The Origin, Structure, and Evolution of the Stars
... that are about 100 times brighter than the sun lying above and to the right of the main sequence A few stars are found in the supergiant region at the upper edge of the diagram and another group of white and yellow stars hundreds of times less luminous than the sun called white dwarfs is found in th ...
... that are about 100 times brighter than the sun lying above and to the right of the main sequence A few stars are found in the supergiant region at the upper edge of the diagram and another group of white and yellow stars hundreds of times less luminous than the sun called white dwarfs is found in th ...
The Hipparcos Star Globe Booklet - Cosmos
... Galaxy with positions, distances and velocities of stars. Significantly, Gaia’s observing programme will be complete and unbiased, thereby producing a representative sample of the Galactic population, whilst Hipparcos based its observations on a pre-selected set of bright stars. Hipparcos brought hu ...
... Galaxy with positions, distances and velocities of stars. Significantly, Gaia’s observing programme will be complete and unbiased, thereby producing a representative sample of the Galactic population, whilst Hipparcos based its observations on a pre-selected set of bright stars. Hipparcos brought hu ...
CH. 7 - science1d
... With enough time and a fast enough spacecraft to transport us on this imaginary journey, we would eventually travel among the stars. The next nearest star to Earth after the Sun is actually part of a group of three stars that orbit each other. This group is called the Centauri system (Figure 7.8). I ...
... With enough time and a fast enough spacecraft to transport us on this imaginary journey, we would eventually travel among the stars. The next nearest star to Earth after the Sun is actually part of a group of three stars that orbit each other. This group is called the Centauri system (Figure 7.8). I ...
Document
... hydrogen and dust that have survived the UV radiation from nearby hot stars As the pillars are eroded by the UV light, small globules of denser gas buried within the pillars are uncovered ...
... hydrogen and dust that have survived the UV radiation from nearby hot stars As the pillars are eroded by the UV light, small globules of denser gas buried within the pillars are uncovered ...
Stellar Census
... Is the Sun an "average'' or "typical''? The meaning of "average'' depends on how one chooses the sample! Compared to the nearby stars, the Sun is luminous, hot, and big Compared to the apparently bright stars, the Sun is dim, cool, and small Compared to the stars in globular clusters, the Sun is ver ...
... Is the Sun an "average'' or "typical''? The meaning of "average'' depends on how one chooses the sample! Compared to the nearby stars, the Sun is luminous, hot, and big Compared to the apparently bright stars, the Sun is dim, cool, and small Compared to the stars in globular clusters, the Sun is ver ...
Star Formation in the Rosette Complex
... A low resolution, single slit investigation by Hensberge et al. (1998) of 2 members and 3 field stars in the region of NGC 2244 yielded evidence that these were chemically peculiar, possibly magnetic stars. Hensberge et al. (2000) performed spectroscopic analysis of the binary member V578 Mon, which ...
... A low resolution, single slit investigation by Hensberge et al. (1998) of 2 members and 3 field stars in the region of NGC 2244 yielded evidence that these were chemically peculiar, possibly magnetic stars. Hensberge et al. (2000) performed spectroscopic analysis of the binary member V578 Mon, which ...
Observations of binary systems with pulsating components
... • Periodic motion of stars around the common center of mass has one more important consequence: periodic change of radial velocities. • The change in radial velocities causes an observable Doppler effect on stellar spectral lines: ...
... • Periodic motion of stars around the common center of mass has one more important consequence: periodic change of radial velocities. • The change in radial velocities causes an observable Doppler effect on stellar spectral lines: ...
Calculating Parallax Lab
... 12. Parallax is only one method (known as “standard candles”) to determine the distance to nearby stars. There are several other methods that are used by astronomers. These methods each have their own specific technique and purpose, with some overlap to help confirm accuracy of other methods. Look a ...
... 12. Parallax is only one method (known as “standard candles”) to determine the distance to nearby stars. There are several other methods that are used by astronomers. These methods each have their own specific technique and purpose, with some overlap to help confirm accuracy of other methods. Look a ...
main sequence stars of a open cluster
... Q.1. Find the main sequence from the printed-out CM diagram. Enclose the main sequence by line with a width as narrow as possible. Q.2. What are the characteristics of the main-sequence stars? Explain considering meanings of absolute magnitude in the vertical line and color index in the horizontal l ...
