The Peripheral Nervous System
... from the cord and exit through the openings between the stacked vertebrae of the vertebral column ...
... from the cord and exit through the openings between the stacked vertebrae of the vertebral column ...
Ch 3 lec 1
... Roots – a bundle of axons surrounded by connective tissue that occur in pairs, which fuse and form a spinal nerve Dorsal Roots – the spinal roots that contain incoming (afferent) sensory fibers Ventral Roots - the spinal roots that contain outgoing (efferent) motor fibers ...
... Roots – a bundle of axons surrounded by connective tissue that occur in pairs, which fuse and form a spinal nerve Dorsal Roots – the spinal roots that contain incoming (afferent) sensory fibers Ventral Roots - the spinal roots that contain outgoing (efferent) motor fibers ...
Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory
... • Several input and output measures • Harder than sensory mapping • Activation of muscles in isolation is difficult • Motor fields: all movements that engage a neuron • Functional (type of movement) • Structural (target muscles) • Neuroantomic labeling • TMS ...
... • Several input and output measures • Harder than sensory mapping • Activation of muscles in isolation is difficult • Motor fields: all movements that engage a neuron • Functional (type of movement) • Structural (target muscles) • Neuroantomic labeling • TMS ...
Ch 35 PowerPoint - Damien Rutkoski
... Hearing: Vibrations enter the ear through the auditory canal, causing the tympanum to vibrate. The vibrations are picked up by three tiny bones, the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup. These bones transmit the vibrations to a thin membrane called the oval window. Vibrations of the oval window crate p ...
... Hearing: Vibrations enter the ear through the auditory canal, causing the tympanum to vibrate. The vibrations are picked up by three tiny bones, the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup. These bones transmit the vibrations to a thin membrane called the oval window. Vibrations of the oval window crate p ...
nervous system
... and tiny hairs. Only these hairs are not responsible for hearing, but for balance. As you move, the fluid in the canals causes the hairs to bend in response to gravity. The way the hairs bend sends signals to the brain that allows us to achieve balance and equilibrium. ...
... and tiny hairs. Only these hairs are not responsible for hearing, but for balance. As you move, the fluid in the canals causes the hairs to bend in response to gravity. The way the hairs bend sends signals to the brain that allows us to achieve balance and equilibrium. ...
Chapter 2
... responsible for higher mental processes, decision making, and the production of fluent speech. • Motor cortex – responsible for sending motor commands to the muscles of the somatic nervous system. ...
... responsible for higher mental processes, decision making, and the production of fluent speech. • Motor cortex – responsible for sending motor commands to the muscles of the somatic nervous system. ...
MRINeuroanatomy
... – Measure hemispheric lateralization of language prior to temporal lobe surgery for drug-resistant epilepsy ...
... – Measure hemispheric lateralization of language prior to temporal lobe surgery for drug-resistant epilepsy ...
Lab 9
... accounts for 40% of the mass of the brain • It enables sensation, communication, memory, understanding, and voluntary movements • Each hemisphere acts contralaterally (controls the opposite side of the body) • Hemispheres are not equal in function • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior ...
... accounts for 40% of the mass of the brain • It enables sensation, communication, memory, understanding, and voluntary movements • Each hemisphere acts contralaterally (controls the opposite side of the body) • Hemispheres are not equal in function • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior ...
Lecture 2 Imaging, Brain Development
... differentiating tissue types, so it is better for soft-tissue structural imaging. • There are no known harmful effects at reasonable magnetic fields. • MRI studies are more expensive than CT studies. ...
... differentiating tissue types, so it is better for soft-tissue structural imaging. • There are no known harmful effects at reasonable magnetic fields. • MRI studies are more expensive than CT studies. ...
The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... More evidence for the role of LTP in learning comes from studies indicating that drugs which enhance synaptic transmission tend to enhance learning NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) a neurotransmitter receptor found on dendrites particularly in the hippocampal region NMDA is specialised to receive th ...
