Star Formation - University of Redlands
... • Stars and other interstellar material are in a perpetual battle between forces pulling in (gravity) and forces pushing out (pressure). • Gravity comes from the mass of the cloud or star. • Pressure comes from the motion of the atoms or molecules. – Think of hot air balloons. – The hotter the air, ...
... • Stars and other interstellar material are in a perpetual battle between forces pulling in (gravity) and forces pushing out (pressure). • Gravity comes from the mass of the cloud or star. • Pressure comes from the motion of the atoms or molecules. – Think of hot air balloons. – The hotter the air, ...
Lecture 4
... subtypes WC, WN or WO (for Carbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen) (Possible GRB/Hypernovae progenitors) Carbon stars, C (originally R and N classification), red-giants/supergiants near end of lives with excess, Carbon in atmosphere WDs, D – stars are no longer undergoing thermonuclear reactions, simply coolin ...
... subtypes WC, WN or WO (for Carbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen) (Possible GRB/Hypernovae progenitors) Carbon stars, C (originally R and N classification), red-giants/supergiants near end of lives with excess, Carbon in atmosphere WDs, D – stars are no longer undergoing thermonuclear reactions, simply coolin ...
ISP205L, Week 13 Computer Lab Activity The Distance to the Pleiades
... should cycle back to step (g) and then guide the star farther away from the entrance aperture this time. (k) Click the Start Count button. The photometer will automatically cycle through a series of readings, the number of which is set by the Integrations button, with each reading being for the amou ...
... should cycle back to step (g) and then guide the star farther away from the entrance aperture this time. (k) Click the Start Count button. The photometer will automatically cycle through a series of readings, the number of which is set by the Integrations button, with each reading being for the amou ...
Aries The Ram - Maverick`s E-portfolio
... with a visual magnitude of 2.64. Its name means “the two signs” and is referring to the vernal equinox with marked together with Gamma Arietis or Hamal, which would mark the beginning of spring[5]. Mesarthim, Gamma Arietis once was the most visible star in the vernal equinox. It is a triple star sys ...
... with a visual magnitude of 2.64. Its name means “the two signs” and is referring to the vernal equinox with marked together with Gamma Arietis or Hamal, which would mark the beginning of spring[5]. Mesarthim, Gamma Arietis once was the most visible star in the vernal equinox. It is a triple star sys ...
CARBON STARS
... solar neighborhood (within a few 100 parsecs) • Seem to be more common than giants in this region ...
... solar neighborhood (within a few 100 parsecs) • Seem to be more common than giants in this region ...
sky science study notes
... The ‘Big Dipper’ is part of Ursa Major. The stars that make the edge of the Big Dipper can be used as pointer stars. The line they make points towards Polaris (The North Star). Polaris happens to be part of the constellation Ursa Minor (The Little Bear). Constellations also seem to change position i ...
... The ‘Big Dipper’ is part of Ursa Major. The stars that make the edge of the Big Dipper can be used as pointer stars. The line they make points towards Polaris (The North Star). Polaris happens to be part of the constellation Ursa Minor (The Little Bear). Constellations also seem to change position i ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
... Observing the formation and evolution of circumstellar disks is crucial for understanding the star formation and planet-building processes. If a disk becomes sufficiently massive, compared to the central object that it surrounds, a gravitational instability in the system may cause the disk to accumu ...
... Observing the formation and evolution of circumstellar disks is crucial for understanding the star formation and planet-building processes. If a disk becomes sufficiently massive, compared to the central object that it surrounds, a gravitational instability in the system may cause the disk to accumu ...
Slide 1
... Other Constellations you should know Killed by a scorpion and placed in the sky. Source: Dr. Islam’s Constellation page http://www2.potsdam.edu/islamma/Phys335Constellations.htm ...
... Other Constellations you should know Killed by a scorpion and placed in the sky. Source: Dr. Islam’s Constellation page http://www2.potsdam.edu/islamma/Phys335Constellations.htm ...
Searching for stars in high-velocity clouds
... feature. We conclude that (i) the compact HVCs contain no stars; or (ii) they are at greater distances than M31; or (iii) they have much lower surface brightnesses than the dwarf companions of M31 found by Armandroff et al. (the density of stars is very low); or (iv) the stars are not coincident wit ...
... feature. We conclude that (i) the compact HVCs contain no stars; or (ii) they are at greater distances than M31; or (iii) they have much lower surface brightnesses than the dwarf companions of M31 found by Armandroff et al. (the density of stars is very low); or (iv) the stars are not coincident wit ...
