ABSOLUTE AND APPARENT MAGNITUDES
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
Observers` Forum - British Astronomical Association
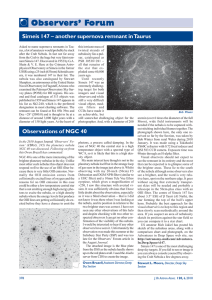
... which is impacting on the local medium. At the points of impact the bow shock generates Herbig−Haro (HH) objects as pairs on either side of the star. In the case of PV Cep three major pairs are clearly seen, with other knots of material present. There is circumstantial evidence that PV Cep is moving ...
... which is impacting on the local medium. At the points of impact the bow shock generates Herbig−Haro (HH) objects as pairs on either side of the star. In the case of PV Cep three major pairs are clearly seen, with other knots of material present. There is circumstantial evidence that PV Cep is moving ...
Geography
... find the Big Dipper. Draw a straight line between the two stars of the Big Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... find the Big Dipper. Draw a straight line between the two stars of the Big Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
Lecture 11
... More Mass = More Fuel More Luminosity = Greater Burn Rate We can scale from the Sun: M = 1M ...
... More Mass = More Fuel More Luminosity = Greater Burn Rate We can scale from the Sun: M = 1M ...
Lecture 18
... above the surface to cause radiation. Since its close to the surface, the light gets redshifted escaping, but it carries energy with it! ...
... above the surface to cause radiation. Since its close to the surface, the light gets redshifted escaping, but it carries energy with it! ...
Summer - Dark Sky Discovery
... charts here are far simpler and have fewer stars. You can just hold these up in front of you when you’re facing the appropriate direction and look up! Looking North The plough is perhaps the most easily recognised group of stars in the northern sky and it is a very useful ‘skymark’. The plough is al ...
... charts here are far simpler and have fewer stars. You can just hold these up in front of you when you’re facing the appropriate direction and look up! Looking North The plough is perhaps the most easily recognised group of stars in the northern sky and it is a very useful ‘skymark’. The plough is al ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... choosing constant to make scale consistent with Hipparchus. Absolute magnitude M is defined as the apparent magnitude a star ...
... choosing constant to make scale consistent with Hipparchus. Absolute magnitude M is defined as the apparent magnitude a star ...
Lecture 11, PPT version
... The more massive star has the smaller orbit. The relative amount of the Doppler shift of the two sets of lines tells us the ratio of the stellar masses. If both sets of lines shift by the same amount, the stars have the same mass. If one set of lines shifts twice as far as the other set, the big sta ...
... The more massive star has the smaller orbit. The relative amount of the Doppler shift of the two sets of lines tells us the ratio of the stellar masses. If both sets of lines shift by the same amount, the stars have the same mass. If one set of lines shifts twice as far as the other set, the big sta ...
canopus e.g procyon
... Some specific nearby stars: • The sun – a typical yellow dwarf star. Type “G2” with 8 planets • Proxima Centauri – closest of the triplet of stars loosely known as alpha-Centauri Proxima Centauri is a faint red star that orbits Alpha-Centauri A and B with a period of about one million years. Prox ...
... Some specific nearby stars: • The sun – a typical yellow dwarf star. Type “G2” with 8 planets • Proxima Centauri – closest of the triplet of stars loosely known as alpha-Centauri Proxima Centauri is a faint red star that orbits Alpha-Centauri A and B with a period of about one million years. Prox ...
Planisphere Exercise
... progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. ...
... progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. ...
NASC 1100
... The surface temperature also determines the line spectrum of a star. Hot stars display lines of highly ionized elements, while cool stars show molecular lines. Stars are classified by assigning a spectral type. The hottest stars are called spectral type O, followed by B, A, F, G, K, M as the surface ...
... The surface temperature also determines the line spectrum of a star. Hot stars display lines of highly ionized elements, while cool stars show molecular lines. Stars are classified by assigning a spectral type. The hottest stars are called spectral type O, followed by B, A, F, G, K, M as the surface ...
Big Bear Valley Astronomical Society
... over the Bull, which was then placed in the heavens, but for his sacrilege the gods declared that the life of his best friend, Enkidu, should be taken as a forfeit. The chief star, Aldebaran is the 1st magnitude star referred to by Ptolemy as 'the Torch' on account of its bright, rose-colored lumin ...
... over the Bull, which was then placed in the heavens, but for his sacrilege the gods declared that the life of his best friend, Enkidu, should be taken as a forfeit. The chief star, Aldebaran is the 1st magnitude star referred to by Ptolemy as 'the Torch' on account of its bright, rose-colored lumin ...
For instance, two hydrogen atoms may fuse together to form one
... elements fuse into heavier ones is called nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion releases huge amounts of energy. When the core of a clump becomes a hot, dense ball of hydrogen gas fusing into helium gas, a star is born. Astronomers classify stars based on their age, color, and brightness. These characteris ...
... elements fuse into heavier ones is called nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion releases huge amounts of energy. When the core of a clump becomes a hot, dense ball of hydrogen gas fusing into helium gas, a star is born. Astronomers classify stars based on their age, color, and brightness. These characteris ...
LAB: Star Classification
... KPD 0005+5106. The team who present these observations show that this white dwarf is among the hottest stars known so far, with a temperature of 200,000º K at its surface. Stars of intermediate mass (1-8 solar masses) terminate their life as an Earth-sized white dwarf after the exhaustion of their n ...
... KPD 0005+5106. The team who present these observations show that this white dwarf is among the hottest stars known so far, with a temperature of 200,000º K at its surface. Stars of intermediate mass (1-8 solar masses) terminate their life as an Earth-sized white dwarf after the exhaustion of their n ...
stars and planets
... There are around 200 billion stars in the Milky Way alone. VY Canis Majoris is the largest known star in our galaxy, if this star was in the center of our solar system it would reach the orbit of Saturn. One of the smallest known stars in the galaxy is VB 10, it is only around 20% larger than Jupite ...
... There are around 200 billion stars in the Milky Way alone. VY Canis Majoris is the largest known star in our galaxy, if this star was in the center of our solar system it would reach the orbit of Saturn. One of the smallest known stars in the galaxy is VB 10, it is only around 20% larger than Jupite ...
Stargazing Rules 01162013
... Moon is shaped like a "C", it bulges to the left. 18. Even though most of the objects we observe in the night sky appear not to move in relation to each other, in reality they are all moving at great speed relative to us and to each other. They appear not to be moving because of their great distanc ...
... Moon is shaped like a "C", it bulges to the left. 18. Even though most of the objects we observe in the night sky appear not to move in relation to each other, in reality they are all moving at great speed relative to us and to each other. They appear not to be moving because of their great distanc ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.