
Stars
... • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star • Most ...
... • Gravity may cause the nebula to contract • Matter in the gas cloud will begin to condense into a dense region called a protostar • The protostar continues to condense, it heats up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star • Most ...
Assessment 1 - Stars - Teacher Key
... A red giant forms when the star’s hydrogen level drops. 4 ...
... A red giant forms when the star’s hydrogen level drops. 4 ...
Death of Stars
... Birth Place of Stars: Dark and cold inter-stellar clouds These clouds are made of more hydrogen than helium. These clouds have very small amount of heavier elements. ...
... Birth Place of Stars: Dark and cold inter-stellar clouds These clouds are made of more hydrogen than helium. These clouds have very small amount of heavier elements. ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
... lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
FRIENDS OF THE PLANETARIUM NEWSLETTER April2002
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
HERE
... -440 degrees Fahrenheit. Since gas is more compact in a colder climate, it is easier for gravity to collapse it to form new stars. ...
... -440 degrees Fahrenheit. Since gas is more compact in a colder climate, it is easier for gravity to collapse it to form new stars. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... Within the range of this spectrum, there are yellow or orange stars (like our sun which is a G star) and white stars. White stars contain mostly green emissions but since green is in the middle of the color spectrum, they blend together and the color we see is white. Sadly there are no green stars. ...
... Within the range of this spectrum, there are yellow or orange stars (like our sun which is a G star) and white stars. White stars contain mostly green emissions but since green is in the middle of the color spectrum, they blend together and the color we see is white. Sadly there are no green stars. ...
Mar 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is extremely bright Open clusters reside in our Milky Way Galaxy. Our Sun is no and hugs close to the Sun, so you see it for a short time in the longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters loo ...
... cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is extremely bright Open clusters reside in our Milky Way Galaxy. Our Sun is no and hugs close to the Sun, so you see it for a short time in the longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters loo ...
The Life of a Star
... When clumps have enough hydrogen and dust – nuclear fusion starts. They have become new stars. They get hotter and hotter from the nuclear fusion. You would think that the larger a star is the longer it would live, ...
... When clumps have enough hydrogen and dust – nuclear fusion starts. They have become new stars. They get hotter and hotter from the nuclear fusion. You would think that the larger a star is the longer it would live, ...
Standard Set 2 - Atascadero High School
... stars in the galaxy. If viewed under a low-powered telescope from a planet in another galaxy, the Milky Way would look like a fuzzy patch of light. If viewed with more powerful telescopes from that far planet, the Milky Way would look like a typical spiral galaxy. One would need to travel at the spe ...
... stars in the galaxy. If viewed under a low-powered telescope from a planet in another galaxy, the Milky Way would look like a fuzzy patch of light. If viewed with more powerful telescopes from that far planet, the Milky Way would look like a typical spiral galaxy. One would need to travel at the spe ...
Stars - Weebly
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
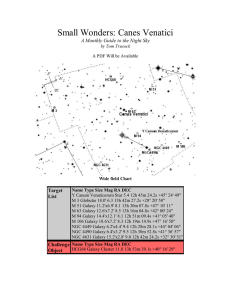
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the constellation may not have been "stand alone" until sometime in the late 17th century w ...
... on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the constellation may not have been "stand alone" until sometime in the late 17th century w ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Which star has the smallest diameter? Which is the hottest star? Which is the star most like the sun? Which star is a cool supergiant? Which star has strong lines of ionized helium in its spectrum? Which star is the white dwarf? Which star has spectrum lines due to molecules? ...
... Which star has the smallest diameter? Which is the hottest star? Which is the star most like the sun? Which star is a cool supergiant? Which star has strong lines of ionized helium in its spectrum? Which star is the white dwarf? Which star has spectrum lines due to molecules? ...
File
... Use language we can comprehend. Tell us what elements you blend. It gives us strangely little aid, But does tell something in the end. And steadfast as Keats' Eremite, Not even stooping from its sphere, It asks a little of us here. It asks of us a certain height, So when at times the mob is swayed T ...
... Use language we can comprehend. Tell us what elements you blend. It gives us strangely little aid, But does tell something in the end. And steadfast as Keats' Eremite, Not even stooping from its sphere, It asks a little of us here. It asks of us a certain height, So when at times the mob is swayed T ...
02-02Stars_Part_One
... size, temperature, and distance. -1 is bright, 6 is dim •Absolute magnitude: Apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Factor of only size and temperature ...
... size, temperature, and distance. -1 is bright, 6 is dim •Absolute magnitude: Apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Factor of only size and temperature ...
December 2015
... ionized by high energy photons emitted from stars that have often been formed within the nebula. These star forming nebula are officially called H II (H two) regions. The color red orange is due to their large amounts of hydrogen. Of course the term nebula means “fuzzy cloud” and came about when ear ...
... ionized by high energy photons emitted from stars that have often been formed within the nebula. These star forming nebula are officially called H II (H two) regions. The color red orange is due to their large amounts of hydrogen. Of course the term nebula means “fuzzy cloud” and came about when ear ...
What is a Star
... and whose nuclear energy supplies have been used up. White dwarfs consist of degenerate matter with a very high density due to gravitational effects, one spoonful of a white dwarf has a mass of a thousand kilograms. White dwarfs have approximately the diameter of the Earth, and will cool to "black ...
... and whose nuclear energy supplies have been used up. White dwarfs consist of degenerate matter with a very high density due to gravitational effects, one spoonful of a white dwarf has a mass of a thousand kilograms. White dwarfs have approximately the diameter of the Earth, and will cool to "black ...
Nebulas & Stars
... • A pulsar is a neutron star that emits beams of radiation that sweep through Earth's line of sight • Quasars are extremely bright masses of energy and light • The name quasar is actually short for quasi-stellar ...
... • A pulsar is a neutron star that emits beams of radiation that sweep through Earth's line of sight • Quasars are extremely bright masses of energy and light • The name quasar is actually short for quasi-stellar ...
dm curvas de rotacion
... • Here r and v are the star’s average radial distance from the center of the galaxy and its orbital velocity. G is the universal gravity constant and M is the mass of the galaxy within radius r. • NOTE: only mass lying within a star's orbit affects the star's motion. So we need to consider the mass ...
... • Here r and v are the star’s average radial distance from the center of the galaxy and its orbital velocity. G is the universal gravity constant and M is the mass of the galaxy within radius r. • NOTE: only mass lying within a star's orbit affects the star's motion. So we need to consider the mass ...
PowerPoint file - Northwest Creation Network
... cloud collapses gravitationally into a star … is still a challenging theoretical problem… Astronomers have yet to find an interstellar cloud in the actual process of collapse.” ...
... cloud collapses gravitationally into a star … is still a challenging theoretical problem… Astronomers have yet to find an interstellar cloud in the actual process of collapse.” ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.

















![constellations[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081352_2-f872c73597ccdde4cfed49c9b322d3b2-300x300.png)