... Q.1. Find the main sequence from the printed-out CM diagram. Enclose the main sequence by line with a width as narrow as possible. Q.2. What are the characteristics of the main-sequence stars? Explain considering meanings of absolute magnitude in the vertical line and color index in the horizontal l ...
che
... Strong precessional variability in hard X-rays with an amplitude Lxmax/Lxmin ~ 7 Peculiar and variable shape of ascending eclipse branch Wide, deep hard X-ray eclipse HOT (wider than in soft X-rays!) EXTENDED Hard X-ray spectrum independent CORONA of the precessional phase ...
... Strong precessional variability in hard X-rays with an amplitude Lxmax/Lxmin ~ 7 Peculiar and variable shape of ascending eclipse branch Wide, deep hard X-ray eclipse HOT (wider than in soft X-rays!) EXTENDED Hard X-ray spectrum independent CORONA of the precessional phase ...
aaswinter06
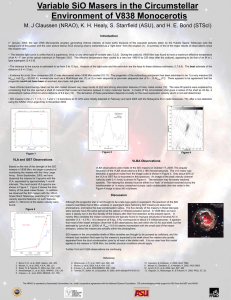
... • Evidence for a hot, blue companion (B3 V) was discovered when V838 Mon cooled (10,11). The progenitor of the outbursting component has been estimated to be 1) a very massive (65 Msolar), hot (Teff ~ 50,000 K), evolved star such as a Wolf-Rayet star (7); or 2) a main sequence or pre-main sequence s ...
... • Evidence for a hot, blue companion (B3 V) was discovered when V838 Mon cooled (10,11). The progenitor of the outbursting component has been estimated to be 1) a very massive (65 Msolar), hot (Teff ~ 50,000 K), evolved star such as a Wolf-Rayet star (7); or 2) a main sequence or pre-main sequence s ...
November News Letter - Boise Astronomical Society
... stars below and right of the moon. However, above Orion’s body is his raised arm and club. The moon is located on top of his club and Orion is about to bat the moon with his club. Be sure to look for the horizontal row of three stars located in the middle of the rectangle of Orion’s body; this is Or ...
... stars below and right of the moon. However, above Orion’s body is his raised arm and club. The moon is located on top of his club and Orion is about to bat the moon with his club. Be sure to look for the horizontal row of three stars located in the middle of the rectangle of Orion’s body; this is Or ...
Calculating Radial Velocities of Low Mass Eclipsing Binaries
... occur during the eclipse of each system, and this was observed in almost every case. Notable exceptions include EBLM11 and EBLM19, whose radial velocities did not vary over time. It remains unclear why, but we can speculate that these were perhaps ...
... occur during the eclipse of each system, and this was observed in almost every case. Notable exceptions include EBLM11 and EBLM19, whose radial velocities did not vary over time. It remains unclear why, but we can speculate that these were perhaps ...
FREE Sample Here
... The brightest stars were placed in the first group, magnitude 1, the next brightest stars were placed in the second group, magnitude 2 and so on. Consequently, bright stars have small numerical magnitude values, while faint stars have very large numerical magnitude values. This seems backwards becau ...
... The brightest stars were placed in the first group, magnitude 1, the next brightest stars were placed in the second group, magnitude 2 and so on. Consequently, bright stars have small numerical magnitude values, while faint stars have very large numerical magnitude values. This seems backwards becau ...
star formation and galactic evolution
... may depend mainly on the amount that is initially ionized, even though winds and supernovae may later play more important roles in actually dispersing this gas. The amount of cloud gas that can be ionized by a cluster of newly formed stars has been estimated by Whitworth (1979) and Franco, Shore, & ...
... may depend mainly on the amount that is initially ionized, even though winds and supernovae may later play more important roles in actually dispersing this gas. The amount of cloud gas that can be ionized by a cluster of newly formed stars has been estimated by Whitworth (1979) and Franco, Shore, & ...
