Photographs of a Star Cluster Spectra of a Star Cluster
... Star Q would appear red and Star T would appear blue. Star Q would appear blue and Star T would appear red. Both stars would appear the same color. The color of the stars cannot be determined from this information. ...
... Star Q would appear red and Star T would appear blue. Star Q would appear blue and Star T would appear red. Both stars would appear the same color. The color of the stars cannot be determined from this information. ...
A Study of the Spectroscopic Variability of Select RV Tauri... Charles Kurgatt , Donald K. Walter , Steve Howell
... RV Tauri and Semi-Regular stars are examples of variable stars, a star that is unable to maintain a steady apparent brightness. These changes in brightness may have many causes such as eclipses, stellar rotation, and pulsation. The two types studied here vary in brightness due to pulsations in the p ...
... RV Tauri and Semi-Regular stars are examples of variable stars, a star that is unable to maintain a steady apparent brightness. These changes in brightness may have many causes such as eclipses, stellar rotation, and pulsation. The two types studied here vary in brightness due to pulsations in the p ...
All_Stars
... • Eventually, the entire envelope is ejected as a planetary nebula, leaving behind its hot, degenerate core: a white dwarf • The expanding envelope is ionized by UV photons from the hot white dwarf; it will glow as an emission nebula for up to 50,000 years ...
... • Eventually, the entire envelope is ejected as a planetary nebula, leaving behind its hot, degenerate core: a white dwarf • The expanding envelope is ionized by UV photons from the hot white dwarf; it will glow as an emission nebula for up to 50,000 years ...
Star Light, Star Bright
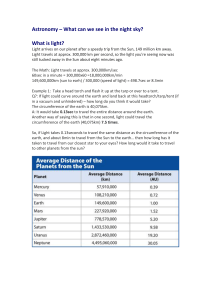
... students that our star, the Sun, is a great distance from Earth, but that the next closest star is 272 times that distance from Earth! Write 149,600,000 km = Earth to Sun on the board; under it, write 40,678,000,000 km = Earth to Alpha Centauri. Tell students that Alpha Centauri is actually a triple ...
... students that our star, the Sun, is a great distance from Earth, but that the next closest star is 272 times that distance from Earth! Write 149,600,000 km = Earth to Sun on the board; under it, write 40,678,000,000 km = Earth to Alpha Centauri. Tell students that Alpha Centauri is actually a triple ...
Review: How does a star*s mass determine its life story?
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas • It’s a black hole if it’s not a star and its mass exceeds the neutron star limit (~3 MSun). ...
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas • It’s a black hole if it’s not a star and its mass exceeds the neutron star limit (~3 MSun). ...
doc - Eu-Hou
... Supernovae of type Ia can be used as standard candles to measure the distance D of galaxies. It is one method among others (see also the exercise on Cepheid method) to scale the Universe. This method enables to study very distant objects because supernovae are very bright. The luminosity of supernov ...
... Supernovae of type Ia can be used as standard candles to measure the distance D of galaxies. It is one method among others (see also the exercise on Cepheid method) to scale the Universe. This method enables to study very distant objects because supernovae are very bright. The luminosity of supernov ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... The list of stars with precise estimates of mass and luminosity grew and the value of a could be fixed quite precisely. Interestingly, it was found that the value of a was different for different ranges of mass. For 1< M/M0 < 10, the value of awas 3< a < 4.5 (Figure 5). This curve represents the mas ...
... The list of stars with precise estimates of mass and luminosity grew and the value of a could be fixed quite precisely. Interestingly, it was found that the value of a was different for different ranges of mass. For 1< M/M0 < 10, the value of awas 3< a < 4.5 (Figure 5). This curve represents the mas ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... the Milky Way or Deep Space. This image captures neither of those, but what it does capture is the true sense of a New Zealand starry sky as seen from many of the towns throughout the country. It’s a beautifully composed and natural looking image overlooking the South Island coastal village of Kaiko ...
... the Milky Way or Deep Space. This image captures neither of those, but what it does capture is the true sense of a New Zealand starry sky as seen from many of the towns throughout the country. It’s a beautifully composed and natural looking image overlooking the South Island coastal village of Kaiko ...
The Great Nebula in Orion
... under the reasonable assumption that the Orion Nebula is a typical star-forming region, it presents astronomers with a valuable laboratory for observing star and planetary system formation in a controlled—or at least understandable—setting. The exact correspondences to the situation of the early Sol ...
... under the reasonable assumption that the Orion Nebula is a typical star-forming region, it presents astronomers with a valuable laboratory for observing star and planetary system formation in a controlled—or at least understandable—setting. The exact correspondences to the situation of the early Sol ...
What is a star?
... How are the surface temperatures of stars measured? • If an object’s color depends only on temperature, the object is called a blackbody. • As the temperature of a blackbody rises, it glows brighter and brighter red. • As it gets hotter, its color changes to orange, yellow, white, and blue-white. ...
... How are the surface temperatures of stars measured? • If an object’s color depends only on temperature, the object is called a blackbody. • As the temperature of a blackbody rises, it glows brighter and brighter red. • As it gets hotter, its color changes to orange, yellow, white, and blue-white. ...
PHYSICS – Astrophysics Section I
... the atmosphere of the star selectively absorbs wavelengths, forming an absorption spectrum. This is used to identify elements on the surface of the star. Emission nebulae produce emission spectra. The spectra result when interstellar gas clouds surrounding hot stars are excited by radiation from the ...
... the atmosphere of the star selectively absorbs wavelengths, forming an absorption spectrum. This is used to identify elements on the surface of the star. Emission nebulae produce emission spectra. The spectra result when interstellar gas clouds surrounding hot stars are excited by radiation from the ...
April - Magic Valley Astronomical Society
... 4/1 Mercury is at the ascending node at 1:00; Pluto is 3.3 degrees south of the Moon at 3:00; the Curtiss Cross, an Xshaped clair-obscure illumination effect located between the craters Parry and Gambart, is predicted to begin at 4:20; a double Galilean satellite shadow transit begins at 20:18 4/2 A ...
... 4/1 Mercury is at the ascending node at 1:00; Pluto is 3.3 degrees south of the Moon at 3:00; the Curtiss Cross, an Xshaped clair-obscure illumination effect located between the craters Parry and Gambart, is predicted to begin at 4:20; a double Galilean satellite shadow transit begins at 20:18 4/2 A ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... at a raised finger on an outstretched arm, one will notice its shift (with respect to a background) when seen with one eye closed, and then the other. The apparent shift will gradually disappear as we see objects farther and farther away1. Thus, even if one saw a star from two equatorially opposite ...
... at a raised finger on an outstretched arm, one will notice its shift (with respect to a background) when seen with one eye closed, and then the other. The apparent shift will gradually disappear as we see objects farther and farther away1. Thus, even if one saw a star from two equatorially opposite ...
Introduction This book will teach you all you need to know about the
... dwarf is the left over core after the star explodes and its outer layers are thrust into space. A white dwarf may only be the size of the earth, but it has a mass the is equal to half of our sun. That is really dense! Because of the explosion and because it is so dense a white dwarf is white because ...
... dwarf is the left over core after the star explodes and its outer layers are thrust into space. A white dwarf may only be the size of the earth, but it has a mass the is equal to half of our sun. That is really dense! Because of the explosion and because it is so dense a white dwarf is white because ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.