Some Examples of Virtual Observatory Enabled Science What Are the Some Distinguishing
... • Clusters are perhaps the most striking elements of the LSS • Typically a few Mpc across, contain ~ 100 - 1000 luminous galaxies and many more dwarfs, masses ~ 1014 - 1015 M! • Gravitationally bound, but may not be fully virialized • Filled with hot X-ray gas, mass of the gas may exceed the mass of ...
... • Clusters are perhaps the most striking elements of the LSS • Typically a few Mpc across, contain ~ 100 - 1000 luminous galaxies and many more dwarfs, masses ~ 1014 - 1015 M! • Gravitationally bound, but may not be fully virialized • Filled with hot X-ray gas, mass of the gas may exceed the mass of ...
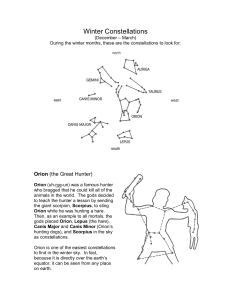
seven winter constellations
... a small goat, marked by one bright star known as “the Mother Goat.” Just below “the Mother Goat” is a triangle of three smaller stars called “the Baby Goats.” ...
... a small goat, marked by one bright star known as “the Mother Goat.” Just below “the Mother Goat” is a triangle of three smaller stars called “the Baby Goats.” ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... A star orbited by a large planet will move in a small circle. This will cause its spectrum to be slightly redshifted part of the time and blueshifted at other times. ...
... A star orbited by a large planet will move in a small circle. This will cause its spectrum to be slightly redshifted part of the time and blueshifted at other times. ...
Notes_ stars and sun
... A higher number of sun spots generally occur every 11 years. This is known as the Saros cycle. White areas on the sun are areas where the temperatures are hotter than normal. There are times when the sun is very active and releases massive amounts of gas into the atmosphere. These are called sola ...
... A higher number of sun spots generally occur every 11 years. This is known as the Saros cycle. White areas on the sun are areas where the temperatures are hotter than normal. There are times when the sun is very active and releases massive amounts of gas into the atmosphere. These are called sola ...
July 2013 - Skyscrapers, Inc.
... towards the north is Perseus. Between the two patterns we can easily see the Double Cluster with the naked eye. While binoculars will enhance the view, a telescope under low magnification will reveal the magnificent beauty of this open cluster of stars. Our next stop “down” (south) the Milky Way is ...
... towards the north is Perseus. Between the two patterns we can easily see the Double Cluster with the naked eye. While binoculars will enhance the view, a telescope under low magnification will reveal the magnificent beauty of this open cluster of stars. Our next stop “down” (south) the Milky Way is ...
Astronomy PPT
... Because of Earth’s rotation, the sun appears to move across the sky. Likewise, if you look at the night sky long enough, the stars also appear to move. All of the stars appear to rotate around Polaris, the North Star, which is almost directly above the Earth’s North Pole. Because of Earth’s rotation ...
... Because of Earth’s rotation, the sun appears to move across the sky. Likewise, if you look at the night sky long enough, the stars also appear to move. All of the stars appear to rotate around Polaris, the North Star, which is almost directly above the Earth’s North Pole. Because of Earth’s rotation ...
34ReviewNuclear
... A. Studying the continuous spectrum of stars B. Studying absorption lines in stars C. Studying binary star orbits D. Studying the brightnesses of stars E. Only by estimation Hotter stars will be bluer, cooler stars will be redder. However, there’s a possibility you might get confused by intervening ...
... A. Studying the continuous spectrum of stars B. Studying absorption lines in stars C. Studying binary star orbits D. Studying the brightnesses of stars E. Only by estimation Hotter stars will be bluer, cooler stars will be redder. However, there’s a possibility you might get confused by intervening ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... though it is not nearly as hot. When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction in which hydrogen atoms are converted to helium atoms plus energy. This energy (radiation) production prevents further contraction of the star. The protostar i ...
... though it is not nearly as hot. When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction in which hydrogen atoms are converted to helium atoms plus energy. This energy (radiation) production prevents further contraction of the star. The protostar i ...
Chapter21
... close together for their images to be separated so that they would be seen as a visual binary. 3. If the binary doesn’t appear to obey Kepler’s laws, the orbit must be tipped. 4. More widely separated stars orbit each other too slowly for their Doppler shifts to be easily detected. 5. Primary and se ...
... close together for their images to be separated so that they would be seen as a visual binary. 3. If the binary doesn’t appear to obey Kepler’s laws, the orbit must be tipped. 4. More widely separated stars orbit each other too slowly for their Doppler shifts to be easily detected. 5. Primary and se ...
final fate of a massive star
... A tremendous creation and destruction of particles will take place in its vicinity. One could imagine it as the `cosmic dance' of basic forces of nature, which may come together in a unified manner. This is because the energies and all physical quantities reach their extreme values in the vicinity ...
... A tremendous creation and destruction of particles will take place in its vicinity. One could imagine it as the `cosmic dance' of basic forces of nature, which may come together in a unified manner. This is because the energies and all physical quantities reach their extreme values in the vicinity ...
HW11
... a white dwarf. Also understand how we can use white dwarf temperatures to estimate the age of the universe. 9) Understand all aspects of high mass star evolution. How high masses stars move on the H-R diagram and why. Understand why the core can only produce elements up to Iron. What happens when th ...
... a white dwarf. Also understand how we can use white dwarf temperatures to estimate the age of the universe. 9) Understand all aspects of high mass star evolution. How high masses stars move on the H-R diagram and why. Understand why the core can only produce elements up to Iron. What happens when th ...
the galaxy in which we live - Cosmos
... As it sweeps the sky, Gaia will observe everything that crosses its sensitive fields of view. Within our Solar System it will provide a whole range of spectacular results. Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies the asteroid belt. At present about 460000 asteroids or minor planets have been dete ...
