V Example: our SUN (G2V)
... Modified in part from http://astronomyonline.org/Stars/HighMassEvolution.asp A white dwarf is the degenerate carbon core of a low mass star (like our Sun). A neutron star is the degenerate iron core of a high mass star. A pulsar is spinning neutron star. A black hole is the remnant of the collapse o ...
... Modified in part from http://astronomyonline.org/Stars/HighMassEvolution.asp A white dwarf is the degenerate carbon core of a low mass star (like our Sun). A neutron star is the degenerate iron core of a high mass star. A pulsar is spinning neutron star. A black hole is the remnant of the collapse o ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... determined, the distances of all planets can be found from Kepler’s third law. • Actually not a law, an emprical relation that has to be explained by the underlying physics. ...
... determined, the distances of all planets can be found from Kepler’s third law. • Actually not a law, an emprical relation that has to be explained by the underlying physics. ...
Chapter 12
... low pressure gas) but in size they are much smaller than the emission nebulae (HII regions) ...
... low pressure gas) but in size they are much smaller than the emission nebulae (HII regions) ...
CHAPTER 30: STARS, GALAXIES AND THE UNIVERSE Analyzing
... Stars such as our sun are considered medium-sized stars. The sun has a diameter of 1,390,000 km. Most of the stars you can see in the night sky are medium-sized stars. Many stars also have about the same mass as the sun, however some stars may be more or less massive. Stellar Motion Apparent Motion ...
... Stars such as our sun are considered medium-sized stars. The sun has a diameter of 1,390,000 km. Most of the stars you can see in the night sky are medium-sized stars. Many stars also have about the same mass as the sun, however some stars may be more or less massive. Stellar Motion Apparent Motion ...
Basic data of CoRoT-Exo-2b - tls
... Roll the spacecraft 90 degrees about the line-of-sight every 3 months to maintain the sun on the solar arrays and the radiator pointed to deep space. Earth-trailing orbit (heliocentric orbit with 372.5 day ...
... Roll the spacecraft 90 degrees about the line-of-sight every 3 months to maintain the sun on the solar arrays and the radiator pointed to deep space. Earth-trailing orbit (heliocentric orbit with 372.5 day ...
The Sky is Our Laboratory
... • A galaxy is a body of stars, gas, and dark matter kept together by gravity; • The `cosmos’ is a loose definition to indicate the Universe, or components of it. It comes from Greek, to indicate an harmonious whole, opposed to chaos. ...
... • A galaxy is a body of stars, gas, and dark matter kept together by gravity; • The `cosmos’ is a loose definition to indicate the Universe, or components of it. It comes from Greek, to indicate an harmonious whole, opposed to chaos. ...
PPT
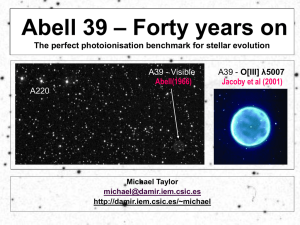
... 4) Stellar atmosphere theory and the mass loss stage of PNs It is relatively unstudied (only 1 dedicated publication!) Ideal case to assess our progress in astrophysics after 40 years ...
... 4) Stellar atmosphere theory and the mass loss stage of PNs It is relatively unstudied (only 1 dedicated publication!) Ideal case to assess our progress in astrophysics after 40 years ...
Name Date Life and Death of a Star 2015 1. In the main
... B. collision with another star C. gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star 29. When helium fusion takes over in a star's core, what happens? A. the energy output decreases B. energy output stays the same C. the energy output increases 30. A star that is gravitationally bound to another m ...
... B. collision with another star C. gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star 29. When helium fusion takes over in a star's core, what happens? A. the energy output decreases B. energy output stays the same C. the energy output increases 30. A star that is gravitationally bound to another m ...
an evening`s viewing with your new `scope
... perhaps the moon is not visible. Unfortunately there are no planets visible at the moment; we must wait until the summer for Jupiter. Other targets worth looking at are the well-known major astronomical objects. Try the Pleaides in Taurus and the Orion Nebula if you can catch them before they set. A ...
... perhaps the moon is not visible. Unfortunately there are no planets visible at the moment; we must wait until the summer for Jupiter. Other targets worth looking at are the well-known major astronomical objects. Try the Pleaides in Taurus and the Orion Nebula if you can catch them before they set. A ...
Presentation available here - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... All core collapse explosions are asymmetric, maybe produced by magnetic jets. How can this be proved? Gamma-ray bursts are caused by jets of material moving at nearly the speed of light. Do they mark the birth of black holes? At least some gamma-ray bursts (and maybe all) arise in supernova ex ...
... All core collapse explosions are asymmetric, maybe produced by magnetic jets. How can this be proved? Gamma-ray bursts are caused by jets of material moving at nearly the speed of light. Do they mark the birth of black holes? At least some gamma-ray bursts (and maybe all) arise in supernova ex ...
6-Where to Survey - The Challenger Learning Center
... from the stars death, spreading left over star material back into space and possibly leaving a black hole. If a black hole is not produced by a supermassive star’s death, a pulsar may result where the star use to reside. They are rotating neutron stars. They emit jets of particles from their poles a ...
... from the stars death, spreading left over star material back into space and possibly leaving a black hole. If a black hole is not produced by a supermassive star’s death, a pulsar may result where the star use to reside. They are rotating neutron stars. They emit jets of particles from their poles a ...
Powerpoint - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... One important aspect of this project was creating a way to visualize the results of these simulations. Below are color contour plots of temperature, material density, speed, and a representation of the magnetic field, all of which are data that are included in the output files of the simulations. In ...
... One important aspect of this project was creating a way to visualize the results of these simulations. Below are color contour plots of temperature, material density, speed, and a representation of the magnetic field, all of which are data that are included in the output files of the simulations. In ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... about losses as light travelled through gasses or dust clouds. We can also determine the size of a star by its spectrum. To do this we need to know its Luminosity, the amount of energy given off by each unit area, and an accurate surface temperature. ...
... about losses as light travelled through gasses or dust clouds. We can also determine the size of a star by its spectrum. To do this we need to know its Luminosity, the amount of energy given off by each unit area, and an accurate surface temperature. ...
Approximately 14 billion years ago, all matter and energy was
... All stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity. Death of Low-Mass Stars • Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse ...
... All stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity. Death of Low-Mass Stars • Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and collapse ...
Tour of the Universe
... ● The Kuiper belt is set to be the next frontier of exploration in our solar system. ● 6 of the planets have moons orbiting them. Them bigger ones have more moons than the smaller ones. ● Earth's moon was formed 4.5 billion years ago from material ejected when a collision occurred between a Mar ...
... ● The Kuiper belt is set to be the next frontier of exploration in our solar system. ● 6 of the planets have moons orbiting them. Them bigger ones have more moons than the smaller ones. ● Earth's moon was formed 4.5 billion years ago from material ejected when a collision occurred between a Mar ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.