... More evidence for the role of LTP in learning comes from studies indicating that drugs which enhance synaptic transmission tend to enhance learning NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) a neurotransmitter receptor found on dendrites particularly in the hippocampal region NMDA is specialised to receive th ...
Nervous System Crossword Puzzle
... 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body; there's 31 pairs 46. barrier a layer of tightly packed cells that make up the walls of the brain capillaries and prevent substances in the blood from diffusing freely into the brain: pas ...
... 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body; there's 31 pairs 46. barrier a layer of tightly packed cells that make up the walls of the brain capillaries and prevent substances in the blood from diffusing freely into the brain: pas ...
Nervous System Crossword Puzzle
... motor info from one body part to the other 22. part of the nervous system responsible for control of the bodily functions not consciously directed, such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes 26. branch out and receives signals from the nerve cells 27. a traumatic injury to soft tissue ...
... motor info from one body part to the other 22. part of the nervous system responsible for control of the bodily functions not consciously directed, such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes 26. branch out and receives signals from the nerve cells 27. a traumatic injury to soft tissue ...
The Nervous System
... what happens in our nervous system when we step on tack. (Start with the sensory receptors and end with the movement off of the tack. What nervous structures are involved and in what part of the nervous system are they located.) ...
... what happens in our nervous system when we step on tack. (Start with the sensory receptors and end with the movement off of the tack. What nervous structures are involved and in what part of the nervous system are they located.) ...
Лекция 15
... numerous vital functions, most of which relate directly or indirectly to the regulation of visceral activities by way of other brain regions and the autonomic nervous system. ...
... numerous vital functions, most of which relate directly or indirectly to the regulation of visceral activities by way of other brain regions and the autonomic nervous system. ...
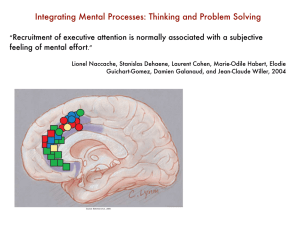
Integrating Mental Processes: Thinking and Problem Solving
... areas active for other executive tasks in frontal and parietal lobes. ...
... areas active for other executive tasks in frontal and parietal lobes. ...
303A.pdf
... Antecedents and determinants of an intelligent performance. Nature, 308, 61-62. Kimble, G. A. (2000). Behaviorism and unity in psychology. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9, 208-212. ...
... Antecedents and determinants of an intelligent performance. Nature, 308, 61-62. Kimble, G. A. (2000). Behaviorism and unity in psychology. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9, 208-212. ...
The Science of Psychology
... responsible for higher mental processes, decision making, and the production of fluent speech. • Motor cortex – responsible for sending motor commands to the muscles of the somatic nervous system. ...
... responsible for higher mental processes, decision making, and the production of fluent speech. • Motor cortex – responsible for sending motor commands to the muscles of the somatic nervous system. ...
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding glial
... Introduction to Psychology 2e Chapter 10 ...
... Introduction to Psychology 2e Chapter 10 ...
Central Nervous System
... gyrus – primary motor area – Neurons in this area control individual muscles ...
... gyrus – primary motor area – Neurons in this area control individual muscles ...
The anatomy and physiology of personality The brain
... nervous system is affected in important ways by the amounts of various neurotransmitters available at the moment • This availability can vary as a function of what the individual is doing and can fluctuate widely over short periods of time • People also differ from each other in their average levels ...
... nervous system is affected in important ways by the amounts of various neurotransmitters available at the moment • This availability can vary as a function of what the individual is doing and can fluctuate widely over short periods of time • People also differ from each other in their average levels ...
VNS Worksheet - Rice CAAM Department
... 11. Where is the hippocampus and why is it called a sea horse? 12. What happens if the hippocampus is removed? 13. What part of the cortex both sends to and receives from the hippocampus? ...
... 11. Where is the hippocampus and why is it called a sea horse? 12. What happens if the hippocampus is removed? 13. What part of the cortex both sends to and receives from the hippocampus? ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.