... As it sweeps the sky, Gaia will observe everything that crosses its sensitive fields of view. Within our Solar System it will provide a whole range of spectacular results. Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies the asteroid belt. At present about 460000 asteroids or minor planets have been dete ...
galctr
... constancy of S2 in K band => disk either optically thin at K or large inner hole L band excess possibly interpreted as reprocessing from disk Overall conclusion: no current cold disk is present ...
... constancy of S2 in K band => disk either optically thin at K or large inner hole L band excess possibly interpreted as reprocessing from disk Overall conclusion: no current cold disk is present ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... field, offset by just a few arc minutes. Then the technique was reversed, giving us an unprecedentedly deep view of two closely aligned fields simultaneously, with wavelengths ranging from 435 to 1600 nanometers. With a huge, towering galaxy cluster in one field and no comparably massive objects in ...
... field, offset by just a few arc minutes. Then the technique was reversed, giving us an unprecedentedly deep view of two closely aligned fields simultaneously, with wavelengths ranging from 435 to 1600 nanometers. With a huge, towering galaxy cluster in one field and no comparably massive objects in ...
Ch. 25 - UTK Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 25.5 The Universe on Large Scales This appeared at first to be a double quasar, but on closer inspection the two quasars turned out to be not just similar, but identical – down to their ...
... 25.5 The Universe on Large Scales This appeared at first to be a double quasar, but on closer inspection the two quasars turned out to be not just similar, but identical – down to their ...
How many planets are there in the galaxy?
... and 400 billion stars (though some think there could be as many as a trillion). Doing the math, we can then say that the Milky Way galaxy has – on average – between 800 billion and 3.2 trillion planets, with some estimates placing that number as high a 8 trillion! However, in order to determine just ...
... and 400 billion stars (though some think there could be as many as a trillion). Doing the math, we can then say that the Milky Way galaxy has – on average – between 800 billion and 3.2 trillion planets, with some estimates placing that number as high a 8 trillion! However, in order to determine just ...
Types of Stars http://space.about.com/od/stars/tp/What-Are
... times the mass of the Sun. Unlike a relatively stable star like the Sun, supergiants are consuming hydrogen fuel at an enormous rate and will consume all the fuel in their cores within just a few million years. Supergiant stars live fast and die young, detonating as supernovae; completely disintegra ...
... times the mass of the Sun. Unlike a relatively stable star like the Sun, supergiants are consuming hydrogen fuel at an enormous rate and will consume all the fuel in their cores within just a few million years. Supergiant stars live fast and die young, detonating as supernovae; completely disintegra ...
Constellations Reading
... constellations (Argo) into 3 parts. In 1930 the International Astronomical Union officially listed 88 modern and ancient constellations (with Argo divided into 3 parts) and drew a boundary around each. There are now 88 modern constellations and boundaries. The boundary edges meet, dividing the imagi ...
... constellations (Argo) into 3 parts. In 1930 the International Astronomical Union officially listed 88 modern and ancient constellations (with Argo divided into 3 parts) and drew a boundary around each. There are now 88 modern constellations and boundaries. The boundary edges meet, dividing the imagi ...
Chapter 8: Stars
... • The HR Diagram is a graph that shows the relationship between a stars’ surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • The modern HR Diagram is shown below. ...
... • The HR Diagram is a graph that shows the relationship between a stars’ surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • The modern HR Diagram is shown below. ...
The Kunlun Infrared Sky Survey
... systems and stellar ejection • ~30% O stars are runaways with V>30 km/s • Binary fraction for massive stars higher than low-mass stars • Hypothesis⟹ Ejection + Formation of tight binary in multiple-systems • PMs of sources BN, I (binary), n ⟹ encounter ~500 yrs ago. ...
... systems and stellar ejection • ~30% O stars are runaways with V>30 km/s • Binary fraction for massive stars higher than low-mass stars • Hypothesis⟹ Ejection + Formation of tight binary in multiple-systems • PMs of sources BN, I (binary), n ⟹ encounter ~500 yrs ago. ...
Astrophysics by Daniel Yang
... Active optics uses a slow feedback system to correct for changes in the surface shape of the primary mirror of reflector telescopes. These deformities may occur due to gravity at different inclination angles (sagging) or due to temperature changes (expansion and contraction). The back of the primary ...
... Active optics uses a slow feedback system to correct for changes in the surface shape of the primary mirror of reflector telescopes. These deformities may occur due to gravity at different inclination angles (sagging) or due to temperature changes (expansion and contraction). The back of the primary ...
The Solar Neighborhood
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
Section 19.3
... This image is from the telescope on an object Hubble Space Telescope, thought to be a nebula named for Edwin Hubble. in the constellation Can you tell the difference Andromeda. between starscould and see that • Hubble galaxies? the “nebula” actually consisted of faint, distant stars. ...
... This image is from the telescope on an object Hubble Space Telescope, thought to be a nebula named for Edwin Hubble. in the constellation Can you tell the difference Andromeda. between starscould and see that • Hubble galaxies? the “nebula” actually consisted of faint, distant stars. ...
Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... to dense. The size of the grains and their composition also vary from place to place. Some form into aggregates of grains, and others become coated with mantles of ice. Both silicate and carbon grains can be found in interstellar space. Dust interacts with light by both scattering and by absorption. ...
... to dense. The size of the grains and their composition also vary from place to place. Some form into aggregates of grains, and others become coated with mantles of ice. Both silicate and carbon grains can be found in interstellar space. Dust interacts with light by both scattering and by absorption. ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.