Northern and Southern Hemisphere Star Chart
... the process until eventually all the star’s outer layers have been blown away into space. The tiny shrunken core, about the size of the Earth, remains as a white dwarf. White dwarf stars no longer produce light by nuclear fusion, merely continuing to glow like dying embers until they have slowly coo ...
... the process until eventually all the star’s outer layers have been blown away into space. The tiny shrunken core, about the size of the Earth, remains as a white dwarf. White dwarf stars no longer produce light by nuclear fusion, merely continuing to glow like dying embers until they have slowly coo ...
Nebulae
... • They are found near hot, luminous stars of spectral types O and B • They are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot stars • They are composed of ionized hydrogen atoms; the so called H II region. • They emit light through a ...
... • They are found near hot, luminous stars of spectral types O and B • They are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot stars • They are composed of ionized hydrogen atoms; the so called H II region. • They emit light through a ...
Mapping the Stars
... • They are forced together to form neutrons. • What is a neutron star? • It is a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point at which all of its particles are neutrons. • What is a spinning neutron star called? • Pulsar ...
... • They are forced together to form neutrons. • What is a neutron star? • It is a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point at which all of its particles are neutrons. • What is a spinning neutron star called? • Pulsar ...
Constellations
... • The sun blocks star light during the day. • The earth blocks stars too far to the south. • The horizon is the line of the ground for an observer. • A star finder provides a cover that act as the horizon. – You use a different cover depending on your latitude • The planisphere’s wheel turns to set ...
... • The sun blocks star light during the day. • The earth blocks stars too far to the south. • The horizon is the line of the ground for an observer. • A star finder provides a cover that act as the horizon. – You use a different cover depending on your latitude • The planisphere’s wheel turns to set ...
Science 1 (MillinerSci1)
... D. telescope 13. In a family of rabbits, half the rabbits are brown and half are white. Which statement BEST explains why the rabbits have two different colors? A. The white rabbits were in the Sun more than the brown rabbits. B. The brown rabbits inherited different coat colors than the white rabbi ...
... D. telescope 13. In a family of rabbits, half the rabbits are brown and half are white. Which statement BEST explains why the rabbits have two different colors? A. The white rabbits were in the Sun more than the brown rabbits. B. The brown rabbits inherited different coat colors than the white rabbi ...
ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... At distance R, radiation spread over sphere of radius R: energy falling on each unit area of that sphere is Flux or ...
... At distance R, radiation spread over sphere of radius R: energy falling on each unit area of that sphere is Flux or ...
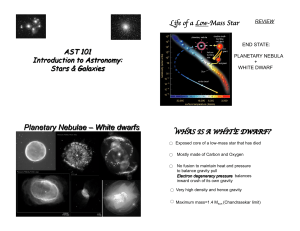
Planetary Nebulae – White dwarfs
... • Our atoms were once parts of stars that died more than 4.6 billion years ago, whose remains were swept up into the solar system when the Sun formed ...
... • Our atoms were once parts of stars that died more than 4.6 billion years ago, whose remains were swept up into the solar system when the Sun formed ...
Dim Stars - granthamkuehl
... Stars come in a range of sizes and masses. Our Sun is a mediumsized star. The largest stars, giant stars have a mass of about 60 times the mass of the Sun. ...
... Stars come in a range of sizes and masses. Our Sun is a mediumsized star. The largest stars, giant stars have a mass of about 60 times the mass of the Sun. ...
Earth
... hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silicon, magnesium and sulfur. The sun shines because it is burning hydrogen into helium in its extremely hot core. This mea ...
... hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silicon, magnesium and sulfur. The sun shines because it is burning hydrogen into helium in its extremely hot core. This mea ...
Universe Now - Course Pages of Physics Department
... – Useful in estimating stellar masses: mass can be calculated when the orbital period is known (as stated by Kepler’s III law). – Can be classified according to the distance between the components: • Detached binaries: the stars affect each other only by gravity, no mass transfer. Most binaries belo ...
... – Useful in estimating stellar masses: mass can be calculated when the orbital period is known (as stated by Kepler’s III law). – Can be classified according to the distance between the components: • Detached binaries: the stars affect each other only by gravity, no mass transfer. Most binaries belo ...
Page 1 of 4 Name PSCI 1055 Test #4 (Form B) Spring 2008 Buckley
... brightness on the H-R diagram? ...
... brightness on the H-R diagram? ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... Coma Bernices. With our night sky pointing away from the hustle and bustle of the plane of the Milky Way, we can see deep into the sky without objects being obscured or dimmed by looking through our galaxy. In spring skies we are treated to views of the closest cluster of galaxies in Virgo of which ...
... Coma Bernices. With our night sky pointing away from the hustle and bustle of the plane of the Milky Way, we can see deep into the sky without objects being obscured or dimmed by looking through our galaxy. In spring skies we are treated to views of the closest cluster of galaxies in Virgo of which ...
The Night Sky
... The biggest problem in navigating using the stars was in determining one’s longitude. Explain why this is so difficult? ...
... The biggest problem in navigating using the stars was in determining one’s longitude. Explain why this is so difficult? ...
MIDTERM #1 AST209 - The Cosmos Feb 10, 2012 50 minutes
... D) explained and predicted the motions of the planets with deferents and epicycles. E) describes the orbits of the planets as being ellipses, not circles. 31. Which of the following statements about the celestial equator is true at all latitudes? A) It represents an extension of Earth's equator onto ...
... D) explained and predicted the motions of the planets with deferents and epicycles. E) describes the orbits of the planets as being ellipses, not circles. 31. Which of the following statements about the celestial equator is true at all latitudes? A) It represents an extension of Earth's equator onto ...
HW #4 (due March 27)
... First, we will classify stars based on the "strength" of their H lines. Look at the spectra of the seven stars at the end of this worksheet. Using their spectra, rank the seven stars according to the strength of their Hα lines. If you can't rank them all easily, try coloring in the area between the ...
... First, we will classify stars based on the "strength" of their H lines. Look at the spectra of the seven stars at the end of this worksheet. Using their spectra, rank the seven stars according to the strength of their Hα lines. If you can't rank them all easily, try coloring in the area between the ...
STELLAR EVOLUTION
... stars of all masses. Astronomers then match these predictions with observed populations of stars, especially the stars found within clusters. Observations of the temperature, density, and motions of interstellar gas and dust clouds, which inform us about the process of star formation. Observatio ...
... stars of all masses. Astronomers then match these predictions with observed populations of stars, especially the stars found within clusters. Observations of the temperature, density, and motions of interstellar gas and dust clouds, which inform us about the process of star formation. Observatio ...
Red Giants
... for fusion to start. The fusion in the layer just outside the core is called shell burning. This fusion is very rapid because the shell layer is still compressing and increasing in temperature. The luminosity of the star increases from its main sequence value. The gas envelope surrounding the core p ...
... for fusion to start. The fusion in the layer just outside the core is called shell burning. This fusion is very rapid because the shell layer is still compressing and increasing in temperature. The luminosity of the star increases from its main sequence value. The gas envelope surrounding the core p ...
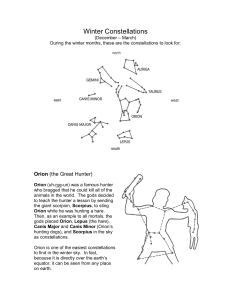
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.