MAPWORK CALCULATIONS 10 APRIL 2014
... Magnetic North: Think of the earth as a giant magnet (it is actually). The shape of the earth's magnetic field is roughly the same shape as the field of a bar magnet. However, the earth's magnetic field is inclined at about 11º from the axis of rotation of the earth, so this means that the earth's m ...
... Magnetic North: Think of the earth as a giant magnet (it is actually). The shape of the earth's magnetic field is roughly the same shape as the field of a bar magnet. However, the earth's magnetic field is inclined at about 11º from the axis of rotation of the earth, so this means that the earth's m ...
Field Surveys and Data Reductions
... archaeological features on known archaeological sites. More exceptionally, magnetometers are used for low-resolution exploratory surveys. Several types of magnetometer are used in terrestrial archaeology. Early surveys, beginning in the 1950s, were conducted with proton precession magnetometers. Dat ...
... archaeological features on known archaeological sites. More exceptionally, magnetometers are used for low-resolution exploratory surveys. Several types of magnetometer are used in terrestrial archaeology. Early surveys, beginning in the 1950s, were conducted with proton precession magnetometers. Dat ...
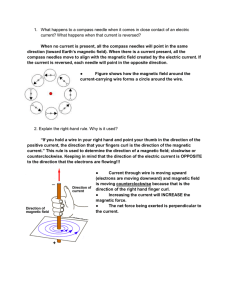
When no current is present, all the compass
... 3. Why is a solenoid used to create a stronger magnetic field? What does it resemble? To increase the magnetic force from the presence of a current, without increasing the current (because that is often dangerous), you can wrap a wire into a coil. This is called a solenoid and it is MUCH safer. By ...
... 3. Why is a solenoid used to create a stronger magnetic field? What does it resemble? To increase the magnetic force from the presence of a current, without increasing the current (because that is often dangerous), you can wrap a wire into a coil. This is called a solenoid and it is MUCH safer. By ...
Powerpoint Chapter 21 Magnetism
... – Most of the time magnets are paired, and the fields cancel out – Magnetic domain – a region that has a large number of electrons with fields in the same direction – Magnetized – most of the domains are pointed in the same direction ...
... – Most of the time magnets are paired, and the fields cancel out – Magnetic domain – a region that has a large number of electrons with fields in the same direction – Magnetized – most of the domains are pointed in the same direction ...