DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
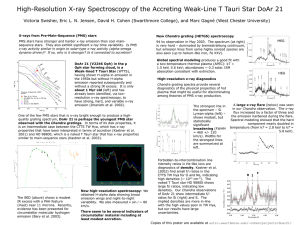
... PMS stars have stronger and harder x-ray emission than cool mainsequence stars. They also exhibit significant x-ray time variability. Is PMS x-ray activity similar in origin to solar-type x-ray activity (alpha-omega dynamo driven)? If so, why is it stronger? Is it connected to accretion? ...
... PMS stars have stronger and harder x-ray emission than cool mainsequence stars. They also exhibit significant x-ray time variability. Is PMS x-ray activity similar in origin to solar-type x-ray activity (alpha-omega dynamo driven)? If so, why is it stronger? Is it connected to accretion? ...
Photons
... Fig. 3. The filter sets used in the present work. From top to bottom, we show the filter+detector transmission curves S λ for the systems: (1) HST/NICMOS, (2) HST/WFPC2, (3) Washington, (4) ESO/EMMI, (5) ESO/WFI U BVRIZ + ESO/SOFI JHK, and (6) Johnson-CousinsGlass. All references are given in Sect. ...
... Fig. 3. The filter sets used in the present work. From top to bottom, we show the filter+detector transmission curves S λ for the systems: (1) HST/NICMOS, (2) HST/WFPC2, (3) Washington, (4) ESO/EMMI, (5) ESO/WFI U BVRIZ + ESO/SOFI JHK, and (6) Johnson-CousinsGlass. All references are given in Sect. ...
Document
... nebula is made of neutral atomic hydrogen. Ultraviolet light from hot O and B stars ionizes the surrounding hydrogen gas. When the electrons recombine with the protons, they emit light mostly at visible wavelengths, and primarily at a wavelength of 656.3 nanometers (giving the hydrogen emission nebu ...
... nebula is made of neutral atomic hydrogen. Ultraviolet light from hot O and B stars ionizes the surrounding hydrogen gas. When the electrons recombine with the protons, they emit light mostly at visible wavelengths, and primarily at a wavelength of 656.3 nanometers (giving the hydrogen emission nebu ...
BASIC PROPERTIES of STARS - 2
... Venus is about 105,000,000 km from the Sun. (1) What is approximate time to get the return signal from Venus when it is at its closest to Earth? C = 3 x 105 km/s (A 150; B 200; C 300; D 400 seconds) (2) What is the approximate time to get a return signal from Venus when Venus is at its most distant ...
... Venus is about 105,000,000 km from the Sun. (1) What is approximate time to get the return signal from Venus when it is at its closest to Earth? C = 3 x 105 km/s (A 150; B 200; C 300; D 400 seconds) (2) What is the approximate time to get a return signal from Venus when Venus is at its most distant ...
Black Hole Sun: A Total Eclipse Free Public Lecture about Eclipses
... We are interpreting E. C. Pickering’s (A. J. Cannon’s boss) spectra of Mizar (a star in the Big Dipper) in 1889. How can the spectral line of hydrogen appear at different wavelengths? A. The star is moving. B. Hydrogen emits at different wavelengths at different times. C. There was something wrong w ...
... We are interpreting E. C. Pickering’s (A. J. Cannon’s boss) spectra of Mizar (a star in the Big Dipper) in 1889. How can the spectral line of hydrogen appear at different wavelengths? A. The star is moving. B. Hydrogen emits at different wavelengths at different times. C. There was something wrong w ...
Omega Centauri
... • The isochrone fitting of the c-m diagrams indicates that the resolved part of the cluster consists of stars having a bimodal age distribution: – a younger population at 10–16 Myr 5 Mo S96 Mass~10 – an older one at 32–100 Myr. • The older population has an age distribution similar to that of the o ...
... • The isochrone fitting of the c-m diagrams indicates that the resolved part of the cluster consists of stars having a bimodal age distribution: – a younger population at 10–16 Myr 5 Mo S96 Mass~10 – an older one at 32–100 Myr. • The older population has an age distribution similar to that of the o ...
How big are stars? How do we know?
... • Many stars are found orbiting another star. These star systems are called binary stars. • Three types: – If we can see from pictures taken over time that the stars are orbiting each other, the system is a visual binary – If the stars are so close together (or distant from Earth) that their spectra ...
