Magnetism and Induction Review
... Magnetism and Induction Review 1. How will a magnet that is free to rotate, like a compass, align itself with earth’s magnetic field? 2. How do opposite poles affect each other? What about like poles? 3. What do you get when you break a magnet in half? 4. Can you ever make it small enough to get jus ...
... Magnetism and Induction Review 1. How will a magnet that is free to rotate, like a compass, align itself with earth’s magnetic field? 2. How do opposite poles affect each other? What about like poles? 3. What do you get when you break a magnet in half? 4. Can you ever make it small enough to get jus ...
An electromagnetic wave in vacuum has the electric and magnetic
... In an electromagnetic wave electrical and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. Wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to both electric and magnetic filed as given by E⃗ B⃗ . Direction of polarization is perpendicular to direction of oscillation. Optical phenomena are due to electr ...
... In an electromagnetic wave electrical and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. Wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to both electric and magnetic filed as given by E⃗ B⃗ . Direction of polarization is perpendicular to direction of oscillation. Optical phenomena are due to electr ...
Introduction to Magnetic Neutron Diffraction and Magnetic Structures
... The determination of magnetic structures of crystalline materials using neutron diffraction is one of the major specific applications of the use of neutrons for studying the properties of condensed matter. The knowledge of the magnetic ordering in materials provides important clues for understanding ...
... The determination of magnetic structures of crystalline materials using neutron diffraction is one of the major specific applications of the use of neutrons for studying the properties of condensed matter. The knowledge of the magnetic ordering in materials provides important clues for understanding ...
F1004
... Course intention within the general study plan context: The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics su ...
... Course intention within the general study plan context: The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics su ...
Imaging of local magnetic structure by polarized neutron holography
... Atomic resolution holography is an emerging technique for investigation of the structure of materials on atomic scale. Using this method questions concerning the local arrangement of nuclei around a specific nucleus can be answered but discovering the local spin arrangement around a specific (e.g. i ...
... Atomic resolution holography is an emerging technique for investigation of the structure of materials on atomic scale. Using this method questions concerning the local arrangement of nuclei around a specific nucleus can be answered but discovering the local spin arrangement around a specific (e.g. i ...
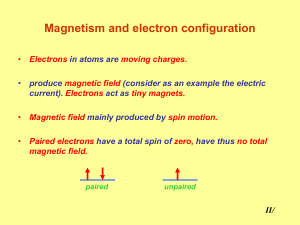
Magnetism and electron configuration
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
Multiferroics

Multiferroics have been formally defined as materials that exhibit more than one primary ferroic order parameter simultaneously (i.e. in a single phase), and many researchers in the field consider materials to be multiferroics only if they exhibit coupling between primary order parameters. However, the definition of multiferroics can be expanded to include non-primary order parameters, such as antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism.The four basic primary ferroic order parameters areferromagnetismferroelectricityferroelasticityferrotoroidicityThe last is a topic of some debate, as there was no evidence for switching ferrotoroidicity until recently.Many multiferroics are transition metal oxides with perovskite crystal structure, and include rare-earth manganites and -ferrites (e.g. TbMnO3, HoMn2O5, LuFe2O4 and recently, ""PZTFT"",). Other examples are the bismuth compounds BiFeO3 and BiMnO3, non-perovskite oxide LiCu2O2, and non-oxides such as BaNiF4 and spinel chalcogenides, e.g. ZnCr2Se4. These alloys show rich phase diagrams combining different ferroic orders in separate phases.Apart from single phase multiferroics, composites and heterostructures exhibiting more than one ferroic order parameter are studied extensively. Some examples include magnetic thin films on piezoelectric PMN-PT substrates and Metglass/PVDF/Metglass trilayer structures.Besides scientific interest in their physical properties, multiferroics have potential for applications as actuators, switches, magnetic field sensors or new types of electronic memory devices.