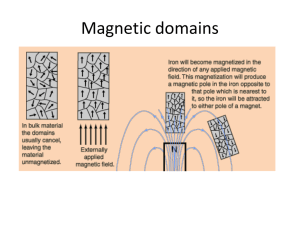
Lecture 7 Extra
... Contains the force unit N for Newton and the unit A is the Ampere, the unit of electric current. With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship ...
... Contains the force unit N for Newton and the unit A is the Ampere, the unit of electric current. With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship ...
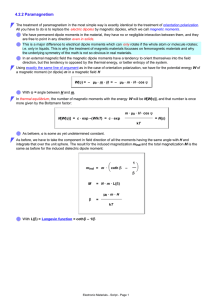
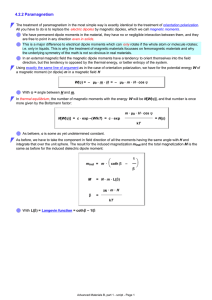
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... exceedingly small effect, but with certain characteristics that will carry over to ferromagnetic materials: There is a strong temperature dependence and it follows the "Curie law": const χpara = T Since ferromagnets of all types turn into paramagnets above the Curie temperature TC, we may simply exp ...
... exceedingly small effect, but with certain characteristics that will carry over to ferromagnetic materials: There is a strong temperature dependence and it follows the "Curie law": const χpara = T Since ferromagnets of all types turn into paramagnets above the Curie temperature TC, we may simply exp ...
Magnetic Fields Worksheet
... 4. A proton moving with a speed of 4.0 x 106 m/s through a magnetic field of 1.7 T experience a magnetic force of magnitude 8.2 x 10-13 N. What is the angle between the proton’s velocity and the field? [48.8° or 131°] 5. A proton is moving in a circular orbit of radius 0.14 m in a uniform magnetic f ...
... 4. A proton moving with a speed of 4.0 x 106 m/s through a magnetic field of 1.7 T experience a magnetic force of magnitude 8.2 x 10-13 N. What is the angle between the proton’s velocity and the field? [48.8° or 131°] 5. A proton is moving in a circular orbit of radius 0.14 m in a uniform magnetic f ...