Lecture 1
... Describe how Star A would appear to move among the distant stars as Earth orbits the Sun counterclockwise from January of one year, through July, to January of the following year. Consider two stars (C and D) that both exhibit parallax. If Star C appears to move back and forth by a greater amount th ...
... Describe how Star A would appear to move among the distant stars as Earth orbits the Sun counterclockwise from January of one year, through July, to January of the following year. Consider two stars (C and D) that both exhibit parallax. If Star C appears to move back and forth by a greater amount th ...
Astronomy Library wk 7.cwk (WP)
... temperatures (~15,000,000K) where the nuclei are moving fast enough to overcome the repulsion. ...
... temperatures (~15,000,000K) where the nuclei are moving fast enough to overcome the repulsion. ...
Energy Transport
... • Nuclei repel each other (Coulomb barrier) • High enough temperature means a small percentage will have a high enough energy to get close enough for strong interaction to occur (Maxwell distribution of velocities) • Sufficiently high pressure ensures that enough reactions occur to supply energy nee ...
... • Nuclei repel each other (Coulomb barrier) • High enough temperature means a small percentage will have a high enough energy to get close enough for strong interaction to occur (Maxwell distribution of velocities) • Sufficiently high pressure ensures that enough reactions occur to supply energy nee ...
Spectrum a Star….. - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... Mystery Star Properties 1. The star appears as a point of light through a telescope. 2. The absorption lines appear split and move over a 4 day period. 3. The brightness of the star also varies over 4 days. Question: Why do you think the brightness of the star is varying? Answer: This could be an e ...
... Mystery Star Properties 1. The star appears as a point of light through a telescope. 2. The absorption lines appear split and move over a 4 day period. 3. The brightness of the star also varies over 4 days. Question: Why do you think the brightness of the star is varying? Answer: This could be an e ...
Hungry Young Stars: A New Explanation for the FU Ori Outbursts
... currently declining in brightness with a decay timescale of 50-100 years. The surrounding material reveals that this is an infant star. It is believed that all young stars undergo multiple eruptions. ...
... currently declining in brightness with a decay timescale of 50-100 years. The surrounding material reveals that this is an infant star. It is believed that all young stars undergo multiple eruptions. ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Create life cycle of sun-like star based on your notes from yesterday. Use arrows to show movement from one step to the next. At each step write a short explanation of what is happening during that stage. Fill the entire poster with you cycle. You may want to sketch it out in your notebook before yo ...
... Create life cycle of sun-like star based on your notes from yesterday. Use arrows to show movement from one step to the next. At each step write a short explanation of what is happening during that stage. Fill the entire poster with you cycle. You may want to sketch it out in your notebook before yo ...
Galactic Structure
... Low mean stellar metallicity, typically less than a tenth solar, combined with invariant IMF, means gas removal from star formation, not by star formation Why are many (most?) stars a few Gyr old? Special epoch of inflow/interactions? Tie to formation of the Local Group (Silk, Wyse & Shields ...
... Low mean stellar metallicity, typically less than a tenth solar, combined with invariant IMF, means gas removal from star formation, not by star formation Why are many (most?) stars a few Gyr old? Special epoch of inflow/interactions? Tie to formation of the Local Group (Silk, Wyse & Shields ...
Neutron Star - Perry Local Schools
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
Dubhe
... On January 22,1996 the star dubhe was named the state centennial star because the light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s ...
... On January 22,1996 the star dubhe was named the state centennial star because the light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s ...
Return both exam and scantron sheet when you
... 26. Typical sizes of main sequence stars (in units of solar radius R⊙ ) are (a) from 0.01 R⊙ to 0.1 R⊙ . (b) from 100 R⊙ to 1000 R⊙ . (c) from 10 R⊙ to 100 R⊙ . (d) [None of the above.] 27. When a star’s light passes through its cooler atmosphere (a) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (b) ph ...
... 26. Typical sizes of main sequence stars (in units of solar radius R⊙ ) are (a) from 0.01 R⊙ to 0.1 R⊙ . (b) from 100 R⊙ to 1000 R⊙ . (c) from 10 R⊙ to 100 R⊙ . (d) [None of the above.] 27. When a star’s light passes through its cooler atmosphere (a) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (b) ph ...
Binocular Objects (MS Word)
... The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the Milky Way seems to emerge from the Teapot's spout like a puff of steam. M22 The Great Sagittarius star cluster is a very large globular -- the best of the constellation's many globulars. At magnitude 5.1 ...
