
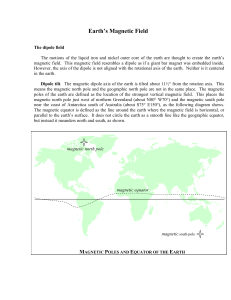
The Earth`s magnetic field
... magnetic North Pole of a compass (in red) is attracted to the magnetic South Pole of the Earth, which lies close to the geographic North Pole . ...
... magnetic North Pole of a compass (in red) is attracted to the magnetic South Pole of the Earth, which lies close to the geographic North Pole . ...
On the Magnet - Colorado Mesa University
... Petrus Peregrinus defines magnetic poles and observes that they are never seen in isolation. ...
... Petrus Peregrinus defines magnetic poles and observes that they are never seen in isolation. ...
il "ferrofluido" ha quelle caratteristiche di comportamento
... surfactant, such as soap, avoids it. The soap molecules possess, in fact, a hydrophilic hydrophobic part that allows them to bind simultaneously with the particle of iron and with the molecule of fat (oil), practically by coating and isolating the individual particles. High temperatures also counter ...
... surfactant, such as soap, avoids it. The soap molecules possess, in fact, a hydrophilic hydrophobic part that allows them to bind simultaneously with the particle of iron and with the molecule of fat (oil), practically by coating and isolating the individual particles. High temperatures also counter ...
Chapter 1 Earth`s Magnetic Field
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
... Dipole offset. The magnetic dipole of the earth is not centered on the earth’s core, but instead is offset by about 700 kilometers towards the direction of southeastern Asia. This creates two features in the magnetic field at the earth’s surface. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The point on the e ...
PHYS_3342_112211
... • Diamagnetism occurs in substances where magnetic moments inside atoms all cancel out, the net magnetic moment of the atom is zero. The induced magnetic moment is directed opposite to the applied field. Diamagnetism is weakly dependent on T. • Diamagnetic (induced atomic moment) effect is overcome ...
... • Diamagnetism occurs in substances where magnetic moments inside atoms all cancel out, the net magnetic moment of the atom is zero. The induced magnetic moment is directed opposite to the applied field. Diamagnetism is weakly dependent on T. • Diamagnetic (induced atomic moment) effect is overcome ...
Lesson 15 and 16
... mechanical vibrations from the strings and converts them to an electrical signal. The vibration from a string modulates the magnetic flux, inducing an alternating electric current. ...
... mechanical vibrations from the strings and converts them to an electrical signal. The vibration from a string modulates the magnetic flux, inducing an alternating electric current. ...
Magnets and Magnetic Field
... Earth’s Magnetic Field • The Earth produces a magnetic field that resembles a giant bar magnet • Because the “north seeking” pole of a magnet (the north pole of the magnet) points towards the north geographic pole, that is actually the south magnetic pole of the Earth ...
... Earth’s Magnetic Field • The Earth produces a magnetic field that resembles a giant bar magnet • Because the “north seeking” pole of a magnet (the north pole of the magnet) points towards the north geographic pole, that is actually the south magnetic pole of the Earth ...







![2016 Farada review sheet[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001271395_1-fc9c1a7e3076b57ba2cfadfbf9c2de3d-300x300.png)












![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057814_1-60bd3a273eeadb9e6de7a28a98376c5d-300x300.png)

