Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... Temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. - Motor Cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front ...
... Temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. - Motor Cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Mirror Neurons*: a neuron that responds when an individual observes another performing a motor action or experiencing a sensation, has implications for social imitation and empathy; only observed in nonhuman primates. Glia cell: “support cells” or scaffolding for neurons ...
... Mirror Neurons*: a neuron that responds when an individual observes another performing a motor action or experiencing a sensation, has implications for social imitation and empathy; only observed in nonhuman primates. Glia cell: “support cells” or scaffolding for neurons ...
Cognitive Architecture www.AssignmentPoint.com A cognitive
... computing, on the other hand, takes sometimes a more bottom-up, decentralised approach; bio-inspired techniques often involve the method of specifying a set of simple generic rules or a set of simple nodes, from the interaction of which emerges the overall behavior. It is hoped to build up complexit ...
... computing, on the other hand, takes sometimes a more bottom-up, decentralised approach; bio-inspired techniques often involve the method of specifying a set of simple generic rules or a set of simple nodes, from the interaction of which emerges the overall behavior. It is hoped to build up complexit ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... _____ – carries message away from cell body (can go to many other cells from 1 cell) Impulse – message carried by a neuron Receptors – in all sense organs Respond to _____ Sensory – _____ Interneurons – _____ Motor neurons – _____ Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – ___ ...
... _____ – carries message away from cell body (can go to many other cells from 1 cell) Impulse – message carried by a neuron Receptors – in all sense organs Respond to _____ Sensory – _____ Interneurons – _____ Motor neurons – _____ Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – ___ ...
Nerve Notes
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
different types of dementia
... small strokes. These “mini-strokes” often go unnoticed but cause damage to the cortex—the area associated with learning, memory and language. Mini-strokes are sometimes referred to as TIAs (transient ischemic attacks). TIAs cause temporary, partial blockages of blood supply and brief impairments in ...
... small strokes. These “mini-strokes” often go unnoticed but cause damage to the cortex—the area associated with learning, memory and language. Mini-strokes are sometimes referred to as TIAs (transient ischemic attacks). TIAs cause temporary, partial blockages of blood supply and brief impairments in ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... of Function The mechanisms and processes noted above provide only the starting place for the formulation of an understanding of how cognitive processes arise from neural activity. There are two contrasting views: (1) The modular approach, championed by David Marr for vision and Noam Chomsky for lang ...
... of Function The mechanisms and processes noted above provide only the starting place for the formulation of an understanding of how cognitive processes arise from neural activity. There are two contrasting views: (1) The modular approach, championed by David Marr for vision and Noam Chomsky for lang ...
glossary - HBO.com
... a hospice center, in a hospital or in a skilled nursing facility. Medicare provides a hospice benefit. ...
... a hospice center, in a hospital or in a skilled nursing facility. Medicare provides a hospice benefit. ...
Unit 03B
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
The Nervous System
... the nervous system that does not include the vertebrae, brain, and retina. The peripheral nervous system is essentially the “wiring” of the body. ...
... the nervous system that does not include the vertebrae, brain, and retina. The peripheral nervous system is essentially the “wiring” of the body. ...
The Biological Perspective - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... – Split into two hemispheres (left and right) which control opposite sides of the body – Hemispheres broken into lobes by 2 major fissures • Central-Splits brain in half roughly, front and back • Lateral-Runs along the side of each hemisphere ...
... – Split into two hemispheres (left and right) which control opposite sides of the body – Hemispheres broken into lobes by 2 major fissures • Central-Splits brain in half roughly, front and back • Lateral-Runs along the side of each hemisphere ...
Slides
... its neighbourhood. At birth a typical neuron in the cortex makes about 2500 synaptic connections, and by the age of two or three this has grown to 5000 on average. Thereafter, the pattern of neuronal connectivity established at this early stage of life is modified in response to experience as we age ...
... its neighbourhood. At birth a typical neuron in the cortex makes about 2500 synaptic connections, and by the age of two or three this has grown to 5000 on average. Thereafter, the pattern of neuronal connectivity established at this early stage of life is modified in response to experience as we age ...
The Nervous System
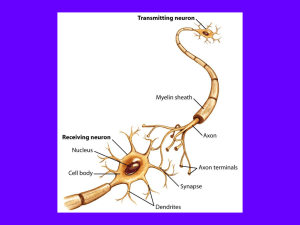
... The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. ...
... The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. ...
Nervous System & Senses
... Messages jump across Drugs and the synapse alcohol disrupts like the an electrical communication current between neurons ...
... Messages jump across Drugs and the synapse alcohol disrupts like the an electrical communication current between neurons ...
Brain Development
... including growth of spines on the branches • Increases capacity of dendrites to form connections with other neurons ...
... including growth of spines on the branches • Increases capacity of dendrites to form connections with other neurons ...
Slide 1
... • Our frontal lobe controls moral reasoning and social behavior. • The autopsy of Phineas Gage confirmed that his front lobe was destroyed which caused the changes to his personality. ...
... • Our frontal lobe controls moral reasoning and social behavior. • The autopsy of Phineas Gage confirmed that his front lobe was destroyed which caused the changes to his personality. ...
The left hemisphere
... These two types are never used, this is used on animals and not much in use today. However, humans can be used if they suffered from an injury. •Simulation method-electric and chemical simulation which allows researchers see what stimulation to different parts of the brain causes. This is in extensi ...
... These two types are never used, this is used on animals and not much in use today. However, humans can be used if they suffered from an injury. •Simulation method-electric and chemical simulation which allows researchers see what stimulation to different parts of the brain causes. This is in extensi ...
Inside the BRAIN: Neurons and Neural Networks
... If two neurons respond together the synapse between them will increase in efficacy. ...
... If two neurons respond together the synapse between them will increase in efficacy. ...
the nervous system
... sense organs to the spinal cord and brain Motor neurons – carry messages from the brain to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... sense organs to the spinal cord and brain Motor neurons – carry messages from the brain to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons ...
Syllabus - University of Pennsylvania
... efficiencies of the market virtually guarantee accurate asset pricing, marketing research and focus groups can test the efficacy of advertising, effective leadership can stimulate innovation and productivity, and sophisticated analytics can leverage big data to improve organizational structure to ma ...
... efficiencies of the market virtually guarantee accurate asset pricing, marketing research and focus groups can test the efficacy of advertising, effective leadership can stimulate innovation and productivity, and sophisticated analytics can leverage big data to improve organizational structure to ma ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... The Limbic System • Amygdala –two almondshaped neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion and fear ...
... The Limbic System • Amygdala –two almondshaped neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion and fear ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... Magneto encephalography – is a noninvasive neurophysiological technique that is similar to the EEG but more accurate and measures deeply into the brain where speech and language centers are located. The “MEG” measures the magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity of the brain. John is pictured ...
... Magneto encephalography – is a noninvasive neurophysiological technique that is similar to the EEG but more accurate and measures deeply into the brain where speech and language centers are located. The “MEG” measures the magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity of the brain. John is pictured ...
heledius - Society for the Advancement of Sexual Health
... coping into long term storage and therefore creates long term change. ...
... coping into long term storage and therefore creates long term change. ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.