Ch 25 - Molecular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... Sensitization of the Gill-Withdrawal Reflex ...
... Sensitization of the Gill-Withdrawal Reflex ...
AACBIS - Brain Injury Alliance of Oregon
... Arousal/Consciousness Sleep/wake functions Attention/concentration ...
... Arousal/Consciousness Sleep/wake functions Attention/concentration ...
Brain and Nervous System— Your Information Superhighway
... static equilibrium: The position of the head in respect to the pull of gravity while it rests. synapse: The region of contact between the axon of one neuron and the cell body of another neuron across which nerve impulses are transmitted in one direction only. theta waves: Brain waves that appear whe ...
... static equilibrium: The position of the head in respect to the pull of gravity while it rests. synapse: The region of contact between the axon of one neuron and the cell body of another neuron across which nerve impulses are transmitted in one direction only. theta waves: Brain waves that appear whe ...
Document
... These power point slides are to only be used as a means to take notes during Mrs. Bartolotti’s lecture. They are not to be reproduced in any way without the permission of the teacher. Also, the slides presented here are not to be the only means of studying for the chapter test. You will still need t ...
... These power point slides are to only be used as a means to take notes during Mrs. Bartolotti’s lecture. They are not to be reproduced in any way without the permission of the teacher. Also, the slides presented here are not to be the only means of studying for the chapter test. You will still need t ...
Introduction to Biological Psychology
... Hypnosis involves a social interaction during which a person, responding to suggestions, experiences changes in memory, perception, and/or voluntary action ...
... Hypnosis involves a social interaction during which a person, responding to suggestions, experiences changes in memory, perception, and/or voluntary action ...
Building a Brain in a Box
... Putting this setup to work, Spaun's virtual sensory neurons pick up visual information, which consists of letters, shapes and numbers. The visual data gets sent to the "brain" to be stored in its memory. The brain then processes the input and sends a new signal to virtual motor neurons, allowing Spa ...
... Putting this setup to work, Spaun's virtual sensory neurons pick up visual information, which consists of letters, shapes and numbers. The visual data gets sent to the "brain" to be stored in its memory. The brain then processes the input and sends a new signal to virtual motor neurons, allowing Spa ...
Brightness and Lightness
... border are excited by an overlying photoreceptor but also inhibited by adjacent, similarly illuminated photoreceptors. The same is true far to the left of the dark/light border. Equal illumination of exciting and inhibiting photoreceptors balances out, output neurons far from the edge in either dire ...
... border are excited by an overlying photoreceptor but also inhibited by adjacent, similarly illuminated photoreceptors. The same is true far to the left of the dark/light border. Equal illumination of exciting and inhibiting photoreceptors balances out, output neurons far from the edge in either dire ...
Not a Miracle From Coma to Consciousness: A Discussion on Traditional
... coordination, and cognition. According to his experience of consulting stroke patients for years, Dr. ...
... coordination, and cognition. According to his experience of consulting stroke patients for years, Dr. ...
The Nervous System
... • The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column. • The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendri ...
... • The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column. • The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendri ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... neurons; they are stored as pathways called engrams, or memory traces that use strengthened or altered synapses. • Immediate memory lasts a few seconds, e.g., remembering the earliest part of a sentence to make sense of it. • Short-term memory (STM) lasts a few seconds to a few ...
... neurons; they are stored as pathways called engrams, or memory traces that use strengthened or altered synapses. • Immediate memory lasts a few seconds, e.g., remembering the earliest part of a sentence to make sense of it. • Short-term memory (STM) lasts a few seconds to a few ...
Mechanistic Explanation in Neuroscience
... these sensory neurons project, and a set of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons that receive input from the sensory neurons and project to the motor neurons. By isolating the neurons that comprise this simple circuit (and other circuits to which it was connected), Kandel and colleagues were able ...
... these sensory neurons project, and a set of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons that receive input from the sensory neurons and project to the motor neurons. By isolating the neurons that comprise this simple circuit (and other circuits to which it was connected), Kandel and colleagues were able ...
