Introduction to Astronomy
... If the star was at 10 parsecs distance from us, then its apparent magnitude would be equal to its absolute magnitude. The absolute magnitude is a measure of the star's luminosity---the total amount of energy radiated by the star every second. ...
... If the star was at 10 parsecs distance from us, then its apparent magnitude would be equal to its absolute magnitude. The absolute magnitude is a measure of the star's luminosity---the total amount of energy radiated by the star every second. ...
AS2001 - University of St Andrews
... More metals near centres of galaxies. Infall of IGM on outskirts + gas migrates to centre. More star generations --> lower at centre. ...
... More metals near centres of galaxies. Infall of IGM on outskirts + gas migrates to centre. More star generations --> lower at centre. ...
V - ESO
... reach the low-mass stellar population of Wd 1 and study in situ the effects of large numbers of massive stars on the IMF. Neutron stars can be descended from very massive stars. Confirmation that the 10.6 s pulsar is a magnetar could show light on the connection with progenitor mass. Radio and X-ray ...
... reach the low-mass stellar population of Wd 1 and study in situ the effects of large numbers of massive stars on the IMF. Neutron stars can be descended from very massive stars. Confirmation that the 10.6 s pulsar is a magnetar could show light on the connection with progenitor mass. Radio and X-ray ...
Section 7.3 - CPO Science
... object that is relatively nearby or a bright object that is far, far away. ...
... object that is relatively nearby or a bright object that is far, far away. ...
What We Know About Stars So Far
... graph using this system (comparing surface temperature and luminosity), you will find that the stars fall into groups. ...
... graph using this system (comparing surface temperature and luminosity), you will find that the stars fall into groups. ...
K-3 Planetarium Lesson: Our Skies
... are like our sun but are very far away. They are so far away that when we look at them from earth, they seem to be tiny. Ask what else they see. Point out the band of the Milky Way (lots of stars together!). Somebody might think of the moon. If it is visible, point it out. Mention how we sometimes d ...
... are like our sun but are very far away. They are so far away that when we look at them from earth, they seem to be tiny. Ask what else they see. Point out the band of the Milky Way (lots of stars together!). Somebody might think of the moon. If it is visible, point it out. Mention how we sometimes d ...
Stars, Constellations, and Quasars
... Great Bear), which includes the Big Dipper, and Ursa Minor (the Little Bear), which includes the Little Dipper. Polaris, which is also known as the North Star or the Pole Star, is an important star in the handle of Ursa Minor. Polaris takes its name from the fact that Earth’s rotational axis (north ...
... Great Bear), which includes the Big Dipper, and Ursa Minor (the Little Bear), which includes the Little Dipper. Polaris, which is also known as the North Star or the Pole Star, is an important star in the handle of Ursa Minor. Polaris takes its name from the fact that Earth’s rotational axis (north ...
The Lifecycle of the Stars
... *white dwarfs may only be the size of the earth, but it has the mass equal to half oh the sun. *it is the 6th stage in forming a star. Lifecycle of a star notes *also called a degenerate dwarf *it is a small star made up of electron-degenerate matter. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_dwarf ...
... *white dwarfs may only be the size of the earth, but it has the mass equal to half oh the sun. *it is the 6th stage in forming a star. Lifecycle of a star notes *also called a degenerate dwarf *it is a small star made up of electron-degenerate matter. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_dwarf ...
4-6 Script
... be used as maps. Constellations divide the sky up into familiar boundaries, just as the United States is divided into familiar boundaries called states. Every major star in the sky is part of a constellation. Constellations give reference to other objects in the sky. Even though most of us only know ...
... be used as maps. Constellations divide the sky up into familiar boundaries, just as the United States is divided into familiar boundaries called states. Every major star in the sky is part of a constellation. Constellations give reference to other objects in the sky. Even though most of us only know ...
Star Formation
... • Evidence: Mg 26 far above standard levels, within the body of meteorites. Mg 26 is the daughter product of Al 26, a radioactive element created in supernova explosions. • Indicates: A supernova went off nearby, seeding the solar system with Al 26 while the material which makes meteorites was still ...
... • Evidence: Mg 26 far above standard levels, within the body of meteorites. Mg 26 is the daughter product of Al 26, a radioactive element created in supernova explosions. • Indicates: A supernova went off nearby, seeding the solar system with Al 26 while the material which makes meteorites was still ...
PHY216_lect1_2014 - Astrophysics Research Institute
... set in the west. The hour angle tells you how long it will be before the star transits (or how much time has passed since it transited!) • Hour Angle - angle between a star's current position and the meridian (measured WESTWARD in hours, where 1 hour is equivalent to 15 degrees – because 24 hours = ...
... set in the west. The hour angle tells you how long it will be before the star transits (or how much time has passed since it transited!) • Hour Angle - angle between a star's current position and the meridian (measured WESTWARD in hours, where 1 hour is equivalent to 15 degrees – because 24 hours = ...
