Electric field
... “The emf induced in a circuit by a time changing magnetic flux linkage will be of a polarity that tends to set up a current which will oppose the change of flux linkage.” • The notion of Lenz’s law is a particular example of the Conservation of Energy Law, whereby every action has an equal and oppo ...
... “The emf induced in a circuit by a time changing magnetic flux linkage will be of a polarity that tends to set up a current which will oppose the change of flux linkage.” • The notion of Lenz’s law is a particular example of the Conservation of Energy Law, whereby every action has an equal and oppo ...
5-Motors
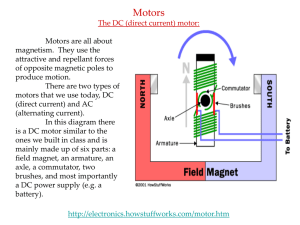
... First we must discuss its parts. Field Magnet - basically just a permanent magnet Armature - an electromagnet If you were to take a horseshoe magnet and place a simple electromagnet (i.e. a nail inside of a closed coil hooked up to a battery) between it’s poles so that the like poles of the permanen ...
... First we must discuss its parts. Field Magnet - basically just a permanent magnet Armature - an electromagnet If you were to take a horseshoe magnet and place a simple electromagnet (i.e. a nail inside of a closed coil hooked up to a battery) between it’s poles so that the like poles of the permanen ...
Volume II Electric and Magnetic Interactions
... Chapter 16: Electric Field of Distributed Charges ...
... Chapter 16: Electric Field of Distributed Charges ...
Chapter 22 Electromagnetic Induction
... The coil of an ac motor has a resistance of 4.1 ohms. The motor is plugged into an outlet where the voltage is 120.0 volts (rms), and the coil develops a back emf of 118.0 volts (rms) when rotating at normal speed. The motor is turning a wheel. Find (a) the current when the motor first starts up and ...
... The coil of an ac motor has a resistance of 4.1 ohms. The motor is plugged into an outlet where the voltage is 120.0 volts (rms), and the coil develops a back emf of 118.0 volts (rms) when rotating at normal speed. The motor is turning a wheel. Find (a) the current when the motor first starts up and ...
Grade-Level Domain MAP
... turning a magnet and a coil of wire in relation to each other; an electric motor works on the reverse principle. A step-up transformer sends alternating current through a smaller coil of wire with just a few turns next to a larger coil with many turns. This induces a higher voltage in the larger coi ...
... turning a magnet and a coil of wire in relation to each other; an electric motor works on the reverse principle. A step-up transformer sends alternating current through a smaller coil of wire with just a few turns next to a larger coil with many turns. This induces a higher voltage in the larger coi ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.