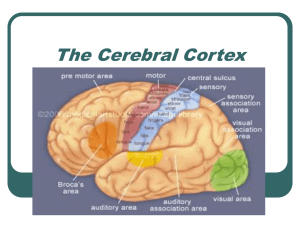
The Cerebral Cortex
... of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
... of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology, Nervous System and Special
... 7. Describe the molecular basis for the symptoms of multiple sclerosis. ______________________ attack on myelin Impulses short-circuit causing disability Classification 8. Name the three functional classes of neurons and give an example of each. ...
... 7. Describe the molecular basis for the symptoms of multiple sclerosis. ______________________ attack on myelin Impulses short-circuit causing disability Classification 8. Name the three functional classes of neurons and give an example of each. ...
nervous system physiology 1
... provides instructions for the assembly and operation of the brain Human genome: about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides i ...
... provides instructions for the assembly and operation of the brain Human genome: about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides i ...
Learning Study Guide
... Hand Luke”. Identify scenes from the movie that represents each drawback. Cognitive Learning What is Cognitive Learning? Who was Wolfgang Kohler? What is Insight Learning? Explain his experiment. What is Latent Learning? Who was Edward Tolman? Explain Explain his experiment. How do we use Cognitive ...
... Hand Luke”. Identify scenes from the movie that represents each drawback. Cognitive Learning What is Cognitive Learning? Who was Wolfgang Kohler? What is Insight Learning? Explain his experiment. What is Latent Learning? Who was Edward Tolman? Explain Explain his experiment. How do we use Cognitive ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... Aristotle believed that the mind was located in the heart Phrenology – Studying bumps on the head to reveal a person’s mental abilities and character traits, ...
... Aristotle believed that the mind was located in the heart Phrenology – Studying bumps on the head to reveal a person’s mental abilities and character traits, ...
Unit 7 PowerPoint (PDF file)
... effects about 11% of the population Fourth leading cause of brain death among the elderly A chronic, organic, mental disorder, a form of pre-senile dementia due to atrophy of neurons of the frontal and ...
... effects about 11% of the population Fourth leading cause of brain death among the elderly A chronic, organic, mental disorder, a form of pre-senile dementia due to atrophy of neurons of the frontal and ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... effects about 11% of the population Fourth leading cause of brain death among the elderly A chronic, organic, mental disorder, a form of pre-senile dementia due to atrophy of neurons of the frontal and ...
... effects about 11% of the population Fourth leading cause of brain death among the elderly A chronic, organic, mental disorder, a form of pre-senile dementia due to atrophy of neurons of the frontal and ...
Dopamine
... stimulation of certain glands. In hippocampus and neocortex of the mammalian brain, GABA has primarily excitatory effects early in development, and is in fact the major excitatory neurotransmitter in many regions of the brain prior to the maturation of glutamate synapses. developing cortex. Whether ...
... stimulation of certain glands. In hippocampus and neocortex of the mammalian brain, GABA has primarily excitatory effects early in development, and is in fact the major excitatory neurotransmitter in many regions of the brain prior to the maturation of glutamate synapses. developing cortex. Whether ...
General principle of nervous system
... General design • Central nervous system neuron – Basic functional unit – 100 billion units – Signals received by synapses • Located in neural dentrites and cell bodies • Few hundreds to 200,000 synaptic connection ...
... General design • Central nervous system neuron – Basic functional unit – 100 billion units – Signals received by synapses • Located in neural dentrites and cell bodies • Few hundreds to 200,000 synaptic connection ...
Control Coordination
... travel across each synapse They are chemical signals that neurons use to talk to each other, which is what makes your brain work. They help determine how you feel, think and act. ...
... travel across each synapse They are chemical signals that neurons use to talk to each other, which is what makes your brain work. They help determine how you feel, think and act. ...
Molecules of Emotion
... five senses—sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch—enter the nervous system. These points have become known as "nodal points", and seem to be designed so that they can be accessed and modulated by almost all neuropeptides as they process and prioritize information. All sensory information goes throug ...
... five senses—sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch—enter the nervous system. These points have become known as "nodal points", and seem to be designed so that they can be accessed and modulated by almost all neuropeptides as they process and prioritize information. All sensory information goes throug ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.