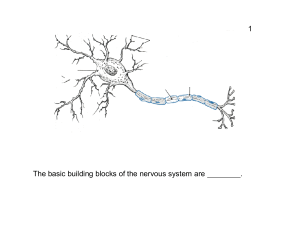
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Programmatic Implications
... Specific = only specific to one gender (Menstruation) Sensitive = present in both genders, but more prevalent or functions differently Biological functions (testosterone) Psychological traits (depression, CD) Need to understand normal physical and psychosocial development of each gender Need to ...
... Specific = only specific to one gender (Menstruation) Sensitive = present in both genders, but more prevalent or functions differently Biological functions (testosterone) Psychological traits (depression, CD) Need to understand normal physical and psychosocial development of each gender Need to ...
test prep
... profane. It is likely that his personality change was the result of injury to his: A) parietal lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) occipital lobe. D) frontal lobe. 2. Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands are called: A) agonists. B) neurotransmitters. C) hormones. D) enzymes. 3. Which is the corre ...
... profane. It is likely that his personality change was the result of injury to his: A) parietal lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) occipital lobe. D) frontal lobe. 2. Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands are called: A) agonists. B) neurotransmitters. C) hormones. D) enzymes. 3. Which is the corre ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS-Central Nervous System PNS
... 1. Pesticides can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate pesticides as the cause for his hospitalization). 2. Food-poisoning can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate Botulism as ...
... 1. Pesticides can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate pesticides as the cause for his hospitalization). 2. Food-poisoning can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate Botulism as ...
Nervous System
... Cerebrum – largest region; right and left hemispheres that are connected by corpus callosum; voluntary activities and higher brain functions Cerebellum – located at the lower back part of brain; coordination and balance ...
... Cerebrum – largest region; right and left hemispheres that are connected by corpus callosum; voluntary activities and higher brain functions Cerebellum – located at the lower back part of brain; coordination and balance ...
Basics of Neuroscience
... Evolving Brain Impact • Modern cortex of brain has great influence over rest of brain • It’s been shaped by evolutionary pressures to develop ever improving abilities to parent, bond, communicate, cooperate love (Dimbar & Shultz, 2007). • Cortex is divided into two “hemispheres” connected by corp ...
... Evolving Brain Impact • Modern cortex of brain has great influence over rest of brain • It’s been shaped by evolutionary pressures to develop ever improving abilities to parent, bond, communicate, cooperate love (Dimbar & Shultz, 2007). • Cortex is divided into two “hemispheres” connected by corp ...
Neurons in the Brain
... • even newborns can imitate • by 2-3 mos. seems to disappear, but researchers argue the infant is instead more interested in other motor skills & social games--the capacity is still present ...
... • even newborns can imitate • by 2-3 mos. seems to disappear, but researchers argue the infant is instead more interested in other motor skills & social games--the capacity is still present ...
Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fMRI image acquisition
... Figure 1. Image shows language processing areas of the brain, including Broca area (blue), located in Brodmann areas (BAs) 44 and 45; and Wernicke area (yellow), located in BAs 22, 37, 39, and 40. a.g. = angular gyrus, m.t.g. = middle temporal gyrus, p.o. ... ...
... Figure 1. Image shows language processing areas of the brain, including Broca area (blue), located in Brodmann areas (BAs) 44 and 45; and Wernicke area (yellow), located in BAs 22, 37, 39, and 40. a.g. = angular gyrus, m.t.g. = middle temporal gyrus, p.o. ... ...
Intro-ANN - Computer Science
... Neural Networks Computational model inspired by the brain Brain ...
... Neural Networks Computational model inspired by the brain Brain ...
what is the brain?? - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Difference It is easier to fix a computer - just get new parts. There are no new or used parts for the brain. However, some work is being done with transplantation of nerve cells for certain neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease. Both a computer and a brain can get "sick" - a computer ...
... Difference It is easier to fix a computer - just get new parts. There are no new or used parts for the brain. However, some work is being done with transplantation of nerve cells for certain neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease. Both a computer and a brain can get "sick" - a computer ...
Chapter 14 Brain Cranial Nerves
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
Biological Impact
... – Information from the optic nerve is sent to the visual cortex located in the occipital lobe – Information from the sensory organs in our ears are sent to the auditory cortex located in the temporal lobes ...
... – Information from the optic nerve is sent to the visual cortex located in the occipital lobe – Information from the sensory organs in our ears are sent to the auditory cortex located in the temporal lobes ...
Word doc version
... central cause for fatigue) as well as of cognitive function. These studies, which link the seemingly bizarre and unconnected symptoms reported by sufferers, should not only revolutionise preconceptions about patients previously considered to be hypochondriacal but encourage them to keep a careful re ...
... central cause for fatigue) as well as of cognitive function. These studies, which link the seemingly bizarre and unconnected symptoms reported by sufferers, should not only revolutionise preconceptions about patients previously considered to be hypochondriacal but encourage them to keep a careful re ...
