public_lector_10
... The black hole itself is invisible, but we can measure its gravitational effect on nearby stars. Turbulence in the earth’s atmosphere blurs out any details smaller than about 0.5 arcsec (0.25 mm at 100 m). To see stars close enough to the black hole (0.1 arcsec), adaptive optics are needed to corre ...
... The black hole itself is invisible, but we can measure its gravitational effect on nearby stars. Turbulence in the earth’s atmosphere blurs out any details smaller than about 0.5 arcsec (0.25 mm at 100 m). To see stars close enough to the black hole (0.1 arcsec), adaptive optics are needed to corre ...
Document
... Solar bisectors take on a „C“ shape due to more flux and more area of rising part of convective cells. There is considerable variations with limb angle due to the change of depth of formation and the view angle. The line profiles themselves become shallower and wider towards the limb. ...
... Solar bisectors take on a „C“ shape due to more flux and more area of rising part of convective cells. There is considerable variations with limb angle due to the change of depth of formation and the view angle. The line profiles themselves become shallower and wider towards the limb. ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... planetary systems that are not fully aligned with our line of sight but still have a component that provides a relative motion towards or away from Earth. Thus, the Wobble method provides for a wider range of planetary systems. If both methods can be used on a exo-system, the size and mass of the pl ...
... planetary systems that are not fully aligned with our line of sight but still have a component that provides a relative motion towards or away from Earth. Thus, the Wobble method provides for a wider range of planetary systems. If both methods can be used on a exo-system, the size and mass of the pl ...
Coordinate Systems - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring 2017!
... The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun, Moon, and planets as seen from the Earth. In another sense, the ecliptic is the path of the Earth’s orbit projected onto the sky. The orbits of the Earth and most of the other planets move in a relatively flat plane around the Sun. ...
... The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun, Moon, and planets as seen from the Earth. In another sense, the ecliptic is the path of the Earth’s orbit projected onto the sky. The orbits of the Earth and most of the other planets move in a relatively flat plane around the Sun. ...
Lyman-α: The Many Applications and Challenges of This Powerful
... Deuterium in the local Galactic disk The deuterium Lyman-α line also plays a critical role in measuring the deuterium-to-hydrogen number density ratio (D/H), which is an important test of the density of ordinary matter and the creation of H, D, and He in the very early Universe. Since, the observed ...
... Deuterium in the local Galactic disk The deuterium Lyman-α line also plays a critical role in measuring the deuterium-to-hydrogen number density ratio (D/H), which is an important test of the density of ordinary matter and the creation of H, D, and He in the very early Universe. Since, the observed ...
Feedback - Cambridge University Press
... clumps (with a maximum density set by the resolution of the simulation), e.g., Bournaud ...
... clumps (with a maximum density set by the resolution of the simulation), e.g., Bournaud ...
6 The mysterious universe
... enough to be seen with the naked eye. The collapse continues under the influence of gravity, forming visible globules in the nebula cloud. As the globules collapse further, the formation of any original gas A quick glance around the night sky shows us that cloud is accelerated. The now dense cloud i ...
... enough to be seen with the naked eye. The collapse continues under the influence of gravity, forming visible globules in the nebula cloud. As the globules collapse further, the formation of any original gas A quick glance around the night sky shows us that cloud is accelerated. The now dense cloud i ...
Stellar Properties
... Determining stellar distances from Earth is the first step to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. ...
... Determining stellar distances from Earth is the first step to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. ...
Review 3 (11-18-10)
... stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Nothing stops the collapse and produces an object so compact that escape velocity is higher than speed of light; hence, not even light can escape. •NOTE: these are the masses of the dead stars NOT the masses they had when th ...
... stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Nothing stops the collapse and produces an object so compact that escape velocity is higher than speed of light; hence, not even light can escape. •NOTE: these are the masses of the dead stars NOT the masses they had when th ...
presentation source
... than an entire galaxy such as M31 could be so far away....… This implied that Cyg A was an extraordinary object. Astronomers began to examine other 3C objects ...
