Class Problem 21 (1) The nuclear magneton is obtained from the
... unit J/T. Calculate the magnetic moment of proton, which is 2.79 times the nuclear magneton. (2) In an MRImachine, the magnetic moment of a proton is made antiparallel to a 3.0T magnetic field by a radiowave. ...
... unit J/T. Calculate the magnetic moment of proton, which is 2.79 times the nuclear magneton. (2) In an MRImachine, the magnetic moment of a proton is made antiparallel to a 3.0T magnetic field by a radiowave. ...
GENERAL MAGNET CHARACTERISTICS (physics 2)
... Below is a circle that represents the earth. The earth has a magnetic field even though there is not an actual bar magnet inside the earth. However, if there were such a magnet inside the earth, draw the orientation of this magnet as it would exist inside the earth. ...
... Below is a circle that represents the earth. The earth has a magnetic field even though there is not an actual bar magnet inside the earth. However, if there were such a magnet inside the earth, draw the orientation of this magnet as it would exist inside the earth. ...
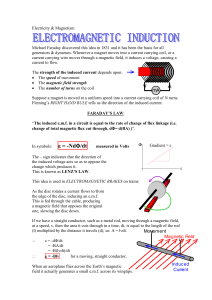
EM_INDUCTION
... “The induced e.m.f. in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage (i.e. change of total magnetic flux cut through, d= d(BA) )”. ...
... “The induced e.m.f. in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage (i.e. change of total magnetic flux cut through, d= d(BA) )”. ...
Magnets
... Using the paperclips at your station, try to find out where the magnet is strongest: North Pole, South Pole, or in the middle. ...
... Using the paperclips at your station, try to find out where the magnet is strongest: North Pole, South Pole, or in the middle. ...
20.3 Motional emf
... When the magnetic force becomes equal to the electric force on a free electron, its motion stop and an induced emf is formed. From previous lessons ...
... When the magnetic force becomes equal to the electric force on a free electron, its motion stop and an induced emf is formed. From previous lessons ...
magnet Any material that attracts iron and materials that contain iron
... found outside the nucleus of an atom. ...
... found outside the nucleus of an atom. ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields
... AEP has followed worldwide scientific studies and developments related to EMF for decades. We have participated in EMF research through membership in trade associations and have communicated with customers and employees on the issue. ...
... AEP has followed worldwide scientific studies and developments related to EMF for decades. We have participated in EMF research through membership in trade associations and have communicated with customers and employees on the issue. ...
Magnetism
... Why are some materials magnetic while others aren’t? Scientists believe that magnetism is due to the motion of electronsparticularly their spin. All electrons spin and create a magnetic field around themselves. ...
... Why are some materials magnetic while others aren’t? Scientists believe that magnetism is due to the motion of electronsparticularly their spin. All electrons spin and create a magnetic field around themselves. ...
The atom in magnetic field
... The unperturbed energy level is characterized by kLSJ, the spin-orbit coupling is not broken. The interaction with the magnetic field in this case is the ...
... The unperturbed energy level is characterized by kLSJ, the spin-orbit coupling is not broken. The interaction with the magnetic field in this case is the ...
Multiferroics

Multiferroics have been formally defined as materials that exhibit more than one primary ferroic order parameter simultaneously (i.e. in a single phase), and many researchers in the field consider materials to be multiferroics only if they exhibit coupling between primary order parameters. However, the definition of multiferroics can be expanded to include non-primary order parameters, such as antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism.The four basic primary ferroic order parameters areferromagnetismferroelectricityferroelasticityferrotoroidicityThe last is a topic of some debate, as there was no evidence for switching ferrotoroidicity until recently.Many multiferroics are transition metal oxides with perovskite crystal structure, and include rare-earth manganites and -ferrites (e.g. TbMnO3, HoMn2O5, LuFe2O4 and recently, ""PZTFT"",). Other examples are the bismuth compounds BiFeO3 and BiMnO3, non-perovskite oxide LiCu2O2, and non-oxides such as BaNiF4 and spinel chalcogenides, e.g. ZnCr2Se4. These alloys show rich phase diagrams combining different ferroic orders in separate phases.Apart from single phase multiferroics, composites and heterostructures exhibiting more than one ferroic order parameter are studied extensively. Some examples include magnetic thin films on piezoelectric PMN-PT substrates and Metglass/PVDF/Metglass trilayer structures.Besides scientific interest in their physical properties, multiferroics have potential for applications as actuators, switches, magnetic field sensors or new types of electronic memory devices.