Baby`s Brain Begins Now: Conception to Age 3
... a chemical signal from another neuron, Neuron A becomes electrically charged in relation to the surrounding fluid outside its membrane. This charge travels down its axon, away from the cell body, until it reaches the axon’s end. Waiting here inside the axon terminals are a group of storage sites, ca ...
... a chemical signal from another neuron, Neuron A becomes electrically charged in relation to the surrounding fluid outside its membrane. This charge travels down its axon, away from the cell body, until it reaches the axon’s end. Waiting here inside the axon terminals are a group of storage sites, ca ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... At the junction of the temporal, parietal and occipital lobes is the area that allows us to RECOGNIZE and INTERPRET written and spoken words ...
... At the junction of the temporal, parietal and occipital lobes is the area that allows us to RECOGNIZE and INTERPRET written and spoken words ...
Ch 10MT and Ch 8-9 BS Nervous System
... drowsiness, and apathy Coma Delirium: associated with high fever, sudden onset where patient is confused, disoriented, and unable to think clearly Dementia: slow, progressive decline in mental abilities including memory, thinking, judgment, and the ability to pay attention ...
... drowsiness, and apathy Coma Delirium: associated with high fever, sudden onset where patient is confused, disoriented, and unable to think clearly Dementia: slow, progressive decline in mental abilities including memory, thinking, judgment, and the ability to pay attention ...
Blue Brain PPT
... • It acts as a supercomputer. • Improvements in processing, speed and memory could make entire human brain simulated. • Things could be remembered without any effort. • Use the intelligence of the person after death. • It can make decisions entirely of its own. • Allowing the deaf to hear via direc ...
... • It acts as a supercomputer. • Improvements in processing, speed and memory could make entire human brain simulated. • Things could be remembered without any effort. • Use the intelligence of the person after death. • It can make decisions entirely of its own. • Allowing the deaf to hear via direc ...
Functional neuroanatomy of pain
... levels of the neuraxis: the medullary dorsal horn, thalamus, and primary somatosensory cortex. In nine subjects, noxious thermal stimuli (46°C) were applied to the facial skin at sites within the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (V1, V2, and V3) and also to the ipsilateral thumb. Anatomical a ...
... levels of the neuraxis: the medullary dorsal horn, thalamus, and primary somatosensory cortex. In nine subjects, noxious thermal stimuli (46°C) were applied to the facial skin at sites within the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (V1, V2, and V3) and also to the ipsilateral thumb. Anatomical a ...
Brain Lecture - Scott County Schools
... • a. PET scans show that the brain areas that light up when people silently say the name of a animal differs from when they say the name of a tool • b. MRI scans of bilingual people’s brain reveal that second languages are represented in the same area as the first if learned early and in different a ...
... • a. PET scans show that the brain areas that light up when people silently say the name of a animal differs from when they say the name of a tool • b. MRI scans of bilingual people’s brain reveal that second languages are represented in the same area as the first if learned early and in different a ...
Control and Coordination
... Imagine yourself to be Galan, the Greek physiologist (A.D.129 - 200). One day a patient came to you and told that he had fallen from his chariot and had a blow in the neck. He complained of loss of feeling in the arm while still retaining normal muscular control of its moment. What questions would a ...
... Imagine yourself to be Galan, the Greek physiologist (A.D.129 - 200). One day a patient came to you and told that he had fallen from his chariot and had a blow in the neck. He complained of loss of feeling in the arm while still retaining normal muscular control of its moment. What questions would a ...
Chapter 17 Review Jeopardy
... – A) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – B) the inside of the axon is negative compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – C) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is NOT ...
... – A) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – B) the inside of the axon is negative compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – C) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is NOT ...
Neuroscience - HuskiesScience
... • In Vitro analysis: “In the Lab” – brain tissue is removed, isolated, and studied on its own. Individual neurons can be studied • In Vivo analysis: “In the Living” – the brain is studied in an intact animal ...
... • In Vitro analysis: “In the Lab” – brain tissue is removed, isolated, and studied on its own. Individual neurons can be studied • In Vivo analysis: “In the Living” – the brain is studied in an intact animal ...
The Fight or Flight Response (as of 7/23/12) Freeze-Flight
... neuroscientists call ‘executive functions’ - need space, a large flat surface where they can organize their reference materials. The brain facing a confrontation also needs space to spread out its reference materials while it decides how to react. This desktop of here-and-now, a component of executi ...
... neuroscientists call ‘executive functions’ - need space, a large flat surface where they can organize their reference materials. The brain facing a confrontation also needs space to spread out its reference materials while it decides how to react. This desktop of here-and-now, a component of executi ...
THE HUMAN BODY
... THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • LINK BETWEEN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM AND THE REST OF THE BODY • CONSISTS OF 43 PAIRS OF NERVES THAT ARISE FROM THE BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD AND LEAD TO ORGANS THROUGHOUT THE BODY ...
... THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • LINK BETWEEN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM AND THE REST OF THE BODY • CONSISTS OF 43 PAIRS OF NERVES THAT ARISE FROM THE BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD AND LEAD TO ORGANS THROUGHOUT THE BODY ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.























