Sun and Stars
... The closest star to Earth; the Sun The Sun contains more than 99.8% of the total mass of the Solar System. The sun is also the largest star in the solar system. We know this star as “The Sun”, though in the past, the Greeks have called it “Helios”, and the Romans have called it “Sol”. Around 40.5 b ...
... The closest star to Earth; the Sun The Sun contains more than 99.8% of the total mass of the Solar System. The sun is also the largest star in the solar system. We know this star as “The Sun”, though in the past, the Greeks have called it “Helios”, and the Romans have called it “Sol”. Around 40.5 b ...
Untitled - New Zealand Science Teacher
... Centaurus, with the bright 'Pointers', and Crux the Southern Cross, are in the southwest sky. They make a tight grouping of bright stars. Originally Crux was the hind legs of the Centaur, the horse-man of Greek mythology. The complete Centaur, with bow, is outlined at left. It was only in the 17th C ...
... Centaurus, with the bright 'Pointers', and Crux the Southern Cross, are in the southwest sky. They make a tight grouping of bright stars. Originally Crux was the hind legs of the Centaur, the horse-man of Greek mythology. The complete Centaur, with bow, is outlined at left. It was only in the 17th C ...
Stars - winterk
... followed by an outward projection of particles • Depending of the star’s size, its collapse is either in the form of a planetary nebula or a supernova • After that, it then becomes one of the following: 1) White dwarf (small/medium-sized stars) 2) Neutron star (large stars) 3) Black hole (extremely ...
... followed by an outward projection of particles • Depending of the star’s size, its collapse is either in the form of a planetary nebula or a supernova • After that, it then becomes one of the following: 1) White dwarf (small/medium-sized stars) 2) Neutron star (large stars) 3) Black hole (extremely ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... The Beginning of the End: Red Giants After Hydrogen is exhausted in core ... Energy released from nuclear fusion counter-acts inward force of gravity. ...
... The Beginning of the End: Red Giants After Hydrogen is exhausted in core ... Energy released from nuclear fusion counter-acts inward force of gravity. ...
Star Life Cycle
... When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming wh ...
... When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming wh ...
Astronomy PowerPoint - Petal School District
... (no man has ever been farther than the moon) One way: space telescopes! the Hubble Space Telescope (looks at distant galaxies & at planets in our solar system) ...
... (no man has ever been farther than the moon) One way: space telescopes! the Hubble Space Telescope (looks at distant galaxies & at planets in our solar system) ...
Quiz Solution: 1 April 2013 What does it mean when an astronomer
... Quiz Solution: 1 April 2013 What does it mean when an astronomer says that a star "moves" from one place to another on an H-R Diagram? Can you provide an example of this? As stars evolve and change structure, their radii and temperatures also change. Since a star's luminosity is dependent on both te ...
... Quiz Solution: 1 April 2013 What does it mean when an astronomer says that a star "moves" from one place to another on an H-R Diagram? Can you provide an example of this? As stars evolve and change structure, their radii and temperatures also change. Since a star's luminosity is dependent on both te ...
Space Test: Practice Questions and Answers 1. Who discovered
... The Steady State Theory believed that the universe doesn’t change with time. However, more matter is added as it expands. It also stated that the universe had not beginning or end. In Big Bang the ...
... The Steady State Theory believed that the universe doesn’t change with time. However, more matter is added as it expands. It also stated that the universe had not beginning or end. In Big Bang the ...
3 rd stage of a star`s life = red giant
... Main Sequence Stars 1. The life span of a star depends on its size. 2. Very massive stars will become blue giants during their main sequence. Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years. 3. Smaller stars, like the Sun, will burn for several billion years during their main sequenc ...
... Main Sequence Stars 1. The life span of a star depends on its size. 2. Very massive stars will become blue giants during their main sequence. Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years. 3. Smaller stars, like the Sun, will burn for several billion years during their main sequenc ...
Chapter13
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
Star project
... • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
... • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
w 2012-01-13 Stellar Life Cycle
... Planetary nebulae are shells of gas thrown out by some stars near the end of their lives. Our Sun will probably produce a planetary nebula in about 5 billion years. They have nothing at all to do with planets; the terminology was invented because they often look a little like planets in small telesc ...
... Planetary nebulae are shells of gas thrown out by some stars near the end of their lives. Our Sun will probably produce a planetary nebula in about 5 billion years. They have nothing at all to do with planets; the terminology was invented because they often look a little like planets in small telesc ...
Monday, April 15
... Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
... Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
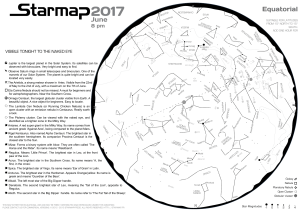
Mar 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
Yes, we are all star dust. Even Gary!
... Stars condense from “birthing” nebulae and die as “funerary” nebulae. The “life steps” taken depend on the mass of the star: 0.1 – 1.4 solar masses = condense, main sequence star of Hertzprung-Russell Diagram (ie like our Sun). Core condenses and outer layers expand to a giant star, possible nebula, ...
... Stars condense from “birthing” nebulae and die as “funerary” nebulae. The “life steps” taken depend on the mass of the star: 0.1 – 1.4 solar masses = condense, main sequence star of Hertzprung-Russell Diagram (ie like our Sun). Core condenses and outer layers expand to a giant star, possible nebula, ...
Uniqueness of the Earth, Lebo, 7-30
... Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locations the star densities are too high – the planetary orbits would be unstable. ...
... Most all stars in the Milky Way are in the central bulge, a globular cluster or a spiral arm. In each of these locations the star densities are too high – the planetary orbits would be unstable. ...
a star is born reading
... hot a star is from its color. Dwarf stars are very common. Their sizes range from half the size to one hundred times smaller than our Sun. The red dwarf is the most common star in the galaxy. However, they are not easily seen. They burn their fuel very slowly and are not as bright as others in the s ...
... hot a star is from its color. Dwarf stars are very common. Their sizes range from half the size to one hundred times smaller than our Sun. The red dwarf is the most common star in the galaxy. However, they are not easily seen. They burn their fuel very slowly and are not as bright as others in the s ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.