aaswinter07ppt
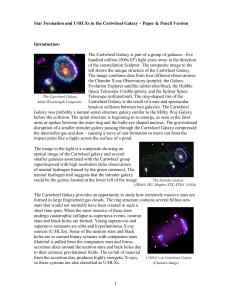
... In January 2002, the star V838 Monocerotis erupted, generating intense interest, at least partly because of the exquisite pictures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see the background of this poster and the color picture below) ACS showing what is interpreted as a “light echo” from the eruption ( ...
... In January 2002, the star V838 Monocerotis erupted, generating intense interest, at least partly because of the exquisite pictures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see the background of this poster and the color picture below) ACS showing what is interpreted as a “light echo” from the eruption ( ...
H-Band spectroscopic classification of OB stars
... All basic data reduction was accomplished using IRAF2 . Each image was flat–fielded using dome flats and then sky subtracted using another image from the grid with the star displaced by several positions along the slit (cross–dispersed mode) or with a median combination sky image (long slit mode). I ...
... All basic data reduction was accomplished using IRAF2 . Each image was flat–fielded using dome flats and then sky subtracted using another image from the grid with the star displaced by several positions along the slit (cross–dispersed mode) or with a median combination sky image (long slit mode). I ...
copyright 2002 scientific american, inc.
... a mere point to a discernible disk. “Discernible” in this case means a few lightweeks across. To reach that size, the source must have been expanding at a considerable rate— close to the speed of light. The BeppoSAX and follow-up observations have transformed astronomers’ view of GRBs. The old conce ...
... a mere point to a discernible disk. “Discernible” in this case means a few lightweeks across. To reach that size, the source must have been expanding at a considerable rate— close to the speed of light. The BeppoSAX and follow-up observations have transformed astronomers’ view of GRBs. The old conce ...
Chapter 27 Quasars, Active Galaxies, and Gamma
... • Early radio telescopes found radio emission from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
... • Early radio telescopes found radio emission from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
Planets orbiting stars more massive than the Sun
... surveys for planets of these types of stars are not efficient (Desort 2009a; Desort 2009b; Guenther et al. 2009; Galland et al. 2006; Galland et al. 2010; Borgniet et al. 2014). Transit surveys are more suitable, because they do not suffer from these difficulties. The only challenges of transit surv ...
... surveys for planets of these types of stars are not efficient (Desort 2009a; Desort 2009b; Guenther et al. 2009; Galland et al. 2006; Galland et al. 2010; Borgniet et al. 2014). Transit surveys are more suitable, because they do not suffer from these difficulties. The only challenges of transit surv ...
Arcturus - bYTEBoss
... Exactly whom Boötes is supposed to represent is not clear. According to one version, he was a ploughman who drove the oxen in the constellation Ursa Major using his two dogs Chara and Asterion (from the constellation Canes Venatici). The oxen were tied to the polar axis and so the action of Boötes k ...
... Exactly whom Boötes is supposed to represent is not clear. According to one version, he was a ploughman who drove the oxen in the constellation Ursa Major using his two dogs Chara and Asterion (from the constellation Canes Venatici). The oxen were tied to the polar axis and so the action of Boötes k ...
Science performance of Gaia, ESA`s space
... • Gaia will detect tens of thousands of brown dwarfs, both drifting through space in isolation and in orbit around other stars (Haywood and Jordi 2002). This data is vital for investigating the physics of star formation since brown dwarfs represent stars that “just did not make it” to core hydrogen ...
... • Gaia will detect tens of thousands of brown dwarfs, both drifting through space in isolation and in orbit around other stars (Haywood and Jordi 2002). This data is vital for investigating the physics of star formation since brown dwarfs represent stars that “just did not make it” to core hydrogen ...
17_Testbank
... A) The giant must once have been the more massive star but transferred some of its mass to its companion. B) Despite the low odds of finding a system with two such massive stars, there is nothing surprising about the fact that such systems exist. C) The two stars probably were once separate but beca ...
... A) The giant must once have been the more massive star but transferred some of its mass to its companion. B) Despite the low odds of finding a system with two such massive stars, there is nothing surprising about the fact that such systems exist. C) The two stars probably were once separate but beca ...
our knowledge of high-mass star formation at the dawn of - CEA-Irfu
... partners. Non-equal mass encounters, circumstellar disks, and binary components could decrease this number to about 106 pc−3 , but such stellar density is highly unlikely to be the general case of high-mass star-forming sites. ...
... partners. Non-equal mass encounters, circumstellar disks, and binary components could decrease this number to about 106 pc−3 , but such stellar density is highly unlikely to be the general case of high-mass star-forming sites. ...
Chapter 26.2 notes
... Properties of Stars Size and Mass Once astronomers know a star’s temperature and absolute brightness, they can estimate its diameter and then calculate its volume. The masses of many stars can be determined by observing the gravitational interaction of stars that occur in pairs. For most stars, ther ...
... Properties of Stars Size and Mass Once astronomers know a star’s temperature and absolute brightness, they can estimate its diameter and then calculate its volume. The masses of many stars can be determined by observing the gravitational interaction of stars that occur in pairs. For most stars, ther ...
