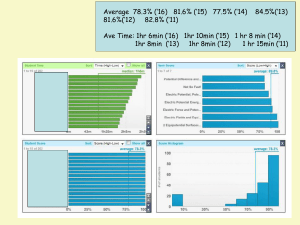
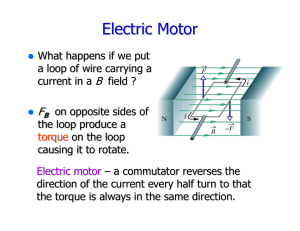
Magnetism - faithphysics
... magnetic field lines bunch up. If you add another loop and another, the magnetic field becomes more and more concentrated. This coil is called an electromagnet. ...
... magnetic field lines bunch up. If you add another loop and another, the magnetic field becomes more and more concentrated. This coil is called an electromagnet. ...
Magnetic Globe - Arbor Scientific
... magnetized chunk of iron like a bar magnet. It is too hot for individual atoms to remain aligned. Currents in the molten part of the earth beneath the crust provide a better explanation for the earth=s magnetic field. Most earth scientists think that moving charges looping around within the earth cr ...
... magnetized chunk of iron like a bar magnet. It is too hot for individual atoms to remain aligned. Currents in the molten part of the earth beneath the crust provide a better explanation for the earth=s magnetic field. Most earth scientists think that moving charges looping around within the earth cr ...
49. Rau Alexander Ngatuni, Irene Chuwa and Witness Shirima
... buying ready made electric bells since we used local available materials to give the same result. For the bell to function properly it needs to have number of turns of coil which when connected to electricity they create electromagnetism and an armature made up of soft iron which is attracted by res ...
... buying ready made electric bells since we used local available materials to give the same result. For the bell to function properly it needs to have number of turns of coil which when connected to electricity they create electromagnetism and an armature made up of soft iron which is attracted by res ...
07magnet_field_s2012
... the center of a loop of current of radius r is easily calculated. The field is increased by “N” the number of turns. • 1820 Johann Schweigger (with Ampere) invent the (tangent) Galvanometer, a coil around a compass needle. The tangent of the angle of deflection is proportional to the current in the ...
... the center of a loop of current of radius r is easily calculated. The field is increased by “N” the number of turns. • 1820 Johann Schweigger (with Ampere) invent the (tangent) Galvanometer, a coil around a compass needle. The tangent of the angle of deflection is proportional to the current in the ...
Earth as a Magnet
... Magnet Maker • Let’s say a piece of iron or iron ore is left somewhere for many years. • Earth’s magnetic field can attract the domains to line up in one direction. • This means that Earth’s magnetic field has turned it into a magnet. • If the desk you are sitting at is metal or if the filing cabin ...
... Magnet Maker • Let’s say a piece of iron or iron ore is left somewhere for many years. • Earth’s magnetic field can attract the domains to line up in one direction. • This means that Earth’s magnetic field has turned it into a magnet. • If the desk you are sitting at is metal or if the filing cabin ...
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5 - Class CBSE
... narrow, parallel gap. These two Ds are connected to a highfrequency oscillator which produces an alternating voltage. This alternating voltage establishes an alternating electric field between the two Ds once from D1 to D2 and then from D2 to D1. This electric field between the Ds accelerates the ch ...
... narrow, parallel gap. These two Ds are connected to a highfrequency oscillator which produces an alternating voltage. This alternating voltage establishes an alternating electric field between the two Ds once from D1 to D2 and then from D2 to D1. This electric field between the Ds accelerates the ch ...
Superconducting magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers and particle accelerators.