Pretty Pictures of the Cosmos
... with the Hubble Space Telescope, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic Tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and f ...
... with the Hubble Space Telescope, distant galaxies form a dramatic backdrop for disrupted spiral galaxy Arp 188, the Tadpole Galaxy. The cosmic Tadpole is a mere 420 million light-years distant toward the northern constellation Draco. Its eye-catching tail is about 280 thousand light-years long and f ...
Astrophysics
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
A Star is a ball of matter that is pulled together by gravity, and that
... How bright a star is when viewed from___________. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. •_____________________Magnitude: the amount of ____________ that is actually given off by a star. 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in spa ...
... How bright a star is when viewed from___________. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. •_____________________Magnitude: the amount of ____________ that is actually given off by a star. 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in spa ...
Kinds of Stars
... radiation stay the same for millions of years. Our sun is in a stable state. When fusion doesn’t balance gravity’s force, core contracts(gets hotter) and outer layers ...
... radiation stay the same for millions of years. Our sun is in a stable state. When fusion doesn’t balance gravity’s force, core contracts(gets hotter) and outer layers ...
Dec 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is extremely bright Open clusters reside in our Milky Way Galaxy. Our Sun is no and hugs close to the Sun, so you see it for a short time in the longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters loo ...
... cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is extremely bright Open clusters reside in our Milky Way Galaxy. Our Sun is no and hugs close to the Sun, so you see it for a short time in the longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters loo ...
How many planets are there in our solar system
... b. The hydrogen that makes up stars portrays a shift in the red part of its spectrum, showing that the stars are moving away from us c. Our planets our shifting to the red side of our galaxy because of gravity d. Female students in California wear red dresses to prom and do a dance called “The Shift ...
... b. The hydrogen that makes up stars portrays a shift in the red part of its spectrum, showing that the stars are moving away from us c. Our planets our shifting to the red side of our galaxy because of gravity d. Female students in California wear red dresses to prom and do a dance called “The Shift ...
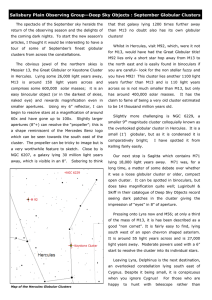
September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
... Skiff in their catalogue of Deep Sky Objects record seeing dark patches in the cluster giving the impression of “eyes” in 8” of aperture. Pressing onto Lyra now and M56; at only a third of the mass of M13, it is has been described as a good “non comet”. It is fairly easy to find, lying south west of ...
... Skiff in their catalogue of Deep Sky Objects record seeing dark patches in the cluster giving the impression of “eyes” in 8” of aperture. Pressing onto Lyra now and M56; at only a third of the mass of M13, it is has been described as a good “non comet”. It is fairly easy to find, lying south west of ...
Sample Answer Sheet for The 10 Tourist Wonders of the
... new (heavier) elements are made, and then distributed at high speed into the Galaxy. In many ways, life on Earth owes its existence to supernovae and the fact that they “recycle” the material of early generations of stars and make them available to form new stars and planets enriched by their elemen ...
... new (heavier) elements are made, and then distributed at high speed into the Galaxy. In many ways, life on Earth owes its existence to supernovae and the fact that they “recycle” the material of early generations of stars and make them available to form new stars and planets enriched by their elemen ...
VISIT TO NORMAN LOCKYER OBSERVATORY IN SIDMOUTH
... Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 i ...
... Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 i ...
Distance measures - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... The closer a star is to us, the larger its angle of parallax will be. Astronomers have defined a standard unit of distance to be the parsec (pc). One parsec is the distance to a point in space that subtends a parallax angle of one arc second. This produces the simple but effective relationship: dist ...
... The closer a star is to us, the larger its angle of parallax will be. Astronomers have defined a standard unit of distance to be the parsec (pc). One parsec is the distance to a point in space that subtends a parallax angle of one arc second. This produces the simple but effective relationship: dist ...
The Galaxy Presentation 2011
... directions. Surrounding hot gas is region of cooler gas (100 light years distant) - We and all our stellar neighbors live inside a hot bubble! - The existence of this LOCAL BUBBLE means that a number of supernovae must have detonated within our stellar neighborhood over past several million years! ...
... directions. Surrounding hot gas is region of cooler gas (100 light years distant) - We and all our stellar neighbors live inside a hot bubble! - The existence of this LOCAL BUBBLE means that a number of supernovae must have detonated within our stellar neighborhood over past several million years! ...
File
... • For stars that are part of a binary system or star cluster- NO (on next slide) • The white dwarf is the dense core left behind from the previous red giant. • 1 tsp. of white dwarf matter would have a mass of several tons. • This will continue to shine for billions of years. ...
... • For stars that are part of a binary system or star cluster- NO (on next slide) • The white dwarf is the dense core left behind from the previous red giant. • 1 tsp. of white dwarf matter would have a mass of several tons. • This will continue to shine for billions of years. ...
- hoganshomepage
... chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
... chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
Stars-Chapter 18
... If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
... If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
... This infrared view of our Galaxy shows much more detail of the galactic center than the visible-light view does, as infrared is not as much absorbed by gas and dust. ...
... This infrared view of our Galaxy shows much more detail of the galactic center than the visible-light view does, as infrared is not as much absorbed by gas and dust. ...
HR Diagram - Geneva 304
... 56. Briefly describe the density and processes involved in each of the layers of a star. Include a diagram of the interior of a star with labeled layers. ...
... 56. Briefly describe the density and processes involved in each of the layers of a star. Include a diagram of the interior of a star with labeled layers. ...
Types of Galaxies - Spring Branch ISD
... They use information about how galaxies are moving. 58. True or false: The farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us. ...
... They use information about how galaxies are moving. 58. True or false: The farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us. ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... They use information about how galaxies are moving. 58. True or false: The farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us. ...
... They use information about how galaxies are moving. 58. True or false: The farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us. ...
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within Comparison to
... • It is actually easier to derive rotation curves for external galaxies. • These can then be fitted by combining the expected gravitational effects due to the mass of the stars in the disk and bulge of the galaxy, plus a hypothetical halo of dark matter. • Such studies show that the total mass of ...
... • It is actually easier to derive rotation curves for external galaxies. • These can then be fitted by combining the expected gravitational effects due to the mass of the stars in the disk and bulge of the galaxy, plus a hypothetical halo of dark matter. • Such studies show that the total mass of ...
Lecture 12
... • How do we measure stellar luminosities? • How do we measure stellar temperatures? • How do we measure stellar masses? ...
... • How do we measure stellar luminosities? • How do we measure stellar temperatures? • How do we measure stellar masses? ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... How Is a Star’s Color Related to Its Temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell ...
... How Is a Star’s Color Related to Its Temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell ...
Galaxies
... light that has a longer wavelength than it had when it was emitted (a redshift), while observers looking at an approaching source see light that is shifted to shorter wavelength (a blueshift). ...
... light that has a longer wavelength than it had when it was emitted (a redshift), while observers looking at an approaching source see light that is shifted to shorter wavelength (a blueshift). ...
Stellar Properties
... 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. Apparent magnitude is measure of: a=light output, b=light received ...
... 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. Apparent magnitude is measure of: a=light output, b=light received ...
constellation - Bucks-Mont Astronomical Association
... When you think about the new stars forming in the Milky Way, you probably think of the giant starforming regions like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacu ...
... When you think about the new stars forming in the Milky Way, you probably think of the giant starforming regions like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacu ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.