Astronomy 311: Magnetism • Atoms consist of protons and neutrons
... • So a lump of liquid iron could by chance condens slowly so that it becomes solid with all the atoms lined up in terms of spin magnetic moments. This is a permanent magnet. • Heating this lump to its Curie temperature destroys the alignment of the spin magnetic moments. • So a planetssimal forms, i ...
... • So a lump of liquid iron could by chance condens slowly so that it becomes solid with all the atoms lined up in terms of spin magnetic moments. This is a permanent magnet. • Heating this lump to its Curie temperature destroys the alignment of the spin magnetic moments. • So a planetssimal forms, i ...
Chapter 18
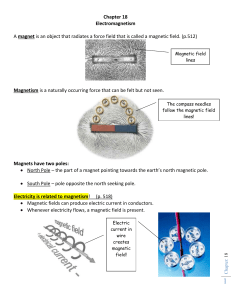
... Magnetic fields can produce electric current in conductors. Whenever electricity flows, a magnetic field is present. ...
... Magnetic fields can produce electric current in conductors. Whenever electricity flows, a magnetic field is present. ...
Warm Up #7 What are two ways that magnets interact with each
... ▪ Magnetic material – any material that a magnet attracts (iron, aluminum, nickel) ...
... ▪ Magnetic material – any material that a magnet attracts (iron, aluminum, nickel) ...
Magnetism - WordPress.com
... Fill the container with the liquid, put the slice of cork in the liquid and put the needle on the cork Observe the direction the needle moves to (N) ...
... Fill the container with the liquid, put the slice of cork in the liquid and put the needle on the cork Observe the direction the needle moves to (N) ...
magnet Any material that attracts iron and materials that contain iron
... The angle between geographic north and the north to which a compass needle points. ...
... The angle between geographic north and the north to which a compass needle points. ...
Magnetism
... All atoms have magnetic fields because of the charged particles inside. Most atoms’ magnetic fields point in random directions, so they all cancel each other out. ...
... All atoms have magnetic fields because of the charged particles inside. Most atoms’ magnetic fields point in random directions, so they all cancel each other out. ...
213 - jpsaos
... Eight pairs of electromagnets are shown below. The current in the left electromagnet is one amp and the current in the right one is two amps in each case. They are also separated by the same distance, and they have the same length and diameter. Carefully observe the orientation of the coil and direc ...
... Eight pairs of electromagnets are shown below. The current in the left electromagnet is one amp and the current in the right one is two amps in each case. They are also separated by the same distance, and they have the same length and diameter. Carefully observe the orientation of the coil and direc ...
Lesson 1: Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles
... strongest around the poles of a magnet. Vocab: magnet Magnetism Magnetic pole Magnetic force Lesson 2: Magnetic fields spread out from one pole to the other. They are curves lines that never cross. The field lines are strongest where they are closest together. Earth is like a giant bar magnet. Compa ...
... strongest around the poles of a magnet. Vocab: magnet Magnetism Magnetic pole Magnetic force Lesson 2: Magnetic fields spread out from one pole to the other. They are curves lines that never cross. The field lines are strongest where they are closest together. Earth is like a giant bar magnet. Compa ...
magnetismintrowebquest8word
... Go to http://istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/earthmag/lodeston.htm and answer following questions about Lodestone 1) What if the Lodestone was never discovered? 2) What is the other name for the rock that is called a Lodestone? 3) What is the difference in between these two rocks? If any. 4) Which is more common ...
... Go to http://istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/earthmag/lodeston.htm and answer following questions about Lodestone 1) What if the Lodestone was never discovered? 2) What is the other name for the rock that is called a Lodestone? 3) What is the difference in between these two rocks? If any. 4) Which is more common ...
CPS: A Cyber-Physical Framework for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guided Motivation Graduate
... deaths each year are due to cancer [1]. In the past decades, chemotherapy has been the only way to treat cancer but there are issues related to this method such as side effects and not being able to destroy all cancer (neoplastic) cells [2]. It is depicted that drug-laden magnetic nanoparticles can ...
... deaths each year are due to cancer [1]. In the past decades, chemotherapy has been the only way to treat cancer but there are issues related to this method such as side effects and not being able to destroy all cancer (neoplastic) cells [2]. It is depicted that drug-laden magnetic nanoparticles can ...
Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...