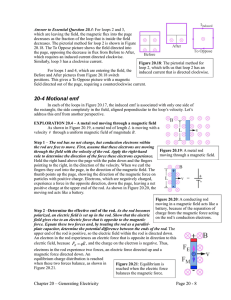
Chapter 22 Gauss`s Law 1 Charge and Electric Flux
... Figure 1: This is Fig. 22.2 show a positive flux (i.e., flow) out of the enclosed volume due to positive charges, and the negative flux, or flow, into the enclosed volume due to negative charge. ...
... Figure 1: This is Fig. 22.2 show a positive flux (i.e., flow) out of the enclosed volume due to positive charges, and the negative flux, or flow, into the enclosed volume due to negative charge. ...
Chapter 7 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... Materials that can be magnetized are called ferromagnetic When there is current through a conductor, it produces an electromagnetic field around the conductor The right-hand rule can be used to establish the direction of the electromagnetic lines of force around a conductor ISU EE ...
... Materials that can be magnetized are called ferromagnetic When there is current through a conductor, it produces an electromagnetic field around the conductor The right-hand rule can be used to establish the direction of the electromagnetic lines of force around a conductor ISU EE ...
North Magnetic Pole - Effingham County Schools
... a wire carrying an electric current always has a magnetic field around it the magnetic field in a straight wire is not ...
... a wire carrying an electric current always has a magnetic field around it the magnetic field in a straight wire is not ...
induced current
... Conceptual Example 7 An Induction Stove Two pots of water are placed on an induction stove at the same time. The stove itself is cool to the touch. The water in the ferromagnetic metal pot is boiling while that in the glass pot is not. How can such a cool stove boil water, and why isn’t the water in ...
... Conceptual Example 7 An Induction Stove Two pots of water are placed on an induction stove at the same time. The stove itself is cool to the touch. The water in the ferromagnetic metal pot is boiling while that in the glass pot is not. How can such a cool stove boil water, and why isn’t the water in ...
chapter32.4 - Colorado Mesa University
... Notice: z is distance measured from the center of dipole. z >> s ...
... Notice: z is distance measured from the center of dipole. z >> s ...
circuits 1.notebook
... no matter how small a magnet is when you break it, there will always be two opposite poles ...
... no matter how small a magnet is when you break it, there will always be two opposite poles ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.