October 2011
... Before our observing session we received a tour of the 60inch and 100-inch domes from Gale Gant. After learning some of the history of Mount Wilson from Dave Jurasevich at the September general meeting it was great getting to see firsthand where it all happened. After the tour, we gathered around th ...
... Before our observing session we received a tour of the 60inch and 100-inch domes from Gale Gant. After learning some of the history of Mount Wilson from Dave Jurasevich at the September general meeting it was great getting to see firsthand where it all happened. After the tour, we gathered around th ...
lecture12
... There is no difference in the lines of the two stars. Star A’s lines are stronger than Star B’s lines. ...
... There is no difference in the lines of the two stars. Star A’s lines are stronger than Star B’s lines. ...
North Star
... Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
... Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
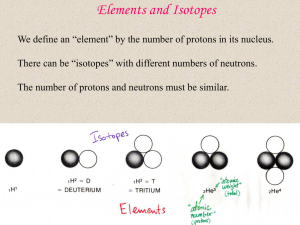
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... in the core are extreme enough for fusion (and the Sun’s gravity keeps them that way). Most energy is produced in the inner 20%. Convection carries the energy in the outer 30%. Most of the mass is in the inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
... in the core are extreme enough for fusion (and the Sun’s gravity keeps them that way). Most energy is produced in the inner 20%. Convection carries the energy in the outer 30%. Most of the mass is in the inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
01 - Ionia Public Schools
... _____ 28. After the supergiant stage, massive stars contract with a gravitational force that is a. a much less than that of small-mass stars. b. much greater than that of large-mass stars. c. much less than that of white dwarf stars. d. much greater than that of small mass stars. 29. What happens wh ...
... _____ 28. After the supergiant stage, massive stars contract with a gravitational force that is a. a much less than that of small-mass stars. b. much greater than that of large-mass stars. c. much less than that of white dwarf stars. d. much greater than that of small mass stars. 29. What happens wh ...
Sample Answer Sheet for The 10 Tourist Wonders of the
... larger than Pluto. Dwarf planets are a population of objects in our home system, consisting of smaller (but still round) worlds which are too small to have cleared out their immediate neighborhoods. There may be many others beyond Neptune which have not yet been discovered (although many others will ...
... larger than Pluto. Dwarf planets are a population of objects in our home system, consisting of smaller (but still round) worlds which are too small to have cleared out their immediate neighborhoods. There may be many others beyond Neptune which have not yet been discovered (although many others will ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... bright a star “appears” to be from Earth. The Apparent Magnitude of a star is affected by Absolute- Magnitude (Volume x Luminosity) and Distance from Observer. Betelgeuse, one of the brightest stars in the Universe, does not appear to be as ...
... bright a star “appears” to be from Earth. The Apparent Magnitude of a star is affected by Absolute- Magnitude (Volume x Luminosity) and Distance from Observer. Betelgeuse, one of the brightest stars in the Universe, does not appear to be as ...
Document
... Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of the star Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
... Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of the star Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
Physical Attributes of Stars
... d. Identify how technology is used to observe distant objects in the sky. S4E2. Students will model the position and motion of the earth in the solar system and will explain the role of relative position and motion in determining sequence of the phases of the moon. a. Explain the day/night cycle of ...
... d. Identify how technology is used to observe distant objects in the sky. S4E2. Students will model the position and motion of the earth in the solar system and will explain the role of relative position and motion in determining sequence of the phases of the moon. a. Explain the day/night cycle of ...
The Life CyCLe of STarS - Origins
... complete life cycle. The scientific model of a stellar life cycle is very solid, explaining many observations and successfully predicting the properties of new stars and star clusters that are discovered. How a star changes over its life cycle is described below. 33 Star Life. A typical star, like o ...
... complete life cycle. The scientific model of a stellar life cycle is very solid, explaining many observations and successfully predicting the properties of new stars and star clusters that are discovered. How a star changes over its life cycle is described below. 33 Star Life. A typical star, like o ...
Hubble Telescope Pictures
... The Sombrero Galaxy - 28 million light years from Earth - was voted best picture taken by the Hubble telescope. The dimensions of the galaxy, officially called M104, are as spectacular as its appearance. It has 800 billion suns and is 50,000 light years across. ...
... The Sombrero Galaxy - 28 million light years from Earth - was voted best picture taken by the Hubble telescope. The dimensions of the galaxy, officially called M104, are as spectacular as its appearance. It has 800 billion suns and is 50,000 light years across. ...
Old Final
... B) the star spins and beams of radio waves cross the Earth periodically C) the star accretes matter causing periodic runaway fusion that we observe as pulses D) the star's binary companion periodically blocks the pulsar's constant radio emission E) a black hole near the star absorbs the pulsar's ene ...
... B) the star spins and beams of radio waves cross the Earth periodically C) the star accretes matter causing periodic runaway fusion that we observe as pulses D) the star's binary companion periodically blocks the pulsar's constant radio emission E) a black hole near the star absorbs the pulsar's ene ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.