... The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the Milky Way seems to emerge from the Teapot's spout like a puff of steam. M22 The Great Sagittarius star cluster is a very large globular -- the best of the constellation's many globulars. At magnitude 5.1 ...
The Universe
... When looking up at the sky during a cloudless night you can see little spots of light. These tiny specks of light can be planets, moons, comets, stars, but also complete star systems (galaxies). Our Solar system is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way. All the (individual) stars we can see on Earth ...
... When looking up at the sky during a cloudless night you can see little spots of light. These tiny specks of light can be planets, moons, comets, stars, but also complete star systems (galaxies). Our Solar system is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way. All the (individual) stars we can see on Earth ...
Powerpoint for today
... Millisecond pulsars: periods of 1 to a few msec. Probably accreted matter from a binary companion that made it spin faster. Gamma-ray Bursts: some pulsars produce bursts of gamma-rays, ...
... Millisecond pulsars: periods of 1 to a few msec. Probably accreted matter from a binary companion that made it spin faster. Gamma-ray Bursts: some pulsars produce bursts of gamma-rays, ...
Station A Star Charts I
... D7. (2 pts) One of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way is Cygnus OB2#12. Based on its size and distance from the Earth astronomers expect that its apparent magnitude should be 1.5. However, interstellar dust causes its apparent magnitude to be 11.4. How many times brighter (or fainter) does the ...
... D7. (2 pts) One of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way is Cygnus OB2#12. Based on its size and distance from the Earth astronomers expect that its apparent magnitude should be 1.5. However, interstellar dust causes its apparent magnitude to be 11.4. How many times brighter (or fainter) does the ...
Star Groups and Big Bang Power Point
... The Expanding Universe Using Hubble’s observations, astronomers have been able to determine that the universe is expanding. The expanding universe can be thought of as a raisin cake rising in the oven. If you were able to sit on one raisin, you would see all the other raisins moving away from y ...
... The Expanding Universe Using Hubble’s observations, astronomers have been able to determine that the universe is expanding. The expanding universe can be thought of as a raisin cake rising in the oven. If you were able to sit on one raisin, you would see all the other raisins moving away from y ...
White Dwarf Stars
... • These objects act as cosmic clocks and are useful for probing the dynamics of stars. ...
... • These objects act as cosmic clocks and are useful for probing the dynamics of stars. ...
Assignment Worksheet
... 1. Your full name, last name first, first name last, and remember to bubble in the letters. 2. Bubble in the 5-digit homework code, 11111, on the form under "Identification Number" in columns A-E (lower left-hand corner of the form). Do not enter your Student ID or any other info into this area, jus ...
... 1. Your full name, last name first, first name last, and remember to bubble in the letters. 2. Bubble in the 5-digit homework code, 11111, on the form under "Identification Number" in columns A-E (lower left-hand corner of the form). Do not enter your Student ID or any other info into this area, jus ...
Masers and high mass star formation Claire Chandler
... the simultaneous presence of disks and jets. • Is this the case in young massive stars? • To study this question, we have to center in the hot molecular core stage. ...
... the simultaneous presence of disks and jets. • Is this the case in young massive stars? • To study this question, we have to center in the hot molecular core stage. ...
THE LIFE CYCLES OF STARS (3)
... The ancient Babylonians 1800 BC put together the first star catalogues. The Greek Hipparchus (180-125 BC) and later Claudius Ptolemy in Alexandria about 150 AD classified stars according to their apparent brightness to the eye, dividing them six into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were c ...
... The ancient Babylonians 1800 BC put together the first star catalogues. The Greek Hipparchus (180-125 BC) and later Claudius Ptolemy in Alexandria about 150 AD classified stars according to their apparent brightness to the eye, dividing them six into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were c ...
Instructor Notes
... Additional heat from contraction raises temperature of a shell of hydrogen outside core to high enough for hydrogen fusion – “shell burning” Fusion of 4 hydrogen to form helium in a shell provides enough heat to support outer layers of star, but doesn’t do anything for core ...
... Additional heat from contraction raises temperature of a shell of hydrogen outside core to high enough for hydrogen fusion – “shell burning” Fusion of 4 hydrogen to form helium in a shell provides enough heat to support outer layers of star, but doesn’t do anything for core ...
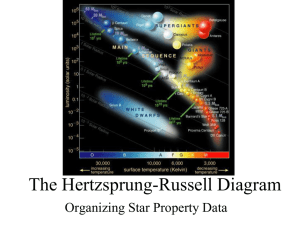
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.