The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The second law of thermodynamics gives information concerning the direction of spontaneous change. If the second law says that a certain process is impossible, you will not be able to get the process to go. On the other hand, note that if the second law says that a process is possible, you still hav ...
... The second law of thermodynamics gives information concerning the direction of spontaneous change. If the second law says that a certain process is impossible, you will not be able to get the process to go. On the other hand, note that if the second law says that a process is possible, you still hav ...
8 second law of thermodynamics : states spontaneous process is
... 8 second law of thermodynamics : states spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in the total entropy of the systems and its surroundings . To take another example of disordering , the melting and boiling of zinc , at its melting temperature the closed backed hexagonal crystal struct ...
... 8 second law of thermodynamics : states spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in the total entropy of the systems and its surroundings . To take another example of disordering , the melting and boiling of zinc , at its melting temperature the closed backed hexagonal crystal struct ...
15.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics
... Refrigerators, air conditioners, and heat pumps are devices that make heat flow from cold to hot. This is called the refrigeration process. ...
... Refrigerators, air conditioners, and heat pumps are devices that make heat flow from cold to hot. This is called the refrigeration process. ...
Introduction into thermodynamics Thermodynamic variables
... Chemical thermodynamics deals with reactions between substances and species. Mechanical thermodynamics, on the other hand, works with engines and their performance. In this class, we will explore chemical thermodynamics. We will ask and nd the answer to questions such as why does ice melt at room t ...
... Chemical thermodynamics deals with reactions between substances and species. Mechanical thermodynamics, on the other hand, works with engines and their performance. In this class, we will explore chemical thermodynamics. We will ask and nd the answer to questions such as why does ice melt at room t ...
BCJ0205-15 Thermal phenomena (3-1-4)
... Important thermodynamic quantities from the atomic/molecular view-point. ...
... Important thermodynamic quantities from the atomic/molecular view-point. ...
thermochemistry - Pace University Webspace
... • Gibbs Free Energy is a measure of nonpV work that must go into a reaction to make it occur (when G is positive) or work that a reaction can do (when negative). It can be shown that the change of Gibbs Free Energy over temperature in a reaction is the change of the total entropy of the reacting sys ...
... • Gibbs Free Energy is a measure of nonpV work that must go into a reaction to make it occur (when G is positive) or work that a reaction can do (when negative). It can be shown that the change of Gibbs Free Energy over temperature in a reaction is the change of the total entropy of the reacting sys ...
Study Guide Answers
... 1. A change of state is a _c__ a. Process by which two states of matter co-exist b. Chemical change c. Physical change that converts a substance from one physical form to another 2. Particles in a ___solid_______ move slower than particles in a ____liquid or gas______. 3. Particles in a _a__ vibrate ...
... 1. A change of state is a _c__ a. Process by which two states of matter co-exist b. Chemical change c. Physical change that converts a substance from one physical form to another 2. Particles in a ___solid_______ move slower than particles in a ____liquid or gas______. 3. Particles in a _a__ vibrate ...
Heat

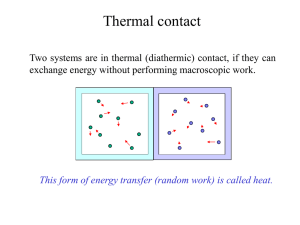
In physics, heat is energy in a process of transfer between a system and its surroundings, other than as work or with the transfer of matter. When there is a suitable physical pathway, heat flows from a hotter body to a colder one. The pathway can be direct, as in conduction and radiation, or indirect, as in convective circulation.Because it refers to a process of transfer between two systems, the system of interest, and its surroundings considered as a system, heat is not a state or property of a single system. If heat transfer is slow and continuous, so that the temperature of the system of interest remains well defined, it can sometimes be described by a process function.Kinetic theory explains heat as a macroscopic manifestation of the motions and interactions of microscopic constituents such as molecules and photons.In calorimetry, sensible heat is defined with respect to a specific chosen state variable of the system, such as pressure or volume. Sensible heat transferred into or out of the system under study causes change of temperature while leaving the chosen state variable unchanged. Heat transfer that occurs with the system at constant temperature and that does change that particular state variable is called latent heat with respect to that variable. For infinitesimal changes, the total incremental heat transfer is then the sum of the latent and sensible heat increments. This is a basic paradigm for thermodynamics, and was important in the historical development of the subject.The quantity of energy transferred as heat is a scalar expressed in an energy unit such as the joule (J) (SI), with a sign that is customarily positive when a transfer adds to the energy of a system. It can be measured by calorimetry, or determined by calculations based on other quantities, relying on the first law of thermodynamics.