CHAPTER OUTLINE
... 1. Newborns’ brain activity is high in the thalamus and low in the part of the forebrain related to smooth movement. This pattern of brain activity and motor function resembles that seen after brain damage in Huntington’s disease patients. 2. In the second and third months, brain activity increases ...
... 1. Newborns’ brain activity is high in the thalamus and low in the part of the forebrain related to smooth movement. This pattern of brain activity and motor function resembles that seen after brain damage in Huntington’s disease patients. 2. In the second and third months, brain activity increases ...
Chapter 9 Lesson Two-Nervous System
... Cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the brain as it is growing. ...
... Cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the brain as it is growing. ...
Brain Development Article and Questions
... developmental events to the cognitive and behavioral changes associated with them. An Overview of Brain Anatomy The easiest way to get to know the brain is to learn the main structures of the adult brain and how they relate to its function (Figure 1). It should be kept in mind that the relationship ...
... developmental events to the cognitive and behavioral changes associated with them. An Overview of Brain Anatomy The easiest way to get to know the brain is to learn the main structures of the adult brain and how they relate to its function (Figure 1). It should be kept in mind that the relationship ...
Nervous System ppt
... Relays messages, processes information and analyzes information. Includes: Brain Spinal Cord ...
... Relays messages, processes information and analyzes information. Includes: Brain Spinal Cord ...
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
... Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and emotional functions. ...
... Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and emotional functions. ...
The Nervous System
... cortex looks like it has many bumps and grooves. A bump or bulge on the cortex is called a gyrus (the plural of the word gyrus is "gyri") and a groove is called a sulcus (the plural of the word sulcus is "sulci"). Lower mammals, such as rats and mice, have very few gyri and sulci. ...
... cortex looks like it has many bumps and grooves. A bump or bulge on the cortex is called a gyrus (the plural of the word gyrus is "gyri") and a groove is called a sulcus (the plural of the word sulcus is "sulci"). Lower mammals, such as rats and mice, have very few gyri and sulci. ...
subjective beings with mental states
... Science usually works from a 3rd person perspective: this means that researchers adopt an objective point of view, seeing all evidence as a physical object. Recently, scientists studying human consciousness have argued for using a 1st person perspective as another means of gathering evidence: collec ...
... Science usually works from a 3rd person perspective: this means that researchers adopt an objective point of view, seeing all evidence as a physical object. Recently, scientists studying human consciousness have argued for using a 1st person perspective as another means of gathering evidence: collec ...
File - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... The movement of the electrical impulse along a neuron involves the movement of ions. When an neuron is Not carrying an impulse ions are pumped in & out of the axon. This results in the inside of the axon being –ive and the outside +ive Threshold, is the minimum stimulus needed to ...
... The movement of the electrical impulse along a neuron involves the movement of ions. When an neuron is Not carrying an impulse ions are pumped in & out of the axon. This results in the inside of the axon being –ive and the outside +ive Threshold, is the minimum stimulus needed to ...
PPT - Wolfweb Websites
... Dr Grant Mastick – FA 311D, X6168 – gmastick@unr.edu – Send me an email: ...
... Dr Grant Mastick – FA 311D, X6168 – gmastick@unr.edu – Send me an email: ...
5104_b4
... ascending 5-HT system3, which likely impairs information processing in its diverse terminal domains, possibly leading to depression and other affective disorders. By sensing the capacity to exert control over stress through instrumental behavior, the mPFCv may modulate the activity of 5-HT neurons i ...
... ascending 5-HT system3, which likely impairs information processing in its diverse terminal domains, possibly leading to depression and other affective disorders. By sensing the capacity to exert control over stress through instrumental behavior, the mPFCv may modulate the activity of 5-HT neurons i ...
Newsletter CSN Info April `16
... model reproduces longer intrinsic time scales in higher compared to early visual areas. Activity propagates down the visual hierarchy, similar to experimental results associated with visual imagery. Cortico-cortical interaction patterns agree well with fMRI resting-state functional connectivity. The ...
... model reproduces longer intrinsic time scales in higher compared to early visual areas. Activity propagates down the visual hierarchy, similar to experimental results associated with visual imagery. Cortico-cortical interaction patterns agree well with fMRI resting-state functional connectivity. The ...
Slide 1
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
The Nervous System
... Take nerve impulses from sensory receptors to CNS Structure is unipolar because process from cell body branches to the periphery and CNS ...
... Take nerve impulses from sensory receptors to CNS Structure is unipolar because process from cell body branches to the periphery and CNS ...
Red Brain, Blue Brain: Evaluative Processes Differ
... This region has been conceptualized as vital for ‘‘theory of mind’’ in processing, or the perception of others as thinking entities [45]. In fact a meta-analysis of over 200 fMRI studies on social cognition, the temporal-parietal junction was shown to be related to understanding immediate action int ...
... This region has been conceptualized as vital for ‘‘theory of mind’’ in processing, or the perception of others as thinking entities [45]. In fact a meta-analysis of over 200 fMRI studies on social cognition, the temporal-parietal junction was shown to be related to understanding immediate action int ...
The basic unit of computation - Zador Lab
... In a digital computer, the basic nonlinearity is of course the transistor. In the brain, however, the answer is not as clear. Among brain modelers, the conventional view, first enunciated by McCulloch and Pitts1, is that the single neuron represents the basic unit. In these models, a neuron is usual ...
... In a digital computer, the basic nonlinearity is of course the transistor. In the brain, however, the answer is not as clear. Among brain modelers, the conventional view, first enunciated by McCulloch and Pitts1, is that the single neuron represents the basic unit. In these models, a neuron is usual ...
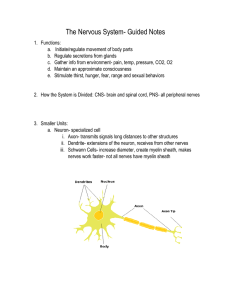
Nervous System Guided Notes
... i. Axon- transmits signals long distances to other structures ii. Dendrite- extensions of the neuron, receives from other nerves iii. Schwann Cells- increase diameter, create myelin sheath, makes nerves work faster- not all nerves have myelin sheath ...
... i. Axon- transmits signals long distances to other structures ii. Dendrite- extensions of the neuron, receives from other nerves iii. Schwann Cells- increase diameter, create myelin sheath, makes nerves work faster- not all nerves have myelin sheath ...
Brain - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
Brain - Pima Community College : Directories
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
Brain
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
... – stage 1 - drifting sensation (claim not sleeping) – stage 2 - light sleep – stage 3 vital signs change -- BP, pulse and breathing rates drop • reached in 20 minutes ...
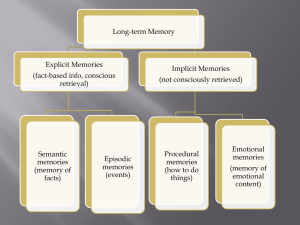
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... forgetting emotional memories. ...
... forgetting emotional memories. ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... Definition of Neural Networks • An information processing system that has been developed as a generalization of mathematical models of human cognition or neurobiology, based on the assumptions that – Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons. – Signals are passed between ...
... Definition of Neural Networks • An information processing system that has been developed as a generalization of mathematical models of human cognition or neurobiology, based on the assumptions that – Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons. – Signals are passed between ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.