sh ...