Electromagnetism - Delta Education
... bulbs will light because the circuit is open and electric current cannot flow.) What happens in a parallel circuit when you remove or turn off one light bulb? Why? (The other bulbs will continue to light because only the path to that one bulb is open. The other paths remain closed, so electric curre ...
... bulbs will light because the circuit is open and electric current cannot flow.) What happens in a parallel circuit when you remove or turn off one light bulb? Why? (The other bulbs will continue to light because only the path to that one bulb is open. The other paths remain closed, so electric curre ...
The Mutual Embrace of Electricity and Magnetism - fflch-usp
... In this picture it is apparent that the quantity of the current would depend on how many lines of tension were undergoing breakup and recombination; that is, on the size of the plates or on the number of lines through any lateral section cutting all of them. Similarly, the power of the current to ov ...
... In this picture it is apparent that the quantity of the current would depend on how many lines of tension were undergoing breakup and recombination; that is, on the size of the plates or on the number of lines through any lateral section cutting all of them. Similarly, the power of the current to ov ...
Trouble with Maxwell`s Electromagnetic Theory: Can Fields Induce
... these changing electric currents, how the waves detach themselves from the antenna and what radio waves really are when traveling through space. These, I contend, are problems still open for argument and will be discussed here. My alternative explanation is that radio waves in vacuum are simply mech ...
... these changing electric currents, how the waves detach themselves from the antenna and what radio waves really are when traveling through space. These, I contend, are problems still open for argument and will be discussed here. My alternative explanation is that radio waves in vacuum are simply mech ...
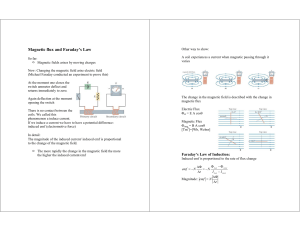
Magnetic flux and Faraday`s Law
... Lenz Law (expresses the meaning of the minus) An induced current always flow in a direction that opposes the change that caused it. ...
... Lenz Law (expresses the meaning of the minus) An induced current always flow in a direction that opposes the change that caused it. ...
INTERACTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION - if
... Both effects are currently discussed mostly as applied to e-m radiation belonging to the γ-range. They depend crucially on the deviation of the photon dispersion curve from the customary shape it has in empty vacuum, k02 = |k|2 , where k0 is the photon energy, and k is its momentum. As long as one r ...
... Both effects are currently discussed mostly as applied to e-m radiation belonging to the γ-range. They depend crucially on the deviation of the photon dispersion curve from the customary shape it has in empty vacuum, k02 = |k|2 , where k0 is the photon energy, and k is its momentum. As long as one r ...
mri safety - Munson Healthcare
... produce detailed three-dimensional pictures of internal body structures. ...
... produce detailed three-dimensional pictures of internal body structures. ...
PPT
... Now transform to the frame of the previously moving charges. Now it’s the positive charges in the wire that are moving. And they will be Lorentz-contracted, so their density will be higher. There will still be a magnetic field, but the test charge now has zero velocity, so its force will be zero. Th ...
... Now transform to the frame of the previously moving charges. Now it’s the positive charges in the wire that are moving. And they will be Lorentz-contracted, so their density will be higher. There will still be a magnetic field, but the test charge now has zero velocity, so its force will be zero. Th ...
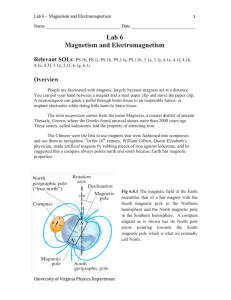
Monopoles and Electricity
... make up the wire; each atom is a small magnetic dipole with its own north and south magnetic monopoles orbiting through its nucleus. When the north pole of a bar magnet passes by the magnetic field of the atom, it attracts all of the south magnetic monopoles that are in orbit through the atom’s nucl ...
... make up the wire; each atom is a small magnetic dipole with its own north and south magnetic monopoles orbiting through its nucleus. When the north pole of a bar magnet passes by the magnetic field of the atom, it attracts all of the south magnetic monopoles that are in orbit through the atom’s nucl ...
How Do Space Energy Devices Work? - Alpha Institute for Advanced
... is applied to two different types of devices: electrical solid-state structures and magnetic motors. Details are found in the scientific papers [1] - [6]. In this article we try to describe the essential points and present them on a level which might be comprehensible to engineers. ...
... is applied to two different types of devices: electrical solid-state structures and magnetic motors. Details are found in the scientific papers [1] - [6]. In this article we try to describe the essential points and present them on a level which might be comprehensible to engineers. ...
Gauss` Law
... Now having Gauss’s law in hand, we can find the electric field inside of the parallel plate capacitor. Let us neglect any effects that may occur close to the ends of the capacitor and consider it as two infinitely big parallel planes. The total electric field inside of this capacitor is a vector sum ...
... Now having Gauss’s law in hand, we can find the electric field inside of the parallel plate capacitor. Let us neglect any effects that may occur close to the ends of the capacitor and consider it as two infinitely big parallel planes. The total electric field inside of this capacitor is a vector sum ...
Multiferroics

Multiferroics have been formally defined as materials that exhibit more than one primary ferroic order parameter simultaneously (i.e. in a single phase), and many researchers in the field consider materials to be multiferroics only if they exhibit coupling between primary order parameters. However, the definition of multiferroics can be expanded to include non-primary order parameters, such as antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism.The four basic primary ferroic order parameters areferromagnetismferroelectricityferroelasticityferrotoroidicityThe last is a topic of some debate, as there was no evidence for switching ferrotoroidicity until recently.Many multiferroics are transition metal oxides with perovskite crystal structure, and include rare-earth manganites and -ferrites (e.g. TbMnO3, HoMn2O5, LuFe2O4 and recently, ""PZTFT"",). Other examples are the bismuth compounds BiFeO3 and BiMnO3, non-perovskite oxide LiCu2O2, and non-oxides such as BaNiF4 and spinel chalcogenides, e.g. ZnCr2Se4. These alloys show rich phase diagrams combining different ferroic orders in separate phases.Apart from single phase multiferroics, composites and heterostructures exhibiting more than one ferroic order parameter are studied extensively. Some examples include magnetic thin films on piezoelectric PMN-PT substrates and Metglass/PVDF/Metglass trilayer structures.Besides scientific interest in their physical properties, multiferroics have potential for applications as actuators, switches, magnetic field sensors or new types of electronic memory devices.