Calculate Inductor AC Flux Density
... Permeability here is expressed as relative permeability times the permeability constant μ = μ r μ 0 = μ r⋅4 π⋅10−7 H / m . The magnetic path length here is magnified by the presence of a gap in the magnetic path: l = l m + μ l g where l m is the path length in the magnetic material and l g is the pa ...
... Permeability here is expressed as relative permeability times the permeability constant μ = μ r μ 0 = μ r⋅4 π⋅10−7 H / m . The magnetic path length here is magnified by the presence of a gap in the magnetic path: l = l m + μ l g where l m is the path length in the magnetic material and l g is the pa ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. Calculate the self inductance of 1m long solenoid of 400 turns and 5 cm diameter. 7. Explain time constant in L-R circuit. 8. Obtain the expression for the mean value of a.c. in terms of the peak value. 9. Define magnetic susceptibility. 10. Define Poynting vector. ...
... 6. Calculate the self inductance of 1m long solenoid of 400 turns and 5 cm diameter. 7. Explain time constant in L-R circuit. 8. Obtain the expression for the mean value of a.c. in terms of the peak value. 9. Define magnetic susceptibility. 10. Define Poynting vector. ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
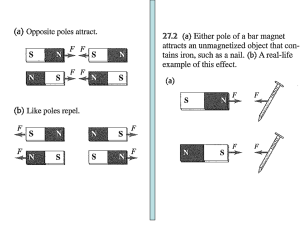
... Part 1: Hold two magnets 1 cm apart, push together and record results, repeat for all combinations N-S, N-N, S-S (3 total trials) Part 2:Using a meter stick, slowly bring two magnets together in all three combinations as part 1 and record to the nearest .5 mm the distance that the other magnet moves ...
... Part 1: Hold two magnets 1 cm apart, push together and record results, repeat for all combinations N-S, N-N, S-S (3 total trials) Part 2:Using a meter stick, slowly bring two magnets together in all three combinations as part 1 and record to the nearest .5 mm the distance that the other magnet moves ...
Science Demos for Carden Elementary
... Current is how many electrons actually flow (analogous to the volume of water per second). Magnets Show Lode Stones (Magnetic Rocks). All magnets have North pole and a South Pole. Test them to see that S-S attracts, but N-N repels. Draw an Electric Field (monopole). Draw a Magnetic Field (Dipole). M ...
... Current is how many electrons actually flow (analogous to the volume of water per second). Magnets Show Lode Stones (Magnetic Rocks). All magnets have North pole and a South Pole. Test them to see that S-S attracts, but N-N repels. Draw an Electric Field (monopole). Draw a Magnetic Field (Dipole). M ...
Guass`s Law for magnetism
... 1. Guass’s Law – The greater the charge, the greater the electric field 2. Guass’s Law for magnetism Magnetic flux is zero through a closed ...
... 1. Guass’s Law – The greater the charge, the greater the electric field 2. Guass’s Law for magnetism Magnetic flux is zero through a closed ...
Permanent magnets are just collections of little current loops
... If we let loops and surfaces get infinitesimally small, we get relationships for derivatives of the fields. There are four relationships, called “Maxwell’s Equations” ...
... If we let loops and surfaces get infinitesimally small, we get relationships for derivatives of the fields. There are four relationships, called “Maxwell’s Equations” ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... North pole there is a magnetic pole which we can refer to as “Magnetic North”. However it is a South pole! Watch the field lines! ...
... North pole there is a magnetic pole which we can refer to as “Magnetic North”. However it is a South pole! Watch the field lines! ...
Power point on Magnetism - EMS Secondary Department
... It is used to make (temporal) electromagnets ...
... It is used to make (temporal) electromagnets ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.