Lecture 4: Telescopes
... Catalog included ~1000 stars Brightest stars given a 1, slightly fainter were given a 2, etc. Some problems ...
... Catalog included ~1000 stars Brightest stars given a 1, slightly fainter were given a 2, etc. Some problems ...
5th Grade - STEMscopes
... The apparent brightness of a star changes depending on which planet it is viewed from. In order to compare stars, astronomers use absolute brightness, how bright it appears at a standard distance. They also measure luminosity, the amount of light a star gives off from its surface. Apparent brightnes ...
... The apparent brightness of a star changes depending on which planet it is viewed from. In order to compare stars, astronomers use absolute brightness, how bright it appears at a standard distance. They also measure luminosity, the amount of light a star gives off from its surface. Apparent brightnes ...
The Celestial Sphere
... You will construct your own celestial sphere which should appear as shown in the diagram above. You will use this to predict the daily motion of the sky for the beginning of each season. Remember, the ECLIPTIC is the apparent path of the Sun on the celestial sphere for the entire year - as the Eart ...
... You will construct your own celestial sphere which should appear as shown in the diagram above. You will use this to predict the daily motion of the sky for the beginning of each season. Remember, the ECLIPTIC is the apparent path of the Sun on the celestial sphere for the entire year - as the Eart ...
Observers` Forum - British Astronomical Association
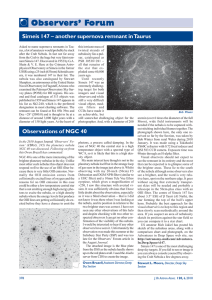
... Naval Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona who examined the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey plates (POSS) for HII regions. His second and final catalogue of 313 objects was published in 1959 and Simeis 147 appears in his list as Sh2-240, which is the preferred designation in most charting software. The ...
... Naval Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona who examined the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey plates (POSS) for HII regions. His second and final catalogue of 313 objects was published in 1959 and Simeis 147 appears in his list as Sh2-240, which is the preferred designation in most charting software. The ...
Ch12&13 Life and Death of Stars
... You’ll have two shells burning around the core -- a H shell and a He shell, but no more fusion in the core. Again, the shells do nothing for the core, but they poof out the star even larger than before. It is at this point that probably our Sun will engulf Earth! ...
... You’ll have two shells burning around the core -- a H shell and a He shell, but no more fusion in the core. Again, the shells do nothing for the core, but they poof out the star even larger than before. It is at this point that probably our Sun will engulf Earth! ...
Section 11: GRAPHIC STIMULUS
... In most large cities [6] like Singapore, we can only see a few of the large bright stars out in space. This is due to the increased pollution of earth [7] s atmosphere especially in the cities. The polluted skies obscure most of the other smaller stars [8] However [9] the stars are fascinating to so ...
... In most large cities [6] like Singapore, we can only see a few of the large bright stars out in space. This is due to the increased pollution of earth [7] s atmosphere especially in the cities. The polluted skies obscure most of the other smaller stars [8] However [9] the stars are fascinating to so ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth
... • As contraction packs the molecules and dust particles of a cloud fragment closer together, it becomes harder for infrared and radio photons to escape • Thermal energy then begins to build up inside, increasing the internal pressure • Contraction slows down, and the center of the cloud fragment bec ...
... • As contraction packs the molecules and dust particles of a cloud fragment closer together, it becomes harder for infrared and radio photons to escape • Thermal energy then begins to build up inside, increasing the internal pressure • Contraction slows down, and the center of the cloud fragment bec ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth Where do stars form? Star
... • Contraction must continue until the core becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion • Contraction stops when the energy released by core fusion balances energy radiated from the surface—the star is now a main-sequence star ...
... • Contraction must continue until the core becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion • Contraction stops when the energy released by core fusion balances energy radiated from the surface—the star is now a main-sequence star ...
star - Cloudfront.net
... 2b. Students know galaxies are made of billions of stars and comprise most of the visible mass of the universe. 2c. Students know the evidence indicating that all elements with an atomic number greater than that of lithium have been formed by nuclear fusion in stars. 2d. Students know that stars dif ...
... 2b. Students know galaxies are made of billions of stars and comprise most of the visible mass of the universe. 2c. Students know the evidence indicating that all elements with an atomic number greater than that of lithium have been formed by nuclear fusion in stars. 2d. Students know that stars dif ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.