1 Introduction - University of Amsterdam
... Krumholz 2014a). One striking aspect that awaits explanation is why all massive stars appear to form as part of multiple systems (Sana et al. 2014a), preferentially in close orbit with one of their companions (Sana et al. 2012). What happens after formation is also poorly constrained, essentially be ...
... Krumholz 2014a). One striking aspect that awaits explanation is why all massive stars appear to form as part of multiple systems (Sana et al. 2014a), preferentially in close orbit with one of their companions (Sana et al. 2012). What happens after formation is also poorly constrained, essentially be ...
Anatomy of a Supernova - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... cal combustion theory and terrestrial experiments show that In the late 1980s a new picture combined the strengths of there are two basic types of explosion. The first is called deflaboth models. Today scientists believe tbat a Type Ia supernova gration. Deflagration waves are subsonic and act like ...
... cal combustion theory and terrestrial experiments show that In the late 1980s a new picture combined the strengths of there are two basic types of explosion. The first is called deflaboth models. Today scientists believe tbat a Type Ia supernova gration. Deflagration waves are subsonic and act like ...
Cartwheel Galaxy - Chandra X
... The Cartwheel Galaxy provides an opportunity to study how extremely massive stars are formed in large fragmented gas clouds. The ring structure contains several billion new stars that would not normally have been created in such a short time span. When the most massive of these stars undergo catastr ...
... The Cartwheel Galaxy provides an opportunity to study how extremely massive stars are formed in large fragmented gas clouds. The ring structure contains several billion new stars that would not normally have been created in such a short time span. When the most massive of these stars undergo catastr ...
Stars - Emera Astronomy Center
... two brightest stars mark opposite ends of the constellation. Regulus, the heart of the lion, is at Leo's western edge. And the second-brightest star, Denebola, marks Leo's tail at the constellation's eastern end. Look for it above and to the left of the full Moon this evening, and to the lower left ...
... two brightest stars mark opposite ends of the constellation. Regulus, the heart of the lion, is at Leo's western edge. And the second-brightest star, Denebola, marks Leo's tail at the constellation's eastern end. Look for it above and to the left of the full Moon this evening, and to the lower left ...
s-process
... -2.1, when low-mass AGB stars begin to contribute from double shell burning. The s-process then dominates Ba production. The origin of heavy metals at the lowest Galactic metallicity ([Fe/H] = -4) is still not understood, but may be dominated by the weak s-process, or by a separate r-process in mass ...
... -2.1, when low-mass AGB stars begin to contribute from double shell burning. The s-process then dominates Ba production. The origin of heavy metals at the lowest Galactic metallicity ([Fe/H] = -4) is still not understood, but may be dominated by the weak s-process, or by a separate r-process in mass ...
The Evolution of Coronal X
... the bar links maximum and minimum observed fluxes where objects have been observed multiple times. Points to note: The Sun is 2-3 orders of magnitude fainter than 100 Myr old ZAMS stars. It also varies in flux by >1 order of magnitude as does alpha Cen A at a similar age. Younger Suns are much more ...
... the bar links maximum and minimum observed fluxes where objects have been observed multiple times. Points to note: The Sun is 2-3 orders of magnitude fainter than 100 Myr old ZAMS stars. It also varies in flux by >1 order of magnitude as does alpha Cen A at a similar age. Younger Suns are much more ...
Astro 27 Solar System Formation and ExoPlanets Slide Show
... So, the Doppler Shifts of the parent star would be tiny. Even mighty Jupiter is only 1/1000 the mass of the sun. It moves at a speed of 12.7 km/sec in its orbit, so the sun moves only 1/1000 of that, or 13 meters/sec So v/c is 4x10-8 or 40 billionths or 1 part in 25 million!! Wavelength shifts of on ...
... So, the Doppler Shifts of the parent star would be tiny. Even mighty Jupiter is only 1/1000 the mass of the sun. It moves at a speed of 12.7 km/sec in its orbit, so the sun moves only 1/1000 of that, or 13 meters/sec So v/c is 4x10-8 or 40 billionths or 1 part in 25 million!! Wavelength shifts of on ...
1. The catalogue structure
... not correspond to zodiacal constellations, which is why the stars that pertain to a single zodiacal constellation can wind up in different zodiacal signs. The canonical version of the Almagest catalogue contained in the work of Peters and Knobel ([1339]) is presented as a table that consists of six ...
... not correspond to zodiacal constellations, which is why the stars that pertain to a single zodiacal constellation can wind up in different zodiacal signs. The canonical version of the Almagest catalogue contained in the work of Peters and Knobel ([1339]) is presented as a table that consists of six ...
1 - Piscataway High School
... becomes trapped in dead ends — white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. But some matter from dying stars escapes back into the interstellar medium and is incorporated into new stars and the planets that circle them. The deaths of stars are part of a great cycle of stellar birth and death that i ...
... becomes trapped in dead ends — white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. But some matter from dying stars escapes back into the interstellar medium and is incorporated into new stars and the planets that circle them. The deaths of stars are part of a great cycle of stellar birth and death that i ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.