What is a Star - Optics Institute of Southern California
... The final ingredient in determining the structure of a main sequence star is the source of heat in the interior, nuclear reactions. There are many of these, and the details are complicated and there is still some uncertainty about the exact rates for the reactions (for example, the solar neutrino pr ...
... The final ingredient in determining the structure of a main sequence star is the source of heat in the interior, nuclear reactions. There are many of these, and the details are complicated and there is still some uncertainty about the exact rates for the reactions (for example, the solar neutrino pr ...
Problem Set 04
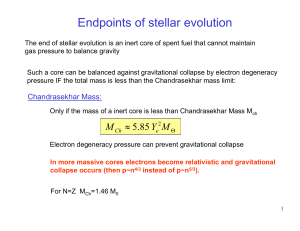
... collapse with electrons and protons combining to form neutrons leading to an extremely dense object known as a "neutron star" (for example, a neutron star with the mass of our sun has a radius of only ~12 km). Currently our sun has a radius 700,000 km and a rotation period of 30 days. If our sun und ...
... collapse with electrons and protons combining to form neutrons leading to an extremely dense object known as a "neutron star" (for example, a neutron star with the mass of our sun has a radius of only ~12 km). Currently our sun has a radius 700,000 km and a rotation period of 30 days. If our sun und ...
Star Life Cycle Web Activity
... element can be used as fuel to burn and equilibrium is reached once again. Eventually the fuel sources run out and the star dies or explodes. The main fuel sources are Hydgroen, then Helium, then Carbon, then cool off to death. ...
... element can be used as fuel to burn and equilibrium is reached once again. Eventually the fuel sources run out and the star dies or explodes. The main fuel sources are Hydgroen, then Helium, then Carbon, then cool off to death. ...
3.5-star-id
... stars, Deneb, Vega, and Altair in the constellations Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila. • Slicing through this triangle is the asterism, the Northern Cross, actually part of Cygnus the Swan. • Tonight you will find the summer triangle above the eastern sky and you’ll see it all through the summer as it rises ...
... stars, Deneb, Vega, and Altair in the constellations Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila. • Slicing through this triangle is the asterism, the Northern Cross, actually part of Cygnus the Swan. • Tonight you will find the summer triangle above the eastern sky and you’ll see it all through the summer as it rises ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Greek astronomer Hipparchus prepared a detailed star catalog ...
... Greek astronomer Hipparchus prepared a detailed star catalog ...
solutions - Las Cumbres Observatory
... its fuel and its mass goes down visibly on the graph. The 1 solar mass star appears to lose very little ...
... its fuel and its mass goes down visibly on the graph. The 1 solar mass star appears to lose very little ...
Star Life Cycle Web Activity
... Based on the diagram, how do all stars start? What is the main determining factors as to whether a star ends up as a black dwarf, neutron star or black hole? II. Go to http://sunshine.chpc.utah.edu/labs/star_life/starlife_main.html This page will give more details on each of these stages. Read the c ...
... Based on the diagram, how do all stars start? What is the main determining factors as to whether a star ends up as a black dwarf, neutron star or black hole? II. Go to http://sunshine.chpc.utah.edu/labs/star_life/starlife_main.html This page will give more details on each of these stages. Read the c ...
Planetary Nebula NGC 7027 Hubble Space Telescope
... shed by the star remains outside of the bright regions. It is invisible in t h i s image because the layers of material i n and near the bright regions are still shielding it from the central star's intense radiation. NGC 7027 i s on e of the smallestobjects of its kind to be imaged by the Hubble te ...
... shed by the star remains outside of the bright regions. It is invisible in t h i s image because the layers of material i n and near the bright regions are still shielding it from the central star's intense radiation. NGC 7027 i s on e of the smallestobjects of its kind to be imaged by the Hubble te ...
Solutions Assignment #3
... Antares is a red supergiant; its spectral type M means it is red, and its luminosity class I indicates a supergiant. i. Antares has the largest radius because it is the only supergiant on the list. j. Aldebaran, Antares, and Canopus have luminosity classes other than V, which means that they have le ...
... Antares is a red supergiant; its spectral type M means it is red, and its luminosity class I indicates a supergiant. i. Antares has the largest radius because it is the only supergiant on the list. j. Aldebaran, Antares, and Canopus have luminosity classes other than V, which means that they have le ...
Lecture 13. Black Holes - Politechnika Wrocławska
... Photons are created in the nuclear fusion cycle. They collide with other charged particles and change their direction (random walk). They also decrease their energy while walking. It takes ~10 million year to get outside. The random bouncing occurs in the radiation zone (from the core to ~70% of the ...
... Photons are created in the nuclear fusion cycle. They collide with other charged particles and change their direction (random walk). They also decrease their energy while walking. It takes ~10 million year to get outside. The random bouncing occurs in the radiation zone (from the core to ~70% of the ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.