Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... Figure 4. (a) If the angular velocity Ω was constant, then a given region of the galaxy would retain the same shape and only change in orientation. In this case, there would be no change in the distance between the Sun and any star. Hence there would be no Doppler shift. However, there would be prop ...
... Figure 4. (a) If the angular velocity Ω was constant, then a given region of the galaxy would retain the same shape and only change in orientation. In this case, there would be no change in the distance between the Sun and any star. Hence there would be no Doppler shift. However, there would be prop ...
No Slide Title
... Solar Eclipse. A solar eclipse can occur when there is a new moon. This does not occur every month because the moon's orbital plane doesn't "lie flat" along the ecliptic, but forms an angle of about 5º as you can see in this diagram (note: the distances in this diagram are not to scale). http://www. ...
... Solar Eclipse. A solar eclipse can occur when there is a new moon. This does not occur every month because the moon's orbital plane doesn't "lie flat" along the ecliptic, but forms an angle of about 5º as you can see in this diagram (note: the distances in this diagram are not to scale). http://www. ...
How the Hubble Telescope Will Look at the Moon to See Venus
... · For deep-sky observers, a favorite springtime telescopic star-hop runs from the end of the Big Dipper's handle to the Whirlpool Galaxy, M51, and on to the Sunflower Galaxy, M63. Did you know there's a red semiregular variable star to check out along the way? See the May Sky & Telescope, page 53. F ...
... · For deep-sky observers, a favorite springtime telescopic star-hop runs from the end of the Big Dipper's handle to the Whirlpool Galaxy, M51, and on to the Sunflower Galaxy, M63. Did you know there's a red semiregular variable star to check out along the way? See the May Sky & Telescope, page 53. F ...
Eclipsing Binary Stars as Astrophysical Laboratories
... nuclear fusion to take place in the core, and the star is born. There are distinct evolutionary tracks on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram for low-mass stars and for high-mass stars. Low-mass stars eventually swell into red giant stars, and then they shed their outer layers as a planetary nebula and ...
... nuclear fusion to take place in the core, and the star is born. There are distinct evolutionary tracks on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram for low-mass stars and for high-mass stars. Low-mass stars eventually swell into red giant stars, and then they shed their outer layers as a planetary nebula and ...
chapter 24 instructor notes
... Sun’s motion relative to the LSR. That is not an easy chore because of the nature of stellar orbits in the Galaxy, which are neither circular nor elliptical, but more like a roseate pattern. The general direction of the Sun’s motion relative to nearby stars is readily detected in stellar proper moti ...
... Sun’s motion relative to the LSR. That is not an easy chore because of the nature of stellar orbits in the Galaxy, which are neither circular nor elliptical, but more like a roseate pattern. The general direction of the Sun’s motion relative to nearby stars is readily detected in stellar proper moti ...
night watch - Warren Astronomical Society
... maximum of .09 for the other planets. Its orbit has the greatest inclination with respect to the ecliptic plane. Pluto’s orbit is inclined by 17 degrees while Mercury’s is inclined by only 7 degrees and the other planets are all inclined by 4 degrees or less. In a drawing of planetary orbits Pluto s ...
... maximum of .09 for the other planets. Its orbit has the greatest inclination with respect to the ecliptic plane. Pluto’s orbit is inclined by 17 degrees while Mercury’s is inclined by only 7 degrees and the other planets are all inclined by 4 degrees or less. In a drawing of planetary orbits Pluto s ...
Astronomy Curriculum
... A. The Origin of the Solar System (Chapter 7) 1. Explore the theories of cosmogony (catastrophe, tidal, and nebular). 2. Explain the evolution of a solar system according to the nebular theory. 3. Analyze the rotation and revolution of the planets (Chapter 7.4). B. The Earth (Chapter 8) 1. Summarize ...
... A. The Origin of the Solar System (Chapter 7) 1. Explore the theories of cosmogony (catastrophe, tidal, and nebular). 2. Explain the evolution of a solar system according to the nebular theory. 3. Analyze the rotation and revolution of the planets (Chapter 7.4). B. The Earth (Chapter 8) 1. Summarize ...
Unit 1
... A black hole can be both very small, and have an accretion disk that can emit enough radiation Likely that at the centers of these galactic nuclei, there are ...
... A black hole can be both very small, and have an accretion disk that can emit enough radiation Likely that at the centers of these galactic nuclei, there are ...
argo and other tidal structures around the milky way
... Several features in these maps can be identified with known satellite galaxies, while others are new findings as the TriAnd + Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004) and Argo. It is apparent that there is a continuity between the Argo and CMa overdensities. We have verified that when these overden ...
... Several features in these maps can be identified with known satellite galaxies, while others are new findings as the TriAnd + Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004) and Argo. It is apparent that there is a continuity between the Argo and CMa overdensities. We have verified that when these overden ...
Lecture 13 - Star Formation
... A star has 4 times the mass and 128 times the luminosity of the Sun. The star's lifetime will be ____ times that of Sun. A) 32 B) 4 C) 1 D) ¼ E) 1/32 ...
... A star has 4 times the mass and 128 times the luminosity of the Sun. The star's lifetime will be ____ times that of Sun. A) 32 B) 4 C) 1 D) ¼ E) 1/32 ...
Document
... “He was one of the finest people I have ever known…but he didn’t really understand physics because, during the eclipse of 1919 he stayed up all night to see if it would confirm the bending of light by the gravitational field. If he had really understood general relativity he would have gone to bed t ...
... “He was one of the finest people I have ever known…but he didn’t really understand physics because, during the eclipse of 1919 he stayed up all night to see if it would confirm the bending of light by the gravitational field. If he had really understood general relativity he would have gone to bed t ...
Astronomy
... ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
Imaging extrasolar planets
... down into their atmospheres and infer their chemical compoThese theoretical models become increasingly uncertain at sition, temperatures, pressures, and cloud properties by very young ages because the exact initial conditions of how studying their brightness at different wavelengths. This spring the ...
... down into their atmospheres and infer their chemical compoThese theoretical models become increasingly uncertain at sition, temperatures, pressures, and cloud properties by very young ages because the exact initial conditions of how studying their brightness at different wavelengths. This spring the ...
Stellar Evolution Task
... Red giants are sooo large that we can actually 'see' their size. Sadly we have to use very special techniques and can't just look through a very large telescope. Many bright red stars we see in the sky are red giants. ...
... Red giants are sooo large that we can actually 'see' their size. Sadly we have to use very special techniques and can't just look through a very large telescope. Many bright red stars we see in the sky are red giants. ...
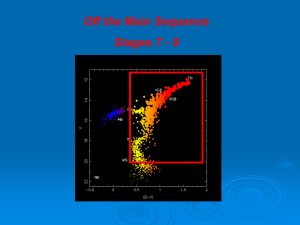
Common Stages 7 to 9
... While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
... While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
Galaxies Powerpoint
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.