
Option_E_Astrophysics_
... this system. Because stars have such a wide range in brightness, magnitudes are on a “log scale” Every one magnitude corresponds to a factor of 2.5 change in brightness Every 5 magnitudes is a factor of 100 change in brightness (because (2.5)5 = 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 = 100) ...
... this system. Because stars have such a wide range in brightness, magnitudes are on a “log scale” Every one magnitude corresponds to a factor of 2.5 change in brightness Every 5 magnitudes is a factor of 100 change in brightness (because (2.5)5 = 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 = 100) ...
Stellar Evolution Before…..During……and After…. The Main
... • The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime ...
... • The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime ...
3rd EXAM VERSION A key - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... A. a galaxy with streams of stars arching out from one region, as if from an explosion B. *a galaxy with an unusually large number of newborn and young stars C. a galaxy that is still in the process of formation from the intergalactic medium and is undergoing its first episode of star formation D. a ...
... A. a galaxy with streams of stars arching out from one region, as if from an explosion B. *a galaxy with an unusually large number of newborn and young stars C. a galaxy that is still in the process of formation from the intergalactic medium and is undergoing its first episode of star formation D. a ...
Name Physics 130 Astronomy Exam 2 August 2, 2004 Multiple Choice
... d.) Heavy hydrogen, 2H 35. _____ Cepheid stars are a.) members of binary systems, in which one star periodically eclipses the other. b.) Stars at an early stage in stellar evolution, pre-main-sequence. c.) White dwarf stars, late in their evolutionary life d.) Giant stars that pulsate in brightness, ...
... d.) Heavy hydrogen, 2H 35. _____ Cepheid stars are a.) members of binary systems, in which one star periodically eclipses the other. b.) Stars at an early stage in stellar evolution, pre-main-sequence. c.) White dwarf stars, late in their evolutionary life d.) Giant stars that pulsate in brightness, ...
EM review
... The brightest stars: m=1. Dimmest stars (visible to the naked eye) m=6. The magnitude scale has been shown to be logarithmic, with a difference of 5 orders of magnitude corresponding to a factor of 100 in actual brightness. ...
... The brightest stars: m=1. Dimmest stars (visible to the naked eye) m=6. The magnitude scale has been shown to be logarithmic, with a difference of 5 orders of magnitude corresponding to a factor of 100 in actual brightness. ...
Pulsar properties - Pulsar Search Collaboratory
... In more detail Size of emission region is bounded by the so-called `light cylinder’ - this is an imaginary surface that co-rotates with the neutron star. Einstein asserts the co-rotation speed cannot be greater than the speed of light, c. This sets a fundamental size for the emission region. ...
... In more detail Size of emission region is bounded by the so-called `light cylinder’ - this is an imaginary surface that co-rotates with the neutron star. Einstein asserts the co-rotation speed cannot be greater than the speed of light, c. This sets a fundamental size for the emission region. ...
Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... V (visual) and I (near-IR). Additional near infrared measurements for stars in IC 4665 are available from the 2 Micron All Sky Survey. The brightness of stars in IC 4665 for the wavelength regions B, V, I, J, H, and K are included in the table below. These measurements are published in the astronom ...
... V (visual) and I (near-IR). Additional near infrared measurements for stars in IC 4665 are available from the 2 Micron All Sky Survey. The brightness of stars in IC 4665 for the wavelength regions B, V, I, J, H, and K are included in the table below. These measurements are published in the astronom ...
Unit 3 - Section 8.9 Life of Stars
... Other forms of electromagnetic radiation are radio waves and x-rays. Waves with different wavelengths make up the electrostatic spectrum. Other devices have been invented that will detect wavelengths different than those detected by the eyes (e.g., infra-red). The Brightness of Stars - The luminosit ...
... Other forms of electromagnetic radiation are radio waves and x-rays. Waves with different wavelengths make up the electrostatic spectrum. Other devices have been invented that will detect wavelengths different than those detected by the eyes (e.g., infra-red). The Brightness of Stars - The luminosit ...
Problem Set 2
... 6. This problem is designed to make you understand Malmquist bias, which affects all measurements (not just distance measurements!) when using samples that are defined in terms of a flux limit (i.e., an apparent magnitude limit). If we observe stars (or anything else) down to a fixed apparent bright ...
... 6. This problem is designed to make you understand Malmquist bias, which affects all measurements (not just distance measurements!) when using samples that are defined in terms of a flux limit (i.e., an apparent magnitude limit). If we observe stars (or anything else) down to a fixed apparent bright ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... Stars are born in groups or clusters when a cold giant molecular cloud collapses under its own gravitational force. If many stars form all at once—that is, if star formation efficiency is high—they will stay together as a gravitationally bound open cluster (like the Pleiades) or a globular cluster ( ...
... Stars are born in groups or clusters when a cold giant molecular cloud collapses under its own gravitational force. If many stars form all at once—that is, if star formation efficiency is high—they will stay together as a gravitationally bound open cluster (like the Pleiades) or a globular cluster ( ...
PPT - Yale University
... formation of compact objects by transporting angular momentum. The formation of objects like stars and black holes is then a much more complex, dynamic, and chaotic process than in standard models. Gravitational interactions tend to couple the mass of a forming object to the mass of the system, ...
... formation of compact objects by transporting angular momentum. The formation of objects like stars and black holes is then a much more complex, dynamic, and chaotic process than in standard models. Gravitational interactions tend to couple the mass of a forming object to the mass of the system, ...
Starlight & Stars - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Consequently, distance is the among the most difficult quantities to measure in astronomy 27 July 2005 ...
... Consequently, distance is the among the most difficult quantities to measure in astronomy 27 July 2005 ...