... • Many stars are found orbiting another star. These star systems are called binary stars. • Three types: – If we can see from pictures taken over time that the stars are orbiting each other, the system is a visual binary – If the stars are so close together (or distant from Earth) that their spectra ...
Merit Badge College 2017 Astronomy
... b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude I or brighter. c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the Nort ...
... b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude I or brighter. c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the Nort ...
Celestial Distances
... In contrast, most stars are constant in their luminosity (at least within a percent or two) ...
... In contrast, most stars are constant in their luminosity (at least within a percent or two) ...
Sun, Moon, Earth,
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
worksheet
... The first strong candidate for a black hole was Cygnus X-1. It was discovered in 1964 by an x-ray detector carried on a rocket. It is one of the strongest x-ray sources seen from Earth. In 1975 Hawking bet Kip Thorne that it was not a black hole and conceded the bet in the 1990’s when he became 95% ...
... The first strong candidate for a black hole was Cygnus X-1. It was discovered in 1964 by an x-ray detector carried on a rocket. It is one of the strongest x-ray sources seen from Earth. In 1975 Hawking bet Kip Thorne that it was not a black hole and conceded the bet in the 1990’s when he became 95% ...
Tutorial: Motion
... another Come to a consensus answer you both agree on If you get stuck or are not sure of your answer ask another group If you get really stuck or don’t understand what the Lecture Tutorial is asking as one of us for help ...
... another Come to a consensus answer you both agree on If you get stuck or are not sure of your answer ask another group If you get really stuck or don’t understand what the Lecture Tutorial is asking as one of us for help ...
Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect—28 Oct Outline • Announcements
... Provisional model: Two stars are in orbit. Test against evidence. How can the two stars move so as to show the same wavelength, for example, as on Oct 1? (If possible, you want explanations that do not depend on special accidents.) A. The stars move in the same direction at the same speed o ...
... Provisional model: Two stars are in orbit. Test against evidence. How can the two stars move so as to show the same wavelength, for example, as on Oct 1? (If possible, you want explanations that do not depend on special accidents.) A. The stars move in the same direction at the same speed o ...
Powerpoint
... As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes ...
... As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes ...
1 Stars
... in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Cre ...
... in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Cre ...
Chapter 14. Stellar Structure and Evolution
... Inevitably a star will exhaust the H in its core, having converted it to He. The Sun is about half way through that process. In the core of the Sun, we believe the present composition is about 50% He. As the He is created, the core of the star must move to slightly higher temperatures and pressures ...
... Inevitably a star will exhaust the H in its core, having converted it to He. The Sun is about half way through that process. In the core of the Sun, we believe the present composition is about 50% He. As the He is created, the core of the star must move to slightly higher temperatures and pressures ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Herschel’s Findings • Stars thinned out very fast at right angles to Milky Way • In the plane of the Milky Way the thinning was slower and depended upon the direction in which he looked • Flaws: – Observations made only in visible spectrum – Did not take into account absorption by interstellar gas ...
... Herschel’s Findings • Stars thinned out very fast at right angles to Milky Way • In the plane of the Milky Way the thinning was slower and depended upon the direction in which he looked • Flaws: – Observations made only in visible spectrum – Did not take into account absorption by interstellar gas ...
Infinity Express
... Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. (By end of grade 2). The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from Earth. (By end of grade 5). Patterns of t ...
... Patterns of the motion of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky can be observed, described, and predicted. (By end of grade 2). The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from Earth. (By end of grade 5). Patterns of t ...
StarIntro_sb12
... The energy output from the surface of a star per second measured in watts. How bright a star is relative to the Sun The brightness of a star depends upon the distance and its luminosity. Think it over The star Rigel in Orion is about 60,000 times larger than our sun. Why does our sun appear brighter ...
... The energy output from the surface of a star per second measured in watts. How bright a star is relative to the Sun The brightness of a star depends upon the distance and its luminosity. Think it over The star Rigel in Orion is about 60,000 times larger than our sun. Why does our sun appear brighter ...
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache
... their keeping: they will be kings under kings and ministers of state, and be charged with guardianship of the people; or, as the stewards of grand houses, they will confine their business to the care of another's home.[1] ...
... their keeping: they will be kings under kings and ministers of state, and be charged with guardianship of the people; or, as the stewards of grand houses, they will confine their business to the care of another's home.[1] ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.























