Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
The role of the helical kink instability in solar coronal ejections
... are powered by the Sun's magnetic field. They are formed as magnetic flux ropes, i.e. magnetic fields twisted about each other. CMEs are the most important drivers of space weather effects on Earth. In particular, the structure of the internal magnetic field of the CME determines the severeness of t ...
... are powered by the Sun's magnetic field. They are formed as magnetic flux ropes, i.e. magnetic fields twisted about each other. CMEs are the most important drivers of space weather effects on Earth. In particular, the structure of the internal magnetic field of the CME determines the severeness of t ...
Maxwell`s Equations, Part IV
... arc above and below the poles in the plane of the Figure. If this Figure extended to infinity in any direction, you would still see evidence – albeit less and less as you proceed farther away from the magnet – of the magnetic field. Third, the strength of the field is indicated by the density of lin ...
... arc above and below the poles in the plane of the Figure. If this Figure extended to infinity in any direction, you would still see evidence – albeit less and less as you proceed farther away from the magnet – of the magnetic field. Third, the strength of the field is indicated by the density of lin ...
Exam 3 problems
... 4. For decades, no one thought to measure the B-field inside a superconductor, assuming that B remains constant inside when the external field is changed, as for a perfect conductor. Obtain a copy of W. Meissner and R. Ochsenfeld, Naturewissenschaften 21 (44), 787-788 (Nov 1933) and describe the exp ...
... 4. For decades, no one thought to measure the B-field inside a superconductor, assuming that B remains constant inside when the external field is changed, as for a perfect conductor. Obtain a copy of W. Meissner and R. Ochsenfeld, Naturewissenschaften 21 (44), 787-788 (Nov 1933) and describe the exp ...
Magnetism
... These pictures show how an electric current affects compasses. When the current flows, the compass needles line up along the lines of a magnetic field. When the current is not flowing, the compass ...
... These pictures show how an electric current affects compasses. When the current flows, the compass needles line up along the lines of a magnetic field. When the current is not flowing, the compass ...
Physics: Principles and Applications
... electrical energy. Can be used as solid state thermal to electrical energy converter (i.e. engine)as well as an accurate temperature sensor. Seebeck engines are currently not very efficient but are much more reliable than heat engines. They are used by NASA for nuclear powered deep-space probes. ...
... electrical energy. Can be used as solid state thermal to electrical energy converter (i.e. engine)as well as an accurate temperature sensor. Seebeck engines are currently not very efficient but are much more reliable than heat engines. They are used by NASA for nuclear powered deep-space probes. ...
Electric motors Electric motors are everywhere! In your house
... An electromagnet is the basis of an electric motor. You can understand how things work in the motor by imagining the following scenario. Say that you created a simple electromagnet by wrapping 100 loops of wire around a nail and connecting it to a battery. The nail would become a magnet and have a ...
... An electromagnet is the basis of an electric motor. You can understand how things work in the motor by imagining the following scenario. Say that you created a simple electromagnet by wrapping 100 loops of wire around a nail and connecting it to a battery. The nail would become a magnet and have a ...
Course Schedule, Syllabus and Grading Policy
... Course Description: This is an introductory course in electromagnetic theory, the course will first introduces the student to the basic concepts in vectors and vector calculus including the curl , divergence , gradient in Cartesian, cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the divergence Theorem, Stok ...
... Course Description: This is an introductory course in electromagnetic theory, the course will first introduces the student to the basic concepts in vectors and vector calculus including the curl , divergence , gradient in Cartesian, cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the divergence Theorem, Stok ...
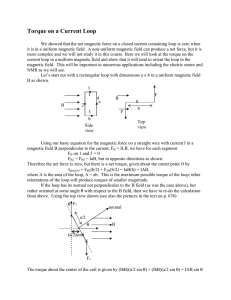
Torque on a Current Loop
... difference to be absorbed – a condition known as a resonance (hence the R in NMR). A spin flip to a higher energy from a lower energy, eventually results in the re-emission of this energy difference in the form of a photon, or packet of energy, at Radio Frequencies (RF), which can be detected and an ...
... difference to be absorbed – a condition known as a resonance (hence the R in NMR). A spin flip to a higher energy from a lower energy, eventually results in the re-emission of this energy difference in the form of a photon, or packet of energy, at Radio Frequencies (RF), which can be detected and an ...
Lecture
... – Amperes’ Law : Analogous to Gauss’ L:aw in electrostatics, Useful in symmetric cases. – Infinitely long straight wire of radius a. Find B outside and inside wire. – Solenoid and Toroid Find B field. – Forces between current carrying wires or parallel moving charges Demos – Torque on a current loop ...
... – Amperes’ Law : Analogous to Gauss’ L:aw in electrostatics, Useful in symmetric cases. – Infinitely long straight wire of radius a. Find B outside and inside wire. – Solenoid and Toroid Find B field. – Forces between current carrying wires or parallel moving charges Demos – Torque on a current loop ...
Why MRI scans CAN make you dizzy: Magnetic fields disrupt fluid in
... particles circulating within the tubes. This in turn exerts a force on the cells which use the fluid's flow to detect motion. The discovery has implications for MRI-based brain research, say the scientists. They point out that the scanner could itself be inducing previously unnoticed brain activity ...
... particles circulating within the tubes. This in turn exerts a force on the cells which use the fluid's flow to detect motion. The discovery has implications for MRI-based brain research, say the scientists. They point out that the scanner could itself be inducing previously unnoticed brain activity ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.