... the work of Notni & Oleak (1958), the star has not been included in other photometric studies. The star is heavily blended with a fainter star, making difficult a precise photometry. For the 2001 season, we could not resolve the pair. In 2000, the sky conditions were better and the star could be sep ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... The brightest stars were placed in the first group, magnitude 1, the next brightest stars were placed in the second group, magnitude 2 and so on. Consequently, bright stars have small numerical magnitude values, while faint stars have very large numerical magnitude values. This seems backwards becau ...
... The brightest stars were placed in the first group, magnitude 1, the next brightest stars were placed in the second group, magnitude 2 and so on. Consequently, bright stars have small numerical magnitude values, while faint stars have very large numerical magnitude values. This seems backwards becau ...
Planetary Nebulae: Observational Properties, Mimics, and Diagnostics
... By definition, a PN surrounds a hot, low-mass CS, which may in fact be off-centre in some old examples due to an asymmetric ISM interaction (see Wareing 2010, and Sabin et al. 2010, in this issue). The CS has a temperature of at least 20,000 K (up to ∼250,000 K), and a mass between the empirical lim ...
... By definition, a PN surrounds a hot, low-mass CS, which may in fact be off-centre in some old examples due to an asymmetric ISM interaction (see Wareing 2010, and Sabin et al. 2010, in this issue). The CS has a temperature of at least 20,000 K (up to ∼250,000 K), and a mass between the empirical lim ...
The Big Bang
... into a spiral galaxy (by conservation of angular momentum) • Disks of galaxies are very fragile; if they get hit with anything bigger than 10% of their own mass, they are destroyed (and don’t come back) • Collisions of galaxies in clusters was much more common in the past than at present ...
... into a spiral galaxy (by conservation of angular momentum) • Disks of galaxies are very fragile; if they get hit with anything bigger than 10% of their own mass, they are destroyed (and don’t come back) • Collisions of galaxies in clusters was much more common in the past than at present ...
Lecture Topics 1023
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
tut35 Magnitudes
... Where ∆ and r are distances in AU from the Earth and Sun, respectively. The IAU has defined a plutoid as a “dwarf planet” with a semi-major axis greater than Neptune. It is usually impossible to optically determine if distant KBOs are in hydrostatic equilibrium (round). The IAU assumes an object is ...
... Where ∆ and r are distances in AU from the Earth and Sun, respectively. The IAU has defined a plutoid as a “dwarf planet” with a semi-major axis greater than Neptune. It is usually impossible to optically determine if distant KBOs are in hydrostatic equilibrium (round). The IAU assumes an object is ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 40-
... It’s the size of the distances between the stars. And this cloud has stars forming in it. And in the upper right drawing — or picture; it’s actually a photograph — you see an arrow pointing at a couple of very bright stars that have just recently formed in this cloud. Now, here are a couple of color ...
... It’s the size of the distances between the stars. And this cloud has stars forming in it. And in the upper right drawing — or picture; it’s actually a photograph — you see an arrow pointing at a couple of very bright stars that have just recently formed in this cloud. Now, here are a couple of color ...
15_Testbank
... A) The magnitude system that we use now is based on a system used by the ancient Greeks over 2,000 years ago that classified stars by how bright they appeared. B) A star with apparent magnitude 1 is brighter than one with apparent magnitude 2. C) The absolute magnitude of a star is another measure o ...
... A) The magnitude system that we use now is based on a system used by the ancient Greeks over 2,000 years ago that classified stars by how bright they appeared. B) A star with apparent magnitude 1 is brighter than one with apparent magnitude 2. C) The absolute magnitude of a star is another measure o ...
File
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
PPT
... velocity = 6x the speed of light!!! Why? Because the redshift is cosmological – due to expansion of space – NOT due to the Doppler Effect, so z is not equal to v/c In fact, 1/1+z is the size of the universe compared to now; z = 6 means that we see the object at a time when the universe was 1/7 of it ...
... velocity = 6x the speed of light!!! Why? Because the redshift is cosmological – due to expansion of space – NOT due to the Doppler Effect, so z is not equal to v/c In fact, 1/1+z is the size of the universe compared to now; z = 6 means that we see the object at a time when the universe was 1/7 of it ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.