... than an entire galaxy such as M31 could be so far away....… This implied that Cyg A was an extraordinary object. Astronomers began to examine other 3C objects ...
Variable Stars – II. Pulsating stars
... Equally, there is no reason why many modes cannot all be excited at the same time – just as with a plucked string, the fundamental and many overtones might be present. In the Sun, modes have been identified from order 0 to over 1500 ! Because we can see the Sun as a well-resolved disk, it has been p ...
... Equally, there is no reason why many modes cannot all be excited at the same time – just as with a plucked string, the fundamental and many overtones might be present. In the Sun, modes have been identified from order 0 to over 1500 ! Because we can see the Sun as a well-resolved disk, it has been p ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Polynesian Voyaging
... names. In more modern times, 40 other constellations have been added. Some of these are just "space fillers" between more prominent groups. Others are groups of stars in the Southern sky, too far south to be seen to advantage by these ancient astronomers, most of whom lived in Greece, Egypt, Persia, ...
... names. In more modern times, 40 other constellations have been added. Some of these are just "space fillers" between more prominent groups. Others are groups of stars in the Southern sky, too far south to be seen to advantage by these ancient astronomers, most of whom lived in Greece, Egypt, Persia, ...
aaswinter06
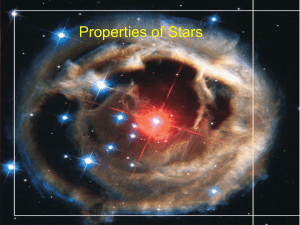
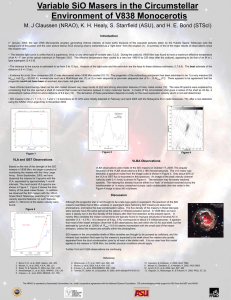
... • Evidence for a hot, blue companion (B3 V) was discovered when V838 Mon cooled (10,11). The progenitor of the outbursting component has been estimated to be 1) a very massive (65 Msolar), hot (Teff ~ 50,000 K), evolved star such as a Wolf-Rayet star (7); or 2) a main sequence or pre-main sequence s ...
... • Evidence for a hot, blue companion (B3 V) was discovered when V838 Mon cooled (10,11). The progenitor of the outbursting component has been estimated to be 1) a very massive (65 Msolar), hot (Teff ~ 50,000 K), evolved star such as a Wolf-Rayet star (7); or 2) a main sequence or pre-main sequence s ...
Slide 1
... “Real” IMF must be steeper than apparent IMF for most clusters. 2. Low-mass stars are forming in the starburst cluster. 3. Correction for effect of segregation still leaves a flat IMF in NGC 3603 ( -0.9), but in the LMC clusters (for 0.7 to 5.0 Mo fits) resulting IMFs are very steep: -1.6 - ...
... “Real” IMF must be steeper than apparent IMF for most clusters. 2. Low-mass stars are forming in the starburst cluster. 3. Correction for effect of segregation still leaves a flat IMF in NGC 3603 ( -0.9), but in the LMC clusters (for 0.7 to 5.0 Mo fits) resulting IMFs are very steep: -1.6 - ...
Document
... Formation of Planets around Stars • Planets outside our solar system are difficult to detect • Planetary searches are done indirectly ...
... Formation of Planets around Stars • Planets outside our solar system are difficult to detect • Planetary searches are done indirectly ...
Are Gamma-Ray Bursts good Star Formation Indicators?
... enshrouded systems. In such galaxies the UV flux from OB stars is largely reprocessed by the dust to far IR wavelengths. Thus submm measurements provide an independent estimate of star formation rate in the host galaxies. Combining our observations of GRB hosts with those of Berger et al. (2003 ApJ ...
... enshrouded systems. In such galaxies the UV flux from OB stars is largely reprocessed by the dust to far IR wavelengths. Thus submm measurements provide an independent estimate of star formation rate in the host galaxies. Combining our observations of GRB hosts with those of Berger et al. (2003 ApJ ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.