Stars
... The Blue Supergiants will begin to burn up all of the hydrogen that they have after a few million years. When this happens, the outer shell of the star begins to expand. It grows to about triple the size that it currently is. The Blue Supergiant now becomes a Supergiant. Supergiants are orange/yello ...
... The Blue Supergiants will begin to burn up all of the hydrogen that they have after a few million years. When this happens, the outer shell of the star begins to expand. It grows to about triple the size that it currently is. The Blue Supergiant now becomes a Supergiant. Supergiants are orange/yello ...
Stars and Deep Time
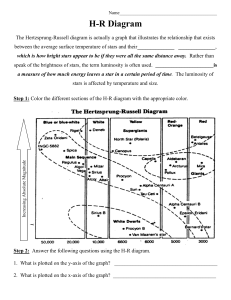
... (brightness) of stars against their color (temperature), and revealed patterns • Most stars fell into a band from the upper left to lower right—the Main Sequence • Some grouped in the upper right—Red ...
... (brightness) of stars against their color (temperature), and revealed patterns • Most stars fell into a band from the upper left to lower right—the Main Sequence • Some grouped in the upper right—Red ...
Uniqueness of the Earth, Lebo, 7-30
... Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locations the star densities are too high – the planetary orbits would be unstable. ...
... Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locations the star densities are too high – the planetary orbits would be unstable. ...
Lecture 14 - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy CASA
... http://casa.colorado.edu/~wcash/APS1200/APS1200.html ...
... http://casa.colorado.edu/~wcash/APS1200/APS1200.html ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Some stars end their lives in cataclysmic explosions: spectacular supernovae, which briefly become the most brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astr ...
... Some stars end their lives in cataclysmic explosions: spectacular supernovae, which briefly become the most brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astr ...
Star Formation
... it will tear itself apart – In the equation above, w is the spin speed and r is the radius. The subscript i means initial and f means final – Squaring intensifies the effect ...
... it will tear itself apart – In the equation above, w is the spin speed and r is the radius. The subscript i means initial and f means final – Squaring intensifies the effect ...
Using a Planisphere - Amateur Observers` Society of New York
... The first thing a new amateur astronomer needs to get and learn to use is a planisphere (Star Finder or Star Wheel). Print the accompanying pieces and follow the instructions for construction. It will help you find the stars and constellations at any time during the year from our latitude. Notice ho ...
... The first thing a new amateur astronomer needs to get and learn to use is a planisphere (Star Finder or Star Wheel). Print the accompanying pieces and follow the instructions for construction. It will help you find the stars and constellations at any time during the year from our latitude. Notice ho ...
Review Quiz No. 22
... belongs to the solar system. belongs to the Milky Way. is located as distances of less than 100 pc from us. is located in galaxies other than the Milky Way. does not belong to a particular galaxy at all. ...
... belongs to the solar system. belongs to the Milky Way. is located as distances of less than 100 pc from us. is located in galaxies other than the Milky Way. does not belong to a particular galaxy at all. ...
The coolest White Dwarf— older than the age of the universe?
... steadily loses its outer gasses and ends its life as a ball of compact degenerate electron gas or a White Dwarf (WD). It may begin this stage with a very high temperature, say 50,000 K and it steadily cools over time following a well-known cooling rate. Eventually this object will cool so much that ...
... steadily loses its outer gasses and ends its life as a ball of compact degenerate electron gas or a White Dwarf (WD). It may begin this stage with a very high temperature, say 50,000 K and it steadily cools over time following a well-known cooling rate. Eventually this object will cool so much that ...
Montage of Jupiter and the Galilean satellites
... supergiants at the very top; giants just below them; and finally mainsequence stars. The relative sizes of the stars are shown correctly within each luminosity class, but not between them. The colors are those as perceived by the eye looking at these stars through a telescope. ...
... supergiants at the very top; giants just below them; and finally mainsequence stars. The relative sizes of the stars are shown correctly within each luminosity class, but not between them. The colors are those as perceived by the eye looking at these stars through a telescope. ...
Due Date: Thursday, November 16, 2006
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
Slide 1
... The Planetary Nebula (show) Glowing gaseous shrouds shed by dying sun-like stars trying to stabilize as they run out of nuclear fuel.. Typically 1,000 times the size of our solar system These Ten have names like Owl, the Cat's Eye, the Ghost of Jupiter, Ring. This glorious final phase in the life of ...
... The Planetary Nebula (show) Glowing gaseous shrouds shed by dying sun-like stars trying to stabilize as they run out of nuclear fuel.. Typically 1,000 times the size of our solar system These Ten have names like Owl, the Cat's Eye, the Ghost of Jupiter, Ring. This glorious final phase in the life of ...
Star Of Wonder
... smaller object, ripping the entire star apart and throwing much of its material out into space. The remaining portion of the star then collapses still further to become either a "neutron star" just a few kilometers across, or a "black hole" that is far smaller than even the tiny nucleus of an atom a ...
... smaller object, ripping the entire star apart and throwing much of its material out into space. The remaining portion of the star then collapses still further to become either a "neutron star" just a few kilometers across, or a "black hole" that is far smaller than even the tiny nucleus of an atom a ...
Night Sky Checklist April–May–June Unaided Eye Astronomy
... third brightest that can be seen from Acadiana). Spica is a blue-white star, the brightest star in Virgo. It’s about 260 light years away. Regulus was one of the Royal Stars of ancient Mesopotamia 5000 years ago, not only because it is fairly bright but also because at that time its position in the ...
... third brightest that can be seen from Acadiana). Spica is a blue-white star, the brightest star in Virgo. It’s about 260 light years away. Regulus was one of the Royal Stars of ancient Mesopotamia 5000 years ago, not only because it is fairly bright but also because at that time its position in the ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... A small mass star uses less fuel so it lasts longer so . . . The smaller the mass the longer it lasts ...
... A small mass star uses less fuel so it lasts longer so . . . The smaller the mass the longer it lasts ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.