Unit 1
... • If you plot the positions of variable stars on the HR diagram, many of them fall in the “instability strip” – Most have surface temperatures of ~5000K, so appear yellow – Most are giants (Yellow Giants) – Instability comes from partial absorption of radiation in the interior of the star • Helium a ...
... • If you plot the positions of variable stars on the HR diagram, many of them fall in the “instability strip” – Most have surface temperatures of ~5000K, so appear yellow – Most are giants (Yellow Giants) – Instability comes from partial absorption of radiation in the interior of the star • Helium a ...
Islip Invitational 2013 Astronomy Examination Student
... b. When a group of stars form, they remove so much material from the cloud that only a big empty place is left, into which new matter from other clouds falls, creating more stars. c. When massive stars form, their UV radiation and later their final explosions compress the gas in the cloud and cause ...
... b. When a group of stars form, they remove so much material from the cloud that only a big empty place is left, into which new matter from other clouds falls, creating more stars. c. When massive stars form, their UV radiation and later their final explosions compress the gas in the cloud and cause ...
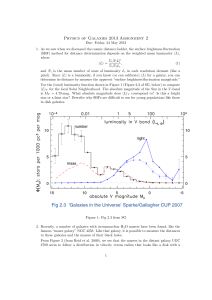
2.3 Peculiar galaxies
... Black hole accretion discs. If the available gas simply fell radially downwards towards the black hole, the energy it would gain would be kinetic energy, and it wouldn’t give much radiation; it would just disappear down the black hole. However, if, as is very likely, the gas is rotating around the b ...
... Black hole accretion discs. If the available gas simply fell radially downwards towards the black hole, the energy it would gain would be kinetic energy, and it wouldn’t give much radiation; it would just disappear down the black hole. However, if, as is very likely, the gas is rotating around the b ...
HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same
... cells told hormones called androgens to turn on during development, causing your body to form male hormones and parts or female hormones and parts. Your brain and spinal cord developed first, and then your cells differentiated (changed) into different organs and parts. By the time your mother was fo ...
... cells told hormones called androgens to turn on during development, causing your body to form male hormones and parts or female hormones and parts. Your brain and spinal cord developed first, and then your cells differentiated (changed) into different organs and parts. By the time your mother was fo ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
... Example III–7. We measure the trigonometric parallax of a visual binary star as 0.20 arcsec and measure an angular separation between the pair of stars in this binary as 5 arcsec. Over a few years of observations, we determine the orbital period of this pair to be 30 years. What is the combined mass ...
Physics-Y11-LP3 - All Saints` Catholic High School
... • understand the role of observations of Cepheid variable stars in establishing the scale of the Universe and the nature of most spiral nebulas as distant galaxies • describe some of the new information that telescopes revealed about the Milky Way and objects beyond the Milky Way • recall the main i ...
... • understand the role of observations of Cepheid variable stars in establishing the scale of the Universe and the nature of most spiral nebulas as distant galaxies • describe some of the new information that telescopes revealed about the Milky Way and objects beyond the Milky Way • recall the main i ...
10438 starlight - The Described and Captioned Media Program
... property of light that depends on wavelength. ...
... property of light that depends on wavelength. ...
charts_set_8
... 3. Gravitational Time Dilation Direct consequence of the redshift. Observers disagree on rate of time passage, depending on strength of gravity they’re in. ...
... 3. Gravitational Time Dilation Direct consequence of the redshift. Observers disagree on rate of time passage, depending on strength of gravity they’re in. ...
- Stevenson High School
... stars are circumpolar (perpetually in the sky, even over a 24 hours’ period). Which one of the constellations below besides Little Dipper contains stars that are circumpolar for our mid-northern hemisphere Star Wheel observer? a) Betelgeuse b) Sagittarius c) Cepheus d) Taurus 22. The daily motion of ...
... stars are circumpolar (perpetually in the sky, even over a 24 hours’ period). Which one of the constellations below besides Little Dipper contains stars that are circumpolar for our mid-northern hemisphere Star Wheel observer? a) Betelgeuse b) Sagittarius c) Cepheus d) Taurus 22. The daily motion of ...
Does size matter (in the SFRs)?
... -SFR increases for latter type galaxies a factor of 50, being the Sm and Irr those with the larger values. -Moreover, the HII regions for these galaxies are brighter (Kennicutt et al. 1989 ApJ, 435, 22) -In addition, there is a relationship between the disk averaged SFR per area and the average gas ...
... -SFR increases for latter type galaxies a factor of 50, being the Sm and Irr those with the larger values. -Moreover, the HII regions for these galaxies are brighter (Kennicutt et al. 1989 ApJ, 435, 22) -In addition, there is a relationship between the disk averaged SFR per area and the average gas ...
project.generative.interactive.music
... Jupiter and is the largest in our solar system with a diameter of 5,262 km (3,280 miles). If Ganymede orbited the Sun instead of Jupiter it could be classified as a planet. Like Callisto, Ganymede is most likely composed of a rocky core with a water/ice mantle and a crust of rock and ice. Its low de ...
... Jupiter and is the largest in our solar system with a diameter of 5,262 km (3,280 miles). If Ganymede orbited the Sun instead of Jupiter it could be classified as a planet. Like Callisto, Ganymede is most likely composed of a rocky core with a water/ice mantle and a crust of rock and ice. Its low de ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
... years. When its heat is all dispersed, it will be a cold, dark black dwarf - essentially a dead star (perhaps replete with diamonds, highly compressed carbon). ...
... years. When its heat is all dispersed, it will be a cold, dark black dwarf - essentially a dead star (perhaps replete with diamonds, highly compressed carbon). ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.














![HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010665051_1-e4f26b4aee29f3f3aaab891d368